Treatment of antibiotic-resistant bacteria colonizing diabetic foot ulcers by OLED induced antimicrobial photodynamic therapy
- PMID: 37640720
- PMCID: PMC10462621
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-39363-4
Treatment of antibiotic-resistant bacteria colonizing diabetic foot ulcers by OLED induced antimicrobial photodynamic therapy
Abstract
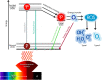
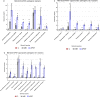
We evaluate the efficacy of antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy (APDT) for inactivating a variety of antibiotic-resistant clinical strains from diabetic foot ulcers. Here we are focused on APDT based on organic light-emitting diodes (OLED). The wound swabs from ten patients diagnosed with diabetic foot ulcers were collected and 32 clinical strains comprising 22 bacterial species were obtained. The isolated strains were identified with the use of mass spectrometry coupled with a protein profile database and tested for antibiotic susceptibility. 74% of isolated bacterial strains exhibited adaptive antibiotic resistance to at least one antibiotic. All strains were subjected to the APDT procedure using an OLED as a light source and 16 µM methylene blue as a photosensitizer. APDT using the OLED led to a large reduction in all cases. For pathogenic bacteria, the reduction ranged from 1.1-log to > 8 log (Klebsiella aerogenes, Enterobacter cloaca, Staphylococcus hominis) even for high antibiotic resistance (MRSA 5-log reduction). Opportunistic bacteria showed a range from 0.4-log reduction for Citrobacter koseri to > 8 log reduction for Kocuria rhizophila. These results show that OLED-driven APDT is effective against pathogens and opportunistic bacteria regardless of drug resistance.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
IDWS is a founder and shareholder of Lustre Skin Ltd which sells products for skincare, including a wearable light source for the treatment of acne.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjuvant effect of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: A case series.J Biophotonics. 2024 Apr;17(4):e202300412. doi: 10.1002/jbio.202300412. Epub 2024 Jan 22. J Biophotonics. 2024. PMID: 38253349
-
Organic light emitting diode for in vitro antimicrobial photodynamic therapy of Candida strains.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021 Dec;36:102567. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102567. Epub 2021 Oct 3. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021. PMID: 34614427
-
_targeted Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy of Biofilm-Embedded and Intracellular Staphylococci with a Phage Endolysin's Cell Binding Domain.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0146621. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01466-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196798 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials enabling clinical translation of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy.J Control Release. 2022 Jun;346:300-316. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.04.035. Epub 2022 Apr 28. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35483636 Review.
-
Microbial Infection and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Diabetic Foot Ulcer in China: Literature Review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 19;13:881659. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.881659. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35663325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Graphene Oxide (GO) for the Treatment of Bone Cancer: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jan 13;14(2):186. doi: 10.3390/nano14020186. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38251150 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th edn (International Diabetes Federation, 2021).
-
- World Health Organisation News/Factsheet. Antimicrobial Resistance. https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resist.... Accessed 17 April 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

