Neurofibromin 1 controls metabolic balance and Notch-dependent quiescence of murine juvenile myogenic progenitors
- PMID: 38360927
- PMCID: PMC10869796
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45618-z
Neurofibromin 1 controls metabolic balance and Notch-dependent quiescence of murine juvenile myogenic progenitors
Abstract
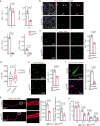
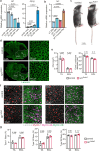
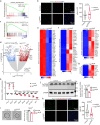
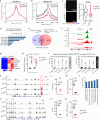
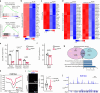
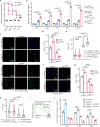
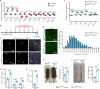
Patients affected by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) frequently show muscle weakness with unknown etiology. Here we show that, in mice, Neurofibromin 1 (Nf1) is not required in muscle fibers, but specifically in early postnatal myogenic progenitors (MPs), where Nf1 loss led to cell cycle exit and differentiation blockade, depleting the MP pool resulting in reduced myonuclear accretion as well as reduced muscle stem cell numbers. This was caused by precocious induction of stem cell quiescence coupled to metabolic reprogramming of MPs impinging on glycolytic shutdown, which was conserved in muscle fibers. We show that a Mek/Erk/NOS pathway hypersensitizes Nf1-deficient MPs to Notch signaling, consequently, early postnatal Notch pathway inhibition ameliorated premature quiescence, metabolic reprogramming and muscle growth. This reveals an unexpected role of Ras/Mek/Erk signaling supporting postnatal MP quiescence in concert with Notch signaling, which is controlled by Nf1 safeguarding coordinated muscle growth and muscle stem cell pool establishment. Furthermore, our data suggest transmission of metabolic reprogramming across cellular differentiation, affecting fiber metabolism and function in NF1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyperactive Ras/MAPK signaling is critical for tibial nonunion fracture in neurofibromin-deficient mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Dec 1;22(23):4818-28. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt333. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23863460 Free PMC article.
-
Ras-Mek-Erk signaling regulates Nf1 heterozygous neointima formation.Am J Pathol. 2014 Jan;184(1):79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.09.022. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Am J Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24211110 Free PMC article.
-
Akt- or MEK-mediated mTOR inhibition suppresses Nf1 optic glioma growth.Neuro Oncol. 2015 Jun;17(6):843-53. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou329. Epub 2014 Dec 21. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25534823 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofibromatosis 1: closing the GAP between mice and men.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003 Feb;13(1):20-7. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(02)00015-1. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003. PMID: 12573431 Review.
-
[Neurofibromin - protein structure and cellular functions in the context of neurofibromatosis type I pathogenesis].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015 Dec 9;69:1331-48. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1185213. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015. PMID: 26671924 Review. Polish.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

