Human gain-of-function variants in HNF1A confer protection from diabetes but independently increase hepatic secretion of atherogenic lipoproteins
- PMID: 37492105
- PMCID: PMC10363808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100339
Human gain-of-function variants in HNF1A confer protection from diabetes but independently increase hepatic secretion of atherogenic lipoproteins
Abstract
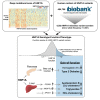
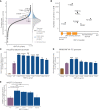
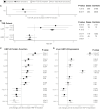
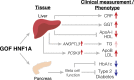
Loss-of-function mutations in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1A (HNF1A) are known to cause rare forms of diabetes and alter hepatic physiology through unclear mechanisms. In the general population, 1:100 individuals carry a rare, protein-coding HNF1A variant, most of unknown functional consequence. To characterize the full allelic series, we performed deep mutational scanning of 11,970 protein-coding HNF1A variants in human hepatocytes and clinical correlation with 553,246 exome-sequenced individuals. Surprisingly, we found that ∼1:5 rare protein-coding HNF1A variants in the general population cause molecular gain of function (GOF), increasing the transcriptional activity of HNF1A by up to 50% and conferring protection from type 2 diabetes (odds ratio [OR] = 0.77, p = 0.007). Increased hepatic expression of HNF1A promoted a pro-atherogenic serum profile mediated in part by enhanced transcription of risk genes including ANGPTL3 and PCSK9. In summary, ∼1:300 individuals carry a GOF variant in HNF1A that protects carriers from diabetes but enhances hepatic secretion of atherogenic lipoproteins.
Keywords: ANGPTL3; HNF1A; PCSK9; UK Biobank; atherosclerosis; coronary artery disease; deep mutational scan; diabetes; gain of function; inflammation; saturation mutagenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M.D. and L.K. are employees and shareholders of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The contribution of functional HNF1A variants and polygenic susceptibility to risk of type 2 diabetes in ancestrally diverse populations.Diabetologia. 2023 Jan;66(1):116-126. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05806-2. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Diabetologia. 2023. PMID: 36216889 Free PMC article.
-
The HNF1A mutant Ala180Val: Clinical challenges in determining causality of a rare HNF1A variant in familial diabetes.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017 Nov;133:142-149. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.08.001. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28934671
-
Unsupervised Clustering of Missense Variants in HNF1A Using Multidimensional Functional Data Aids Clinical Interpretation.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Oct 1;107(4):670-682. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.08.016. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 32910913 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into genetics and clinics of the HNF1A-MODY.Endocr Regul. 2019 Apr 1;53(2):110-134. doi: 10.2478/enr-2019-0013. Endocr Regul. 2019. PMID: 31517624 Review.
-
Primary hepatocellular adenoma due to biallelic HNF1A mutations and its co-occurrence with MODY 3: case-report and review of the literature.Endocrine. 2020 Mar;67(3):544-551. doi: 10.1007/s12020-019-02138-x. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Endocrine. 2020. PMID: 31754975 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heterogeneous enhancer states orchestrate β cell responses to metabolic stress.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 30;15(1):9361. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53717-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39472434 Free PMC article.
-
The biochemistry of melanogenesis: an insight into the function and mechanism of melanogenesis-related proteins.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Aug 20;11:1440187. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1440187. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39228912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide discovery and integrative genomic characterization of insulin resistance loci using serum triglycerides to HDL-cholesterol ratio as a proxy.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 14;15(1):8068. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52105-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39277575 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Myocardial Infarction Management: Exploring Novel Approaches and Strategies.Cureus. 2023 Sep 19;15(9):e45578. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45578. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37868550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic and Transcriptomic Profile of HNF1A-Mutated Liver Adenomas Highlights Molecular Signature and Potential Therapeutic Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 29;25(19):10483. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910483. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lau H.H., Ng N.H.J., Loo L.S.W., Jasmen J.B., Teo A.K.K. The molecular functions of hepatocyte nuclear factors - in and beyond the liver. J. Hepatol. 2018;68:1033–1048. - PubMed
-
- Yamagata K., Oda N., Kaisaki P.J., Menzel S., Furuta H., Vaxillaire M., Southam L., Cox R.D., Lathrop G.M., Boriraj V.V., et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY3) Nature. 1996;384:455–458. - PubMed
-
- McDonald T.J., McEneny J., Pearson E.R., Thanabalasingham G., Szopa M., Shields B.M., Ellard S., Owen K.R., Malecki M.T., Hattersley A.T., et al. Lipoprotein composition in HNF1A-MODY: differentiating between HNF1A-MODY and type 2 diabetes. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2012;413:927–932. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

