Role of senataxin in R-loop-mediated neurodegeneration
- PMID: 39070547
- PMCID: PMC11277865
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae239
Role of senataxin in R-loop-mediated neurodegeneration
Abstract
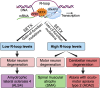
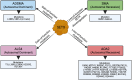
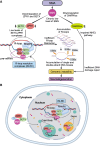
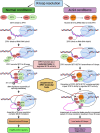
Senataxin is an RNA:DNA helicase that plays an important role in the resolution of RNA:DNA hybrids (R-loops) formed during transcription. R-loops are involved in the regulation of biological processes such as immunoglobulin class switching, gene expression and DNA repair. Excessive accumulation of R-loops results in DNA damage and loss of genomic integrity. Senataxin is critical for maintaining optimal levels of R-loops to prevent DNA damage and acts as a genome guardian. Within the nucleus, senataxin interacts with various RNA processing factors and DNA damage response and repair proteins. Senataxin interactors include survival motor neuron and zinc finger protein 1, with whom it co-localizes in sub-nuclear bodies. Despite its ubiquitous expression, mutations in senataxin specifically affect neurons and result in distinct neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 4 and ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 2, which are attributed to the gain-of-function and the loss-of-function mutations in senataxin, respectively. In addition, low levels of senataxin (loss-of-function) in spinal muscular atrophy result in the accumulation of R-loops causing DNA damage and motor neuron degeneration. Senataxin may play multiple functions in diverse cellular processes; however, its emerging role in R-loop resolution and maintenance of genomic integrity is gaining attention in the field of neurodegenerative diseases. In this review, we highlight the role of senataxin in R-loop resolution and its potential as a therapeutic _target to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: R-loops; SETX; ZPR1; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 4; spinal muscular atrophy.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutation in senataxin alters the mechanism of R-loop resolution in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 4.Brain. 2022 Sep 14;145(9):3072-3094. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab464. Brain. 2022. PMID: 35045161 Free PMC article.
-
SETX (senataxin), the helicase mutated in AOA2 and ALS4, functions in autophagy regulation.Autophagy. 2021 Aug;17(8):1889-1906. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1796292. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 32686621 Free PMC article.
-
ZPR1 prevents R-loop accumulation, upregulates SMN2 expression and rescues spinal muscular atrophy.Brain. 2020 Jan 1;143(1):69-93. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz373. Brain. 2020. PMID: 31828288 Free PMC article.
-
Senataxin: Genome Guardian at the Interface of Transcription and Neurodegeneration.J Mol Biol. 2017 Oct 27;429(21):3181-3195. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.10.021. Epub 2016 Oct 19. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27771483 Review.
-
Senataxin, A Novel Helicase at the Interface of RNA Transcriptome Regulation and Neurobiology: From Normal Function to Pathological Roles in Motor Neuron Disease and Cerebellar Degeneration.Adv Neurobiol. 2018;20:265-281. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-89689-2_10. Adv Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29916023 Review.
Cited by
-
The multifaceted roles of the Ctf4 replisome hub in the maintenance of genome integrity.DNA Repair (Amst). 2024 Oct;142:103742. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2024.103742. Epub 2024 Aug 12. DNA Repair (Amst). 2024. PMID: 39137555 Review.
-
Regulation of R-Loops in DNA Tumor Viruses.Pathogens. 2024 Oct 2;13(10):863. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13100863. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39452734 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
