Cardiac cell senescence: molecular mechanisms, key proteins and therapeutic _targets
- PMID: 38355681
- PMCID: PMC10866973
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-023-01792-5
Cardiac cell senescence: molecular mechanisms, key proteins and therapeutic _targets
Abstract
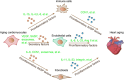
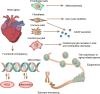
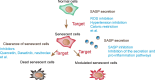
Cardiac aging, particularly cardiac cell senescence, is a natural process that occurs as we age. Heart function gradually declines in old age, leading to continuous heart failure, even in people without a prior history of heart disease. To address this issue and improve cardiac cell function, it is crucial to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying cardiac senescence. This review summarizes the main mechanisms and key proteins involved in cardiac cell senescence. This review further discusses the molecular modulators of cellular senescence in aging hearts. Furthermore, the discussion will encompass comprehensive descriptions of the key drugs, modes of action and potential _targets for intervention in cardiac senescence. By offering a fresh perspective and comprehensive insights into the molecular mechanisms of cardiac senescence, this review seeks to provide a fresh perspective and important theoretical foundations for the development of drugs _targeting this condition.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic landscape in cardiac aging: insights into molecular biology and therapeutic implications.Signal Transduct _target Ther. 2023 Mar 14;8(1):114. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01378-8. Signal Transduct _target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36918543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex- and age-related differences in renal and cardiac injury and senescence in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 May 22;14(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00519-6. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 37217968 Free PMC article.
-
Senescence mechanisms and _targets in the heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Mar 25;118(5):1173-1187. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab161. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33963378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
circHIPK3 prevents cardiac senescence by acting as a scaffold to recruit ubiquitin ligase to degrade HuR.Theranostics. 2022 Oct 31;12(17):7550-7566. doi: 10.7150/thno.77630. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 36438474 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral Adipose Tissue Drives Cardiac Aging Through Modulation of Fibroblast Senescence by Osteopontin Production.Circulation. 2018 Aug 21;138(8):809-822. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031358. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 29500246
Cited by
-
Potential Player of Platelet in the Pathogenesis of Cardiotoxicity: Molecular Insight and Future Perspective.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Dec;24(12):1381-1394. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09924-8. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39397196 Review.
-
FBXL19 in endothelial cells protects the heart from influenza A infection by enhancing antiviral immunity and reducing cellular senescence programs.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):H937-H946. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00371.2024. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39150394
-
A Mitochondrial Basis for Heart Failure Progression.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Dec;38(6):1161-1171. doi: 10.1007/s10557-024-07582-0. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 38878138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical redox imaging to screen synthetic hydrogels for stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte differentiation and maturation.Biophotonics Discov. 2024 May;1(1):015002. doi: 10.1117/1.bios.1.1.015002. Epub 2024 May 20. Biophotonics Discov. 2024. PMID: 39036366 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of flavonoids to mitigate cellular senescence in cardiovascular disease.Biogerontology. 2024 Nov;25(6):985-1010. doi: 10.1007/s10522-024-10141-7. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Biogerontology. 2024. PMID: 39325277 Review.
References
-
- Makino K, Lee S, Bae S, Chiba I, Harada K, Katayama O, et al. Absolute cardiovascular disease risk assessed in old age predicts disability and mortality: a retrospective cohort study of community-dwelling older adults. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;1024:e022004.. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.022004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

