Research progress on oncoprotein hepatitis B X‑interacting protein (Review)
- PMID: 38577934
- PMCID: PMC11019400
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13213
Research progress on oncoprotein hepatitis B X‑interacting protein (Review)
Abstract
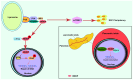
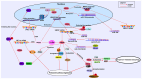
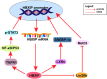
Hepatitis B X‑interacting protein (HBXIP) is a membrane protein located on the lysosomal surface and encoded by the Lamtor gene. It is expressed by a wide range of tumor types, including breast cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, and its expression is associated with certain clinicopathological characteristics. In the past decade, research on the oncogenic mechanisms of HBXIP has increased and the function of HBXIP in normal cells has been gradually elucidated. In the present review, the following was discussed: The normal physiological role of the HBXIP carcinogenic mechanism; the clinical significance of high levels of HBXIP expression in different tumors; HBXIP regulation of transcription, post‑transcription and post‑translation processes in tumors; the role of HBXIP in improving the antioxidant capacity of tumor cells; the inhibition of ferroptosis of tumor cells and regulating the metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells; and the role of HBXIP in promoting the malignant progression of tumors. In conclusion, the present review summarized the existing knowledge of HBXIP, established its carcinogenic mechanism and discussed future related research on HBXIP.
Keywords: ferroptosis; hepatitis B X‑interacting protein; oxidative stress; post‑transcription; review; transcription; translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The oncoprotein HBXIP suppresses gluconeogenesis through modulating PCK1 to enhance the growth of hepatoma cells.Cancer Lett. 2016 Nov 28;382(2):147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.025. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27609066
-
The regulation of acetylation and stability of HMGA2 via the HBXIP-activated Akt-PCAF pathway in promotion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 May 21;48(9):4858-4876. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa232. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32313942 Free PMC article.
-
The oncoprotein HBXIP promotes human breast cancer growth through down-regulating p53 via miR-18b/MDM2 and pAKT/MDM2 pathways.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Nov;39(11):1787-1796. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0034-6. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 30181579 Free PMC article.
-
The oncogenic role of HBXIP.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;133:111045. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111045. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33378953 Review.
-
The Functions of EphA1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Several Tumors.Curr Med Chem. 2023;30(20):2340-2353. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220820125638. Curr Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 35996244 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

