Molecular Mechanisms Associated with the Inhibitory Role of Long Chain n-3 PUFA in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 38708673
- PMCID: PMC11072084
- DOI: 10.1177/15347354241243024
Molecular Mechanisms Associated with the Inhibitory Role of Long Chain n-3 PUFA in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
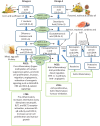
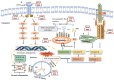
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related death in the world. Multiple evidence suggests that there is an association between excess fat consumption and the risk of CRC. The long chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC n-3 PUFA), especially eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), are essential for human health, and both in vitro and in vivo studies have shown that these fatty acids can prevent CRC development through various molecular mechanisms. These include the modulation of arachidonic acid (AA) derived prostaglandin synthesis, alteration of growth signaling pathways, arrest of the cell cycle, induction of cell apoptosis, suppression of angiogenesis and modulation of inflammatory response. Human clinical studies found that LC n-3 PUFA combined with chemotherapeutic agents can improve the efficacy of treatment and reduce the dosage of chemotherapy and associated side effects. In this review, we discuss comprehensively the anti-cancer effects of LC n-3 PUFA on CRC, with a main focus on the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: DHA; EPA; LC n-3 PUFA; colorectal cancer; molecular mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Krill oil extract suppresses cell growth and induces apoptosis of human colorectal cancer cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Aug 30;16(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1311-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27576529 Free PMC article.
-
n-3 Long-chain PUFA reduce allergy-related mediator release by human mast cells in vitro via inhibition of reactive oxygen species.Br J Nutr. 2013 May 28;109(10):1821-31. doi: 10.1017/S0007114512003959. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Br J Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23021516
-
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Oct;13(8):1162-77. doi: 10.2174/18715206113139990319. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23919748 Review.
-
Distinguishing health benefits of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids.Mar Drugs. 2012 Nov 13;10(11):2535-59. doi: 10.3390/md10112535. Mar Drugs. 2012. PMID: 23203276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of colorectal cancer cell apoptosis by the n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids Docosahexaenoic and Eicosapentaenoic.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009 Aug;2(8):732-42. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0197. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009. PMID: 19638488 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

