Comparing regional brain uptake of incretin receptor agonists after intranasal delivery in CD-1 mice and the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39085976
- PMCID: PMC11293113
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-024-01537-1
Comparing regional brain uptake of incretin receptor agonists after intranasal delivery in CD-1 mice and the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
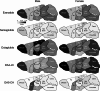
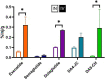
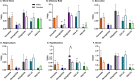
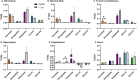
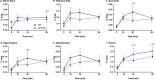
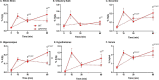
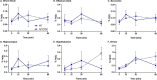
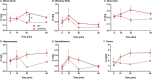
_targeting brain insulin resistance (BIR) has become an attractive alternative to traditional therapeutic treatments for Alzheimer's disease (AD). Incretin receptor agonists (IRAs), _targeting either or both of the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptors, have proven to reverse BIR and improve cognition in mouse models of AD. We previously showed that many, but not all, IRAs can cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) after intravenous (IV) delivery. Here we determined if widespread brain uptake of IRAs could be achieved by circumventing the BBB using intranasal (IN) delivery, which has the added advantage of minimizing adverse gastrointestinal effects of systemically delivered IRAs. Of the 5 radiolabeled IRAs tested (exenatide, dulaglutide, semaglutide, DA4-JC, and DA5-CH) in CD-1 mice, exenatide, dulaglutide, and DA4-JC were successfully distributed throughout the brain following IN delivery. We observed significant sex differences in uptake for DA4-JC. Dulaglutide and DA4-JC exhibited high uptake by the hippocampus and multiple neocortical areas. We further tested and found the presence of AD-associated Aβ pathology minimally affected uptake of dulaglutide and DA4-JC. Of the 5 tested IRAs, dulaglutide and DA4-JC are best capable of accessing brain regions most vulnerable in AD (neocortex and hippocampus) after IN administration. Future studies will need to be performed to determine if IN IRA delivery can reduce BIR in AD or animal models of that disorder.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; GLP-1; Incretin receptor agonist; Insulin signaling; Intranasal.
© 2024. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain uptake pharmacokinetics of incretin receptor agonists showing promise as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease therapeutics.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;180:114187. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114187. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32755557 Free PMC article.
-
Brain uptake pharmacokinetics of albiglutide, dulaglutide, tirzepatide, and DA5-CH in the search for new treatments of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.Tissue Barriers. 2024 Oct;12(4):2292461. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2023.2292461. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Tissue Barriers. 2024. PMID: 38095516 Free PMC article.
-
The Dual GLP-1/GIP Receptor Agonist DA4-JC Shows Superior Protective Properties Compared to the GLP-1 Analogue Liraglutide in the APP/PS1 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2020 Jan-Dec;35:1533317520953041. doi: 10.1177/1533317520953041. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2020. PMID: 32959677 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and mixed-treatment comparison analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Apr;19(4):524-536. doi: 10.1111/dom.12849. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 27981757 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of once-weekly glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists for the management of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015 Nov;17(11):1065-74. doi: 10.1111/dom.12541. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015. PMID: 26395850 Review.
References
-
- 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & dementia: the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association. 2023;19(4):1598 – 695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

