EV-miRNAs from breast cancer patients of plasma as potential prognostic biomarkers of disease recurrence
- PMID: 39104474
- PMCID: PMC11298852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33933
EV-miRNAs from breast cancer patients of plasma as potential prognostic biomarkers of disease recurrence
Abstract
Background: Extracellular vesicles (EVs), ubiquitously released by blood cells, facilitate intercellular communication. In cancer, tumor-derived EVs profoundly affect the microenvironment, promoting tumor progression and raising the risk of recurrence. These EVs contain miRNAs (EV-miRNAs), promising cancer biomarkers. Characterizing plasma EVs and identifying EV-miRNAs associated with breast cancer recurrence are crucial aspects of cancer research since they allow us to discover new biomarkers that are effective for understanding tumor biology and for being used for early detection, disease monitoring, or approaches to personalized medicine. This study aimed to characterize plasma EVs in breast cancer (BC) patients and identify EV-miRNAs associated with BC recurrence.
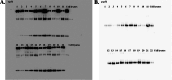
Methods: This retrospective observational study included 24 BC patients divided into recurrence (n= 11) and non-recurrence (n= 13) groups. Plasma EVs were isolated and characterized. Total RNA from EVs was analyzed for miRNA expression using NanoString's nCounter® miRNA Expression Assays panel. MicroRNA _target prediction used mirDIP, and pathway interactions were assessed via Reactome.
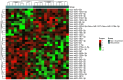
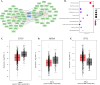
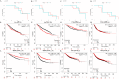
Results: A stronger presence of circulating EVs was found to be linked with a less favorable prognosis (p = 0.0062). We discovered a distinct signature of EV-miRNAs, notably including miR-19a-3p and miR-130b-3p, which are significantly associated with breast cancer recurrence. Furthermore, miR-19a-3p and miR-130b-3p were implicated in the regulation of PTEN and MDM4, potentially contributing to breast cancer progression.A notable association emerged, indicating a high concentration of circulating EVs predicts poor prognosis (p = 0.0062). Our study found a distinct EV-miRNA signature involving miR-19a-3p and miR-130b-3p, strongly associated with disease recurrence. We also presented compelling evidence for their regulatory roles in PTEN and MDM4 genes, contributing to BC development.
Conclusion: This study revealed that increased plasma EV concentration is associated with BC recurrence. The prognostic significance of EVs is closely tied to the unique expression profiles of miR-19a-3p and miR-130b-3p. These findings underscore the potential of EV-associated miRNAs as valuable indicators for BC recurrence, opening new avenues for diagnosis and treatment exploration.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Breast cancer; Disease recurrence; Extracellular vesicles; MicroRNA.
© 2024 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SIV Infection Regulates Compartmentalization of Circulating Blood Plasma miRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) and Extracellular Condensates (ECs) and Decreases EV-Associated miRNA-128.Viruses. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):622. doi: 10.3390/v15030622. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992331 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in Abundance and Compartmentalization of miRNAs in Blood Plasma Extracellular Vesicles and Extracellular Condensates during HIV/SIV Infection and Its Modulation by Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) and Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).Viruses. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):623. doi: 10.3390/v15030623. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992332 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNA-sequence analysis of plasma-derived extracellular vesicle miRNAs in smokers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease as circulating biomarkers.J Extracell Vesicles. 2019 Nov 7;8(1):1684816. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2019.1684816. eCollection 2019. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019. PMID: 31762962 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs in Diagnostics of Gastric Cancer.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024 Jul;89(7):1211-1238. doi: 10.1134/S0006297924070058. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024. PMID: 39218020 Review.
-
The Multifaceted Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Glioblastoma: microRNA Nanocarriers for Disease Progression and Gene Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 29;13(7):988. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13070988. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34210109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IARC Fact sheets by cancer [internet] 2020. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/20-Breast-fact-sheet.pdf Available from:
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca - Cancer J. Clin. 2021 - PubMed
-
- Perou C.M., Sørlie T., Eisen M.B., van de Rijn M., Jeffrey S.S., Rees C.A., et al. Vol. 406. Nature Publishing Group; 2000. pp. 747–752. (Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

