Effects of Switching from Degludec to Glargine U300 in Patients with Insulin-Dependent Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38541176
- PMCID: PMC10972496
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina60030450
Effects of Switching from Degludec to Glargine U300 in Patients with Insulin-Dependent Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
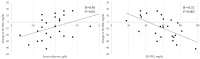
Background and Objectives: Degludec (Deg) and glargine U300 (Gla-300) are insulin analogs with longer and smoother pharmacodynamic action than glargine U100 (Gla-100), a long-acting insulin that has been widely used for many years in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Both improve glycemic variability (GV) and the frequency of hypoglycemia, unlike Gla-100. However, it is unclear which insulin analog affects GV and hypoglycemia better in patients with insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes. We evaluated the effects of switching from Deg to Gla-300 on the day-to-day GV and the frequency of hypoglycemia in patients with insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes treated with Deg-containing basal-bolus insulin therapy (BBT). Materials and Methods: We conducted a retrospective study on 24 patients with insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes whose treatment was switched from Deg-containing BBT to Gla-300-containing BBT. We evaluated the day-to-day GV measured as the standard deviation of fasting blood glucose levels (SD-FBG) calculated by the self-monitoring of blood glucose records, the frequency of hypoglycemia (total, severe, and nocturnal), and blood glucose levels measured as fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). Results: The characteristics of the patients included in the analysis with high SD-FBG had frequent hypoglycemic events, despite the use of Deg-containing BBT. For this population, SD-FBG and the frequency of nocturnal hypoglycemia decreased after the switch from Deg to Gla-300. Despite the decrease in the frequency of nocturnal hypoglycemia, the FPG and HbA1c did not worsen by the switch. The change in the SD-FBG had a negative correlation with the SD-FBG at baseline and a positive correlation with serum albumin levels. Conclusions: Switching from Deg to Gla-300 improved the SD-FBG and decreased the frequency of nocturnal hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent type 1 diabetes treated with Deg-containing BBT, especially in cases with low serum albumin levels and a high GV.
Keywords: degludec; glargine U300; glycemic variability; hypoglycemia; type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec U100 versus insulin glargine U300 in adults with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and indirect treatment comparison.Int J Clin Pharm. 2022 Jun;44(3):587-598. doi: 10.1007/s11096-022-01410-x. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Int J Clin Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35476308 Review.
-
Effect of Insulin Degludec vs Insulin Glargine U100 on Hypoglycemia in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: The SWITCH 2 Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2017 Jul 4;318(1):45-56. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.7117. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 28672317 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Outcomes of glycemic control in type 1 diabetic patients switched from basal insulin glargine 100 U/ml to glargine 300 U/ml in real life.Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2018 May;13(3):167-171. doi: 10.1080/17446651.2018.1469405. Epub 2018 May 2. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30058899
-
Risk of hypoglycaemia with insulin degludec versus insulin glargine U300 in insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes: the randomised, head-to-head CONCLUDE trial.Diabetologia. 2020 Apr;63(4):698-710. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05080-9. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 31984443 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic evaluation of insulin glargine U300 for the treatment of type 1 diabetes.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016 Dec;12(12):1521-1526. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2016.1245722. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27710135 Review.
References
-
- Goff D.C., Gerstein H.C., Ginsberg H.N., Cushman W.C., Margolis K.L., Byington R.P., Buse J.B., Genuth S., Probstfield J.L., Simons-Morton D.G., et al. Prevention of cardiovascular disease in persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Current knowledge and rationale for the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial. Am. J. Cardiol. 2007;99:4i–20i. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.03.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonds D.E., Miller M.E., Bergenstal R.M., Buse J.B., Byington R.P., Cutler J.A., Dudl R.J., Ismail-Beigi F., Kimel A.R., Hoogwerf B., et al. The association between symptomatic, severe hypoglycemia and mortality in type 2 diabetes: Retrospective epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD study. BMJ. 2010;340:b4909. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b4909. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical