Airway epithelial cGAS inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury through CREB signaling
- PMID: 38114479
- PMCID: PMC10730695
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06364-0
Airway epithelial cGAS inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury through CREB signaling
Abstract
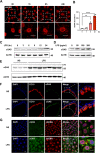
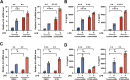
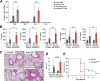
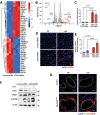
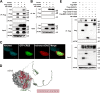
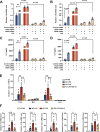
Increased levels of cytosolic DNA in lung tissues play an important role in acute lung injury. However, the detailed mechanisms involved remain elusive. Here, we found that cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS, a cytosolic DNA sensor) expression was increased in airway epithelium in response to increased cytosolic DNA. Conditional deletion of airway epithelial cGAS exacerbated acute lung injury in mice, cGAS knockdown augmented LPS-induced production of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8. Mechanically, deletion of cGAS augmented expression of phosphorylated CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein), and cGAS directly interacted with CREB via its C-terminal domain. Furthermore, CREB knockdown rescued the LPS-induced excessive inflammatory response caused by cGAS deletion. Our study demonstrates that airway epithelial cGAS plays a protective role in acute lung injury and confirms a non-canonical cGAS-CREB pathway that regulates the inflammatory responses in airway epithelium to mediate LPS-induced acute lung injury.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Airway Epithelial cGAS Is Critical for Induction of Experimental Allergic Airway Inflammation.J Immunol. 2020 Mar 15;204(6):1437-1447. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900869. Epub 2020 Feb 7. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32034061
-
Flavonoids derived from licorice suppress LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting the cGAS-STING signaling pathway.Food Chem Toxicol. 2023 May;175:113732. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2023.113732. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Food Chem Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36958387
-
Interference on Cytosolic DNA Activation Attenuates Sepsis Severity: Experiments on Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase (cGAS) Deficient Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 23;22(21):11450. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111450. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768881 Free PMC article.
-
The cGAS-STING pathway: The role of self-DNA sensing in inflammatory lung disease.FASEB J. 2020 Oct;34(10):13156-13170. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001607R. Epub 2020 Aug 28. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32860267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current understanding of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway: Structure, regulatory mechanisms, and related diseases.Zool Res. 2023 Jan 18;44(1):183-218. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.464. Zool Res. 2023. PMID: 36579404 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

