Voltammetric Sensor Based on the Combination of Tin and Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles with Surfactants for Quantification of Sunset Yellow FCF
- PMID: 38339646
- PMCID: PMC10857103
- DOI: 10.3390/s24030930
Voltammetric Sensor Based on the Combination of Tin and Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles with Surfactants for Quantification of Sunset Yellow FCF
Abstract
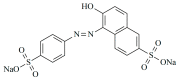
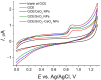
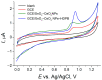
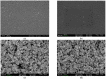
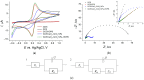
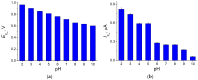
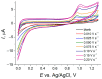
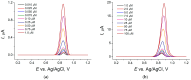
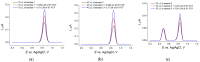
Sunset Yellow FCF (SY FCF) is one of the widely used synthetic azo dyes in the food industry whose content has to be controlled for safety reasons. Electrochemical sensors are a promising tool for this type of task. A voltammetric sensor based on a combination of tin and cerium dioxide nanoparticles (SnO2-CeO2 NPs) with surfactants has been developed for SY FCF determination. The synergetic effect of both types of NPs has been confirmed. Surfactants of various natures (sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), Brij® 35, and hexadecylpyridinium bromide (HDPB)) have been tested as dispersive media. The best effects, i.e., the highest oxidation currents of SY FCF, have been observed in the case of HDPB. The sensor demonstrates a 4.5-fold-higher electroactive surface area and a 38-fold-higher electron transfer rate compared to the bare glassy carbon electrode (GCE). The electrooxidation of SY FCF is an irreversible, two-electron, diffusion-driven process involving proton transfer. In differential pulse mode in Britton-Robinson buffer (BRB) pH 2.0, the sensor gives a linear response to SY FCF from 0.010 to 1.0 μM and from 1.0 to 100 μM with an 8.0 nM detection limit. The absence of an interferent effect from other typical food components and colorants has been shown. The sensor has been tested on soft drinks and validated with the standard chromatographic method.
Keywords: azo dyes; chemically modified electrodes; electrochemical sensors; food colorants; metal oxide nanoparticles; surfactants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
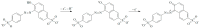
Similar articles
-
Electropolymerized 4-Aminobenzoic Acid Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Simultaneous Determination of Food Azo Dyes.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 11;14(24):5429. doi: 10.3390/polym14245429. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559795 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Voltammetric Sensor for the Simultaneous Quantification of Tartrazine and Brilliant Blue FCF.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;23(3):1094. doi: 10.3390/s23031094. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36772133 Free PMC article.
-
An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Carbon Paper Modified with Graphite Powder for Sensitive Determination of Sunset Yellow and Tartrazine in Drinks.Sensors (Basel). 2022 May 27;22(11):4092. doi: 10.3390/s22114092. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684711 Free PMC article.
-
Cerium(IV) and Iron(III) Oxides Nanoparticles Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Sensitive and Selective Determination of Lipoic Acid.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 17;21(22):7639. doi: 10.3390/s21227639. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833711 Free PMC article.
-
Latest advances on the nanomaterials-based electrochemical analysis of azo toxic dyes Sunset Yellow and Tartrazine in food samples.Food Chem Toxicol. 2021 Oct;156:112524. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112524. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34454997 Review.
References
-
- Subburaj M., Faseela P.M. Synthetic Food Colours. Scholars’ Press; London, UK: 2016. 80p
-
- Matsyura O., Besh L., Besh O., Troyanovska O., Slyuzar Z. Hypersensitivity reactions to food additives in pediatric practice: Two clinical cases. Georgian Med. News. 2020;307:91–95. - PubMed
-
- Rovina K., Prabakaran P.P., Siddiquee S., Shaarani S.M. Methods for the analysis of Sunset Yellow FCF (E110) in food and beverage products—A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016;85:47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2016.05.009. - DOI
-
- EFSA Reconsideration of the temporary ADI and refined exposure assessment for Sunset Yellow FCF (E 110) EFSA J. 2014;12:3765. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3765. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

