Evaluating a Novel AI Tool for Automated Measurement of the Aortic Root and Valve in Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- PMID: 38832163
- PMCID: PMC11146459
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.59647
Evaluating a Novel AI Tool for Automated Measurement of the Aortic Root and Valve in Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Abstract
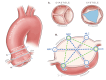
Objective Evaluating an artificial intelligence (AI) tool (AIATELLA, version 1.0; AIATELLA Oy, Helsinki, Finland) in interpreting cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging to produce measurements of the aortic root and valve by comparison of accuracy and efficiency with that of three National Health Service (NHS) cardiologists. Methods AI-derived aortic root and valve measurements were recorded alongside manual measurements from three experienced NHS consultant cardiologists (CCs) over three separate sites in the northeast part of the United Kingdom. The study utilised a comprehensive dataset of CMR images, with the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) being the primary measure of concordance between the AI and the cardiologist assessments. Patient imaging was anonymised and blinded at the point of transfer to a secure data server. Results The study demonstrates a high level of concordance between AI assessment of the aortic root and valve with NHS cardiologists (ICC of 0.98). Notably, the AI delivered results in 2.6 seconds (+/- 0.532) compared to a mean of 334.5 seconds (+/- 61.9) by the cardiologists, a statistically significant improvement in efficiency without compromising accuracy. Conclusion AI's accuracy and speed of analysis suggest that it could be a valuable tool in cardiac diagnostics, addressing the challenges of time-consuming and variable clinician-based assessments. This research reinforces AI's role in optimising the patient journey and improving the efficiency of the diagnostic pathway.
Keywords: aortic root; aortic root dilation; aortic valve; aortic valve disease; artificial intelligence; artificial intelligence in radiology; cardiac magnetic resonance (cmr); cardiovascular radiology; interobserver variability; measurement accuracy.
Copyright © 2024, Parker et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AIATELLA has filed for a patent related to the method utilised by the AI tool to determine key landmarks and produce measurements from medical imaging. Patent application 20235369 - Finland - Machine Learning Based Landmark or Segment Detection From Medical Image Data.. Jack Parker is the CEO and co-founder of AIATELLA. He holds a majority shareholding in the company. James Coey is an unpaid advisor to AIATELLA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical assessment of an AI tool for measuring biventricular parameters on cardiac MR.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Feb 5;11:1279298. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1279298. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38374997 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of asymmetry on measurements of the aortic root using cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging in patients with a bicuspid aortic valve.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Dec;29(8):1769-77. doi: 10.1007/s10554-013-0268-9. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23907165
-
Implementation and prospective clinical validation of AI-based planning and shimming techniques in cardiac MRI.Med Phys. 2022 Jan;49(1):129-143. doi: 10.1002/mp.15327. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 34748660 Free PMC article.
-
AI-Supported Echocardiography for the Detection of Heart Diseases - A Scoping Review.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024 Aug 30;317:219-227. doi: 10.3233/SHTI240860. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2024. PMID: 39234725 Review.
-
Is cardiac magnetic resonance imaging as accurate as echocardiography in the assessment of aortic valve stenosis?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016 Apr;22(4):480-6. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivv362. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 26718319 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
