Recent understanding of the mechanisms of the biological activities of hesperidin and hesperetin and their therapeutic effects on diseases
- PMID: 38486739
- PMCID: PMC10937595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26862
Recent understanding of the mechanisms of the biological activities of hesperidin and hesperetin and their therapeutic effects on diseases
Abstract
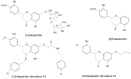
Flavonoids are natural phytochemicals that have therapeutic effects and act in the prevention of several pathologies. These phytochemicals can be found in lemon, sweet orange, bitter orange, clementine. Hesperidin and hesperetin are citrus flavonoids from the flavanones subclass that have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor and antibacterial potential. Preclinical studies and clinical trials demonstrated therapeutical effects of hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin in various diseases, such as bone diseases, cardiovascular diseases, neurological diseases, respiratory diseases, digestive diseases, urinary tract diseases. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the biological activities of hesperidin and hesperetin, their therapeutic potential in various diseases and their associated molecular mechanisms. This article also discusses future considerations for the clinical applications of hesperidin and hesperetin.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Antibacterial; Antioxidant; Antitumor; Hesperetin; Hesperidin.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Effects of Citrus Flavonoids Neohesperidin, Hesperidin and Its Aglycone, Hesperetin on Bone Health.Biomolecules. 2022 Apr 23;12(5):626. doi: 10.3390/biom12050626. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35625554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health-promoting effects of the citrus flavanone hesperidin.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Feb 11;57(3):613-631. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2014.906382. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017. PMID: 25675136 Review.
-
Hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin in breast cancer therapy: A review of recent developments and future prospects.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Dec;28(12):6730-6747. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.07.046. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34866972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comparative Study of Hesperetin, Hesperidin and Hesperidin Glucoside: Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antibacterial Activities In Vitro.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 20;11(8):1618. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081618. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009336 Free PMC article.
-
Biological activity of natural flavonoids as impacted by protein flexibility: an example of flavanones.Mol Biosyst. 2015 Apr;11(4):1119-33. doi: 10.1039/c4mb00662c. Mol Biosyst. 2015. PMID: 25673513
Cited by
-
Hesperetin Attenuates T-2 Toxin-Induced Chondrocyte Injury by Inhibiting the p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 14;16(18):3107. doi: 10.3390/nu16183107. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339707 Free PMC article.
-
Blood circulation effect of fermented citrus bioconversion product (FCBP) in EA.hy926 endothelial cells and high-fat diet-fed mouse model.Food Nutr Res. 2024 Nov 7;68. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v68.10682. eCollection 2024. Food Nutr Res. 2024. PMID: 39534464 Free PMC article.
-
Testicular protective effects of hesperidin against chemical and biological toxicants.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 May 23;13(3):tfae078. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae078. eCollection 2024 Jun. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38799410 Review.
References
-
- Peluso I., Romanelli L., Palmery M. Interactions between prebiotics, probiotics, polyunsaturated fatty aci ds and polyphenols: diet or supplementation for metabolic syndrome pre vention? Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014;65(3):259–267. - PubMed
-
- Asrih M., Jornayvaz F.R. Metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: is insulin re sistance the link? Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015;418(1):55–65. - PubMed
-
- Alissa E.M., Ferns G.A. Dietary fruits and vegetables and cardiovascular diseases risk. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017;57(9):1950–1962. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

