Mitochondrial p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase: Insights into Its Regulation of and Role in LONP1-Deficient Nematodes
- PMID: 38139038
- PMCID: PMC10743222
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242417209
Mitochondrial p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase: Insights into Its Regulation of and Role in LONP1-Deficient Nematodes
Abstract
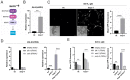
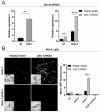
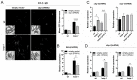
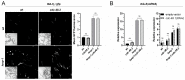
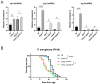
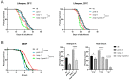
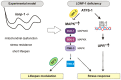
p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) cascades are central regulators of numerous physiological cellular processes, including stress response signaling. In C. elegans, mitochondrial dysfunction activates a PMK-3/p38 MAPK signaling pathway (MAPKmt), but its functional role still remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate the induction of MAPKmt in worms deficient in the lonp-1 gene, which encodes the worm ortholog of mammalian mitochondrial LonP1. This induction is subjected to negative regulation by the ATFS-1 transcription factor through the CREB-binding protein (CBP) ortholog CBP-3, indicating an interplay between both activated MAPKmt and mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response (UPRmt) surveillance pathways. Our results also reveal a genetic interaction in lonp-1 mutants between PMK-3 kinase and the ZIP-2 transcription factor. ZIP-2 has an established role in innate immunity but can also modulate the lifespan by maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis during ageing. We show that in lonp-1 animals, ZIP-2 is activated in a PMK-3-dependent manner but does not confer increased survival to pathogenic bacteria. However, deletion of zip-2 or pmk-3 shortens the lifespan of lonp-1 mutants, suggesting a possible crosstalk under conditions of mitochondrial perturbation that influences the ageing process. Furthermore, loss of pmk-3 specifically diminished the extreme heat tolerance of lonp-1 worms, highlighting the crucial role of PMK-3 in the heat shock response upon mitochondrial LONP-1 inactivation.
Keywords: C. elegans; LONP-1; PMK-3; ZIP-2; ageing; heat stress response; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of the conserved transcription factor ATF-7 by PMK-1 p38 MAPK regulates innate immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2010 Apr 1;6(4):e1000892. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000892. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20369020 Free PMC article.
-
The bZIP transcription factor BATF3/ZIP-10 suppresses innate immunity by attenuating PMK-1/p38 signaling.Int Immunol. 2023 Apr 4;35(4):181-196. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxac053. Int Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36409527
-
Organismal and Cellular Stress Responses upon Disruption of Mitochondrial Lonp1 Protease.Cells. 2022 Apr 16;11(8):1363. doi: 10.3390/cells11081363. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456042 Free PMC article.
-
The p38 MAPK PMK-1 shows heat-induced nuclear translocation, supports chaperone expression, and affects the heat tolerance of Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013 May;18(3):293-306. doi: 10.1007/s12192-012-0382-y. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013. PMID: 23117578 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay of p38 MAPK signaling and mitochondrial metabolism, a dynamic _target in cancer and pathological contexts.Biochem Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;225:116307. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116307. Epub 2024 May 24. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38797269 Review.
Cited by
-
Nervous system guides behavioral immunity in Caenorhabditis elegans.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 15;12:e18289. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18289. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39430568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

