Extending the Shelf Life of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) with Sub-Chilled Storage and Modified Atmosphere Packaging in Recyclable Mono-Material Trays
- PMID: 38201047
- PMCID: PMC10778411
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13010019
Extending the Shelf Life of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) with Sub-Chilled Storage and Modified Atmosphere Packaging in Recyclable Mono-Material Trays
Abstract
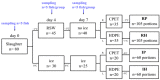
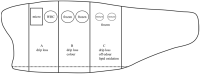
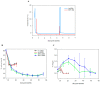
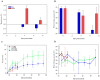
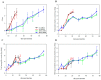
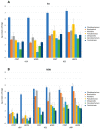
This study investigated the effect of sub-chilling whole gutted salmon and sub-chilled storage at -1 °C in modified-atmosphere packaging in two recyclable mono-material trays (CPET, HDPE). Quality parameters were measured, including water-holding properties, salt content, color, texture, lipid oxidation, and sensory and microbiological shelf life. The oxygen transmission rate was measured for the packages. Compared to traditional fish storage on ice, sub-chilling gave a 0.4% weight gain, better water-holding capacity, and higher salt content. The sub-chilled fish gave a significantly better sensory quality and microbiological shelf life of up to 49 days. Photobacterium was the dominating bacteria during storage. Salmon packaged in CPET trays had a higher drip loss than HDPE trays, but a lower rate of lipid oxidation (1-penten-3-ol). Our results showed the feasibility of significantly extending shelf life with sub-chilling, removing the need for ice. Moreover, using recyclable trays for packaging contributes to a circular economy without compromising food quality.
Keywords: Atlantic salmon; circular economy; modified atmosphere packaging; packaging materials; quality; shelf life; sub-chilling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The quality of frozen-thawed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fillets as affected by sub-chilling before freezing.J Sci Food Agric. 2024 Oct;104(13):8130-8142. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13643. Epub 2024 Jun 6. J Sci Food Agric. 2024. PMID: 38843490
-
A comparative study of Atlantic salmon chilled in refrigerated seawater versus on ice: from whole fish to cold-smoked fillets.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 13;10(1):17160. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73302-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33051493 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial spoilage and formation of biogenic amines in fresh and thawed modified atmosphere-packed salmon (Salmo salar) at 2 degrees C.J Appl Microbiol. 2002;92(4):790-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2002.01588.x. J Appl Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11966922
-
Quality Assessment of Chilled and Frozen Fish-Mini Review.Foods. 2020 Nov 25;9(12):1739. doi: 10.3390/foods9121739. Foods. 2020. PMID: 33255842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Centralized packaging of retail meat cuts: a review.J Food Prot. 1999 Apr;62(4):418-25. doi: 10.4315/0362-028x-62.4.418. J Food Prot. 1999. PMID: 10419219 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on the Effect and Mechanism of Superchilling Preservation Technology on Meat Quality Control.Foods. 2024 Oct 18;13(20):3309. doi: 10.3390/foods13203309. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39456370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sivertsvik M., Jeksrud W.K., Rosnes J.T. A review of modified atmosphere packaging of fish and fishery products—significance of microbial growth, activities and safety. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002;37:107–127. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2621.2002.00548.x. - DOI
-
- Church N. Developments in modified-atmosphere packaging and related technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1994;5:345–352. doi: 10.1016/0924-2244(94)90211-9. - DOI
-
- Rotabakk B.T., Sivertsvik M. 11—Solubility of carbon dioxide in muscle foods and its use to extend the shelf life of packaged products. In: Kerry J.P., editor. Advances in Meat, Poultry and Seafood Packaging. Woodhead Publishing; Sawston, UK: 2012. pp. 314–330.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

