Unveiling the Evolution of Virtual Reality in Medicine: A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Hotspots and Trends over the Past 12 Years
- PMID: 38998801
- PMCID: PMC11241350
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare12131266
Unveiling the Evolution of Virtual Reality in Medicine: A Bibliometric Analysis of Research Hotspots and Trends over the Past 12 Years
Abstract
Background: Virtual reality (VR), widely used in the medical field, may affect future medical training and treatment. Therefore, this study examined VR's potential uses and research directions in medicine.
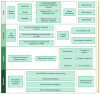
Methods: Citation data were downloaded from the Web of Science Core Collection database (WoSCC) to evaluate VR in medicine in articles published between 1 January 2012 and 31 December 2023. These data were analyzed using CiteSpace 6.2. R2 software. Present limitations and future opportunities were summarized based on the data.
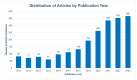
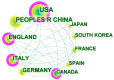
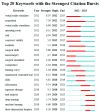
Results: A total of 2143 related publications from 86 countries and regions were analyzed. The country with the highest number of publications is the USA, with 461 articles. The University of London has the most publications among institutions, with 43 articles. The burst keywords represent the research frontier from 2020 to 2023, such as "task analysis", "deep learning", and "machine learning".
Conclusion: The number of publications on VR applications in the medical field has been steadily increasing year by year. The USA is the leading country in this area, while the University of London stands out as the most published, and most influential institution. Currently, there is a strong focus on integrating VR and AI to address complex issues such as medical education and training, rehabilitation, and surgical navigation. Looking ahead, the future trend involves integrating VR, augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) with the Internet of Things (IoT), wireless sensor networks (WSNs), big data analysis (BDA), and cloud computing (CC) technologies to develop intelligent healthcare systems within hospitals or medical centers.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; medicine; research hotspots; trends; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Research in Pediatrics Related to Virtual and Augmented Reality: A Systematic Review.Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024;20(2):178-187. doi: 10.2174/1573396319666230214103103. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2024. PMID: 36786143
-
Virtual reality for neurorehabilitation: A bibliometric analysis of knowledge structure and theme trends.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 10;10:1042618. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1042618. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36438265 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in the Use of Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Mixed Reality in Surgical Research: a Global Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis.Indian J Surg. 2022 Apr;84(Suppl 1):52-69. doi: 10.1007/s12262-021-03243-w. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Indian J Surg. 2022. PMID: 35228782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scientometric Analysis of the World Scientific Production on Augmented and Virtual Reality in Dental Education.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024 Apr 1;25(4):358-364. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3675. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024. PMID: 38956852
-
Virtual and augmented reality in biomedical engineering.Biomed Eng Online. 2023 Jul 31;22(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12938-023-01138-3. Biomed Eng Online. 2023. PMID: 37525193 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steuer J. Defining Virtual Reality: Dimensions Determining Telepresence. J. Commun. 1992;42:73–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-2466.1992.tb00812.x. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

