A Brain-Protective Sterol from Soft Coral Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9-Mediated Astrocytic Migration
- PMID: 38275397
- PMCID: PMC10813456
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12010226
A Brain-Protective Sterol from Soft Coral Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9-Mediated Astrocytic Migration
Abstract
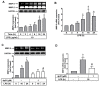
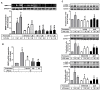
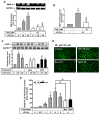
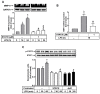
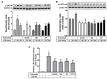
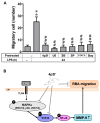
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are proteolytic enzymes, promote blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption, leading to neuronal damage and neuroinflammation. Among them, MMP-9 upregulation serves as an inflammatory biomarker in the central nervous system (CNS). Currently, the development of marine organism-derived bioactive compounds or metabolites as anti-inflammatory drugs has received considerable attention. The 9,11-secosteroid, 3β,11-dihydroxy-9,11-secogorgost-5-en-9-one (4p3f), is a novel sterol compound extracted from the soft coral Sinularia leptoclado with potential anti-inflammatory activity. However, the effect of and potential for brain protection of 4p3f on brain astrocytes remain unclear. Herein, we used rat brain astrocytes (RBAs) to investigate the effects and signaling mechanisms of 4p3f on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced MMP-9 expression via zymographic, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), Western blot, immunofluorescence staining, promoter-reporter, and cell migration analyses. We first found that 4p3f blocked LPS-induced MMP-9 expression in RBAs. Next, we demonstrated that LPS induced MMP-9 expression via the activation of ERK1/2, p38 MAPK, and JNK1/2, which is linked to the STAT3-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Finally, 4p3f effectively inhibited LPS-induced upregulation of MMP-9-triggered RBA cell migration. These data suggest that a novel sterol from soft coral, 4p3f, may have anti-inflammatory and brain-protective effects by attenuating these signaling pathways of MMP-9-mediated events in brain astrocytes. Accordingly, the soft coral-derived sterol 4p3f may emerge as a potential candidate for drug development or as a natural compound with neuroprotective properties.
Keywords: anti-inflammation; brain astrocytes; cell migration; lipopolysaccharide; matrix metalloproteinase-9; soft coral.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rottlerin, a natural polyphenol compound, inhibits upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and brain astrocytic migration by reducing PKC-δ-dependent ROS signal.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jun 6;17(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01859-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32505192 Free PMC article.
-
Pristimerin Inhibits MMP-9 Expression and Cell Migration Through Attenuating NOX/ROS-Dependent NF-κB Activation in Rat Brain Astrocytes Challenged with LPS.J Inflamm Res. 2020 Jul 20;13:325-341. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S252659. eCollection 2020. J Inflamm Res. 2020. PMID: 32765041 Free PMC article.
-
The COX-2-derived PGE2 autocrine contributes to bradykinin-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and astrocytic migration via STAT3 signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Nov 23;18(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00680-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 33228717 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression Associated with Cell Migration in Rat Brain Astrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 30;21(1):259. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010259. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31905967 Free PMC article.
-
Galangin Inhibits LPS-Induced MMP-9 Expression via Suppressing Protein Kinase-Dependent AP-1 and FoxO1 Activation in Rat Brain Astrocytes.J Inflamm Res. 2020 Nov 20;13:945-960. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S276925. eCollection 2020. J Inflamm Res. 2020. PMID: 33244253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bush T.G., Puvanachandra N., Horner C.H., Polito A., Ostenfeld T., Svendsen C.N., Mucke L., Johnson M.H., Sofroniew M.V. Leukocyte infiltration, neuronal degeneration, and neurite outgrowth after ablation of scar-forming, reactive astrocytes in adult transgenic mice. Neuron. 1999;23:297–308. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80781-3. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

