PHB2 promotes SHIP2 ubiquitination via the E3 ligase NEDD4 to regulate AKT signaling in gastric cancer
- PMID: 38200519
- PMCID: PMC10782615
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02937-1
PHB2 promotes SHIP2 ubiquitination via the E3 ligase NEDD4 to regulate AKT signaling in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Prohibitin 2 (PHB2) exhibits opposite functions of promoting or inhibiting tumour across various cancer types. In this study, we aim to investigate its functions and underlying mechanisms in the context of gastric cancer (GC).
Methods: PHB2 protein expression levels in GC and normal tissues were examined using western blot and immunohistochemistry. PHB2 expression level associations with patient outcomes were examined through Kaplan-Meier plotter analysis utilizing GEO datasets (GSE14210 and GSE29272). The biological role of PHB2 and its subsequent regulatory mechanisms were elucidated in vitro and in vivo. GC cell viability and proliferation were assessed using MTT cell viability analysis, clonogenic assays, and BrdU incorporation assays, while the growth of GC xenografted tumours was measured via IHC staining of Ki67. The interaction among PHB2 and SHIP2, as well as between SHIP2 and NEDD4, was identified through co-immunoprecipitation, GST pull-down assays, and deletion-mapping experiments. SHIP2 ubiquitination and degradation were assessed using cycloheximide treatment, plasmid transfection and co-immunoprecipitation, followed by western blot analysis.
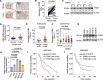
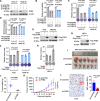
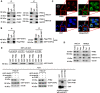
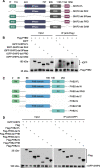
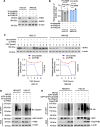
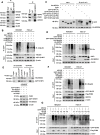
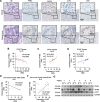
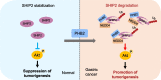
Results: Our analysis revealed a substantial increase in PHB2 expression in GC tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues. Notably, higher PHB2 levels correlated with poorer patient outcomes, suggesting its clinical relevance. Functionally, silencing PHB2 in GC cells significantly reduced cell proliferation and retarded GC tumour growth, whereas overexpression of PHB2 further enhanced GC cell proliferation. Mechanistically, PHB2 physically interacted with Src homology 2-containing inositol 5-phosphatase 2 (SHIP2) in the cytoplasm of GC cells, thus leading to SHIP2 degradation via its novel E3 ligase NEDD4. It subsequently activated the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and thus promoted GC cell proliferation.
Conclusions: Our findings highlight the importance of PHB2 upregulation in driving GC progression and its association with adverse patient outcomes. Understanding the functional impact of PHB2 on GC growth contributes valuable insights into the molecular underpinnings of GC and may pave the way for the development of _targeted therapies to improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; NEDD4; PHB2; SHIP2; Ubiquitination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Suppression of SHIP2 contributes to tumorigenesis and proliferation of gastric cancer cells via activation of Akt.J Gastroenterol. 2016 Mar;51(3):230-40. doi: 10.1007/s00535-015-1101-0. Epub 2015 Jul 23. J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26201869
-
Catalytically inactive SHIP2 inhibits proliferation by attenuating PDGF signaling in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Jan;218(1):228-36. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21595. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18814181
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 mediates cell migration signaling of EGFR in lung cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0784-2. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455656 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN and Other PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 Lipid Phosphatases in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 2;21(23):9189. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239189. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33276499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of the HECT E3 ubiquitin ligases in gastric cancer.Pathol Oncol Res. 2023 Feb 7;29:1610931. doi: 10.3389/pore.2023.1610931. eCollection 2023. Pathol Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 36825281 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alteration of gene expression and protein solubility of the PI 5-phosphatase SHIP2 are correlated with Alzheimer's disease pathology progression.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Jun 4;147(1):94. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02745-7. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 38833073 Free PMC article.
-
NEDD4 and NEDD4L: Ubiquitin Ligases Closely Related to Digestive Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 May 13;14(5):577. doi: 10.3390/biom14050577. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785984 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

