Curcumin regulates autophagy through SIRT3-SOD2-ROS signaling pathway to improve quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy in KOA rat model
- PMID: 38589505
- PMCID: PMC11001965
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-58375-2
Curcumin regulates autophagy through SIRT3-SOD2-ROS signaling pathway to improve quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy in KOA rat model
Abstract
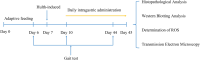
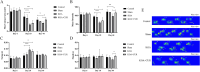
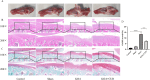
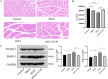
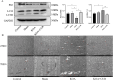
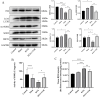
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) usually leads to quadriceps femoris atrophy, which in turn can further aggravate the progression of KOA. Curcumin (CUR) has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects and has been shown to be a protective agent for skeletal muscle. CUR has been shown to have a protective effect on skeletal muscle. However, there are no studies related to whether CUR improves KOA-induced quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy. We established a model of KOA in rats. Rats in the experimental group were fed CUR for 5 weeks. Changes in autophagy levels, reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and changes in the expression of the Sirutin3 (SIRT3)-superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) pathway were detected in the quadriceps femoris muscle of rats. KOA led to quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy, in which autophagy was induced and ROS levels were increased. CUR increased SIRT3 expression, decreased SOD2 acetylation and ROS levels, inhibited the over-activation of autophagy, thereby alleviating quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy and improving KOA. CUR has a protective effect against quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy, and KOA is alleviated after improvement of quadriceps femoris muscle atrophy, with the possible mechanism being the reduction of ROS-induced autophagy via the SIRT3-SOD2 pathway.
Keywords: Autophagy; Curcumin; Knee osteoarthritis; Quadriceps femoris muscle.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A network pharmacology-based study to investigate the mechanism of curcumin-regulated regenerative repair of quadriceps femoris muscle in KOA rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 5;982:176910. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176910. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39154821
-
Iron overload adversely effects bone marrow haematogenesis via SIRT-SOD2-mROS in a process ameliorated by curcumin.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021 Jan 13;26(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-00244-7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33435886 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT3-SOD2-mROS-dependent autophagy in cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and salvage by melatonin.Autophagy. 2015;11(7):1037-51. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1052208. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 26120888 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromuscular joint function in knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2023 Mar;66(2):101662. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2022.101662. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2023. PMID: 35364316 Review.
-
SIRT3 a Major Player in Attenuation of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Reducing ROS via Its Downstream Mediators: SOD2, CYP-D, and HIF-1α.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Nov 13;2018:2976957. doi: 10.1155/2018/2976957. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30538800 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Role of LncRNAs in Osteoarthritis: Inflammatory Pathways Unveiled.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Sep 20;17:6563-6581. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S489682. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39318993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High expression of transcription factor EGR1 is associated with postoperative muscle atrophy in patients with knee osteoarthritis undergoing total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Oct 1;19(1):618. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05109-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39354574 Free PMC article.
-
Honokiol and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Improve Exercise Endurance in Pulmonary Hypertensive Rats Through Increasing SIRT3 Function in Skeletal Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 29;25(21):11600. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111600. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519152 Free PMC article.
-
AGEs impair osteogenesis in orthodontic force-induced periodontal ligament stem cells through the KDM6B/Wnt self-reinforcing loop.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Nov 15;15(1):431. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04058-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39548506 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Epigenomics: Bioactive Dietary Compounds in the Epigenetic Regulation of Osteoarthritis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;17(9):1148. doi: 10.3390/ph17091148. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

