The First Exploratory Personalized Medicine Approach to Improve Bariatric Surgery Outcomes Utilizing Psychosocial and Genetic Risk Assessments: Encouraging Clinical Research
- PMID: 37511777
- PMCID: PMC10381606
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13071164
The First Exploratory Personalized Medicine Approach to Improve Bariatric Surgery Outcomes Utilizing Psychosocial and Genetic Risk Assessments: Encouraging Clinical Research
Abstract
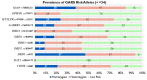
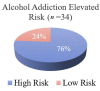
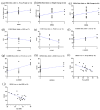
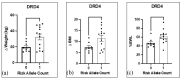
It is predicted that by 2030, globally, an estimated 2.16 billion adults will be overweight, and 1.12 billion will be obese. This study examined genetic data regarding Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS) to evaluate their usefulness in counselling patients undergoing bariatric surgery and gathered preliminary data on the potential use in predicting short term (6-month) weight loss outcomes. Methods: Patients undergoing bariatric surgery (n = 34) were examined for Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) [measures the presence of risk alleles associated with RDS]; as well as their psychosocial traits (questionnaires). BMI changes and sociodemographic data were abstracted from Electronic Health Records. Results: Subjects showed ∆BMI (M = 10.0 ± 1.05 kg/m2) and a mean % excess weight loss (56 ± 13.8%). In addition, 76% of subjects had GARS scores above seven. The homozygote risk alleles for MAO (rs768062321) and DRD1 (rs4532) showed a 38% and 47% prevalence among the subjects. Of the 11 risk alleles identified by GARS, the DRD4 risk allele (rs1800955), was significantly correlated with change in weight and BMI six months post-surgery. We identified correlations with individual risk alleles and psychosocial trait scores. The COMT risk allele (rs4680) showed a negative correlation with EEI scores (r = -0.4983, p < 0.05) and PSQI scores (r = -0.5482, p < 0.05). The GABRB3 risk allele (rs764926719) correlated positively with EEI (r = 0.6161, p < 0.01) and FCQ scores (r = 0.6373, p < 0.01). The OPRM1 risk allele showed a positive correlation with the DERS score (r = 0.5228, p < 0.05). We also identified correlations between DERS and BMI change (r = 0.61; p < 0.01). Conclusions: These data support the potential benefit of a personalized medicinal approach inclusive of genetic testing and psychosocial trait questionnaires when counselling patients with obesity considering bariatric surgery. Future research will explore epigenetic factors that contribute to outcomes of bariatric surgery.
Keywords: Reward Deficiency Syndrome; addiction; bariatric surgery; genetic risk assessment; obesity; psychosocial risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Blum is the inventor of the Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) test and KB220 pro-dopamine variants and through his companies Synaptamine, Inc. and SpliceGen Holdings own all relevant worldwide patents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Correlates as a Predictor of Bariatric Surgery Outcomes after 1 Year.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 27;11(10):2644. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102644. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893019 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical Validation of Risk Alleles in Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Test: Early Identification of Risk for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in 74,566 Case-Control Subjects.J Pers Med. 2022 Aug 26;12(9):1385. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091385. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143170 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and Interventions for Childhood Overweight [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2005 Jul. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2005 Jul. PMID: 20722132 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Genetic Addiction Risk Severity Assessment Identifies Polymorphic Reward Genes as Antecedents to Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS) Hypodopaminergia's Effect on Addictive and Non-Addictive Behaviors in a Nuclear Family.J Pers Med. 2022 Nov 8;12(11):1864. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111864. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36579592 Free PMC article.
-
Bariatric metabolic surgery.Rozhl Chir. 2014 Aug;93(8):404-15. Rozhl Chir. 2014. PMID: 25230385 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Correlates as a Predictor of Bariatric Surgery Outcomes after 1 Year.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 27;11(10):2644. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102644. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893019 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Genetic Risk Scores in Rheumatic Diseases: A Perspective.Genes (Basel). 2023 Dec 1;14(12):2167. doi: 10.3390/genes14122167. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Pharmacogenomics-Based In Silico Investigation of Opioid Prescribing in Post-operative Spine Pain Management and Personalized Therapy.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May 27;44(1):47. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01466-5. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38801645 Free PMC article.
-
Summary Document Research on RDS Anti-addiction Modeling: Annotated Bibliography.J Addict Psychiatry. 2024 Apr 5;8(1):1-33. J Addict Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38765881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grönroos S., Helmiö M., Juuti A., Tiusanen R., Hurme S., Löyttyniemi E., Ovaska J., Leivonen M., Peromaa-Haavisto P., Mäklin S., et al. Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Weight Loss and Quality of Life at 7 Years in Patients With Morbid Obesity: The SLEEVEPASS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2021;156:137–146. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2020.5666. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

