Prognostic value and gene regulatory network of CMSS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38160346
- PMCID: PMC11191500
- DOI: 10.3233/CBM-230209
Prognostic value and gene regulatory network of CMSS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Cms1 ribosomal small subunit homolog (CMSS1) is an RNA-binding protein that may play an important role in tumorigenesis and development.
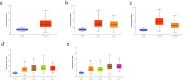
Objective: RNA-seq data from the GEPIA database and the UALCAN database were used to analyze the expression of CMSS1 in liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC) and its relationship with the clinicopathological features of the patients.
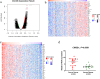
Methods: LinkedOmics was used to identify genes associated with CMSS1 expression and to identify miRNAs and transcription factors significantly associated with CMSS1 by GSEA.
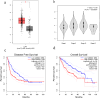
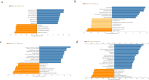
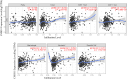
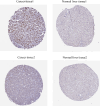
Results: The expression level of CMSS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues was significantly higher than that in normal tissues. In addition, the expression level of CMSS1 in advanced tumors was significantly higher than that in early tumors. The expression level of CMSS1 was higher in TP53-mutated tumors than in non-TP53-mutated tumors. CMSS1 expression levels were strongly correlated with disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in patients with LIHC, and high CMSS1 expression predicted poorer OS (P< 0.01) and DFS (P< 0.01). Meanwhile, our results suggested that CMSS1 is associated with the composition of the immune microenvironment of LIHC.
Conclusions: The present study suggests that CMSS1 is a potential molecular marker for the diagnosis and prognostic of LIHC.
Keywords: . bioinformatics; CMSS1; diagnosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic significance and carcinogenic mechanism of pan-cancer gene POU5F1 in liver hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Dec;9(23):8782-8800. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3486. Epub 2020 Sep 26. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32978904 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential crucial genes associated with the pathogenesis and prognosis of liver hepatocellular carcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2021 Aug;74(8):504-512. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206979. Epub 2020 Oct 1. J Clin Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33004423
-
Prognostic and immunological potential of PPM1G in hepatocellular carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 5;13(9):12929-12954. doi: 10.18632/aging.202964. Epub 2021 May 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33952716 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of liver hepatocellular carcinoma-specific lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on bioinformatics analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 16;16(4):e0249881. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249881. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33861762 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation analysis of RDM1 gene with immune infiltration and clinical prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2021 Sep 30;41(9):BSR20203978. doi: 10.1042/BSR20203978. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34435618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marquardt J.U., Andersen J.B. and Thorgeirsson S.S., Functional and genetic deconstruction of the cellular origin in liver cancer, Nat Rev Cancer 15(11) (2015), 653–667. - PubMed
-
- Seufert L. et al., RNA-binding proteins and their role in kidney disease, Nat Rev Nephrol 18(3) (2022), 153–170. - PubMed
-
- De Conti L., Baralle M. and Buratti E., Neurodegeneration and RNA-binding proteins, Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 8(2) (2017), 1394. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

