Comparative characterisation of extracellular vesicles from canine and human plasma: a necessary step in biomarker discovery
- PMID: 38717732
- PMCID: PMC11315736
- DOI: 10.1007/s11259-024-10405-0
Comparative characterisation of extracellular vesicles from canine and human plasma: a necessary step in biomarker discovery
Abstract
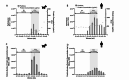
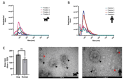
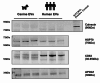
Extracellular Vesicles (EV) have become an interesting focus as novel biomarkers of disease and are increasingly reported upon in humans and other species. The Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018) guidelines were published to improve rigor and standardisation within the EV field and provide a framework for the reliable isolation and characterisation of EV populations. However, this rigor and standardisation has been challenging in the area of comparative medicine. Herein we present the successful isolation of EVs from human and canine plasma using Size Exclusion Chromatography and characterise these EVs according to best international practice. This study provides evidence for the reliable comparison of human and canine EVs isolated by this approach, and a baseline description of the EVs from healthy dogs to inform future biomarker studies. This work also demonstrates that the MISEV2018 guidelines can be successfully applied to EVs isolated from canine plasma.
Keywords: Canine; Comparative medicine; Extracellular vesicles; OneHealth; Size exclusion chromatography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of _targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Medications for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a historical non-interventional cohort study with validation against RCT results.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Aug;25(51):1-70. doi: 10.3310/hta25510. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 34463610 Clinical Trial.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

