_targeting protein methylation in pancreatic cancer cells results in KRAS signaling imbalance and inhibition of autophagy
- PMID: 37996408
- PMCID: PMC10667277
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06288-9
_targeting protein methylation in pancreatic cancer cells results in KRAS signaling imbalance and inhibition of autophagy
Abstract
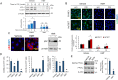
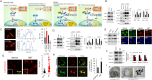
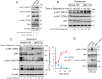
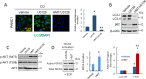
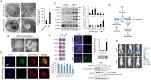
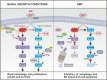
Pancreatic cancer cells with mutant KRAS require strong basal autophagy for viability and growth. Here, we observed that some processes that allow the maintenance of basal autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells are controlled by protein methylation. Thus, by maintaining the methylation status of proteins such as PP2A and MRAS, these cells can sustain their autophagic activity. Protein methylation disruption by a hypomethylating treatment (HMT), which depletes cellular S-adenosylmethionine levels while inducing S-adenosylhomocysteine accumulation, resulted in autophagy inhibition and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. We observed that by reducing the membrane localization of MRAS, hypomethylation conditions produced an imbalance in KRAS signaling, resulting in the partial inactivation of ERK and hyperactivation of the PI3K/AKT-mTORC1 pathway. Interestingly, HMT impeded CRAF activation by disrupting the ternary SHOC2 complex (SHOC2/MRAS/PP1), which functions as a CRAF-S259 holophosphatase. The demethylation events that resulted in PP2A inactivation also favored autophagy inhibition by preventing ULK1 activation while restoring the cytoplasmic retention of the MiT/TFE transcription factors. Since autophagy provides pancreatic cancer cells with metabolic plasticity to cope with various metabolic stress conditions, while at the same time promoting their pathogenesis and resistance to KRAS pathway inhibitors, this hypomethylating treatment could represent a therapeutic opportunity for pancreatic adenocarcinomas.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The University of Murcia holds a patent on the methods used to synthesize and the therapeutic uses of TMCG and the combination therapy with DIPY. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SHOC2 complex-driven RAF dimerization selectively contributes to ERK pathway dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jul 2;116(27):13330-13339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902658116. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31213532 Free PMC article.
-
SHOC2-MRAS-PP1 complex positively regulates RAF activity and contributes to Noonan syndrome pathogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10576-E10585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720352115. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30348783 Free PMC article.
-
ACAGT-007a, an ERK MAPK Signaling Modulator, in Combination with AKT Signaling Inhibition Induces Apoptosis in KRAS Mutant Pancreatic Cancer T3M4 and MIA-Pa-Ca-2 Cells.Cells. 2022 Feb 17;11(4):702. doi: 10.3390/cells11040702. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203351 Free PMC article.
-
KRAS-related proteins in pancreatic cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Dec;168:29-42. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.09.003. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27595930 Review.
-
Crucial Role of Oncogenic KRAS Mutations in Apoptosis and Autophagy Regulation: Therapeutic Implications.Cells. 2022 Jul 13;11(14):2183. doi: 10.3390/cells11142183. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35883626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

