The Neuroprotective Role of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa, Wild) Supplementation in Hippocampal Morphology and Memory of Adolescent Stressed Rats
- PMID: 38337665
- PMCID: PMC10857380
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16030381
The Neuroprotective Role of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa, Wild) Supplementation in Hippocampal Morphology and Memory of Adolescent Stressed Rats
Abstract
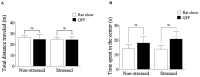
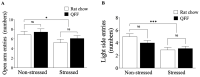
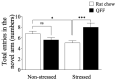
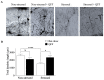
Brain physiology and morphology are vulnerable to chronic stress, impacting cognitive performance and behavior. However, functional compounds found in food may alleviate these alterations. White quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa, Wild) seeds contain a high content of n-3 fatty acids, including alpha-linolenic acid. This study aimed to evaluate the potential neuroprotective role of a quinoa-based functional food (QFF) in rats. Prepubertal male Sprague-Dawley rats were fed with rat chow or QFF (50% rat chow + 50% dehydrated quinoa seeds) and exposed or not to restraint stress protocol (2 h/day; 15 days). Four experimental groups were used: Non-stressed (rat chow), Non-stressed + QFF, Stressed (rat chow) and Stressed + QFF. Weight gain, locomotor activity (open field), anxiety (elevated plus maze, light-dark box), spatial memory (Y-maze), and dendritic length in the hippocampus were measured in all animals. QFF intake did not influence anxiety-like behaviors, while the memory of stressed rats fed with QFF improved compared to those fed with rat chow. Additionally, QFF intake mitigated the stress-induced dendritic atrophy in pyramidal neurons located in the CA3 area of the hippocampus. The results suggest that a quinoa-supplemented diet could play a protective role in the memory of chronically stressed rats.
Keywords: fatty acids; hippocampus; memory; quinoa; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation restored impaired memory and GABAergic synaptic efficacy in the hippocampus of stressed rats.Nutr Neurosci. 2018 Oct;21(8):556-569. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2017.1323609. Epub 2017 May 8. Nutr Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28482757
-
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 modulates the effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids on memory of stressed rats.Nutr Neurosci. 2021 Aug;24(8):583-600. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2019.1659561. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Nutr Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 31637966
-
The effects of chronic stress on hippocampal morphology and function: an evaluation of chronic restraint paradigms.Brain Res. 2007 Aug 3;1161:56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.05.042. Epub 2007 Jun 2. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17603026 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic stress impairs rat spatial memory on the Y maze, and this effect is blocked by tianeptine pretreatment.Behav Neurosci. 1996 Dec;110(6):1321-34. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.110.6.1321. Behav Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8986335
-
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): composition, chemistry, nutritional, and functional properties.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2009;58:1-31. doi: 10.1016/S1043-4526(09)58001-1. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2009. PMID: 19878856 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

