Exploring the predictive factors of heart disease using rare association rule mining
- PMID: 39107391
- PMCID: PMC11303792
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-69071-6
Exploring the predictive factors of heart disease using rare association rule mining
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases continue to be the leading cause of mortality worldwide, claiming a significant number of lives each year. Despite the advancements in predictive models, including logistic regression, neural networks, and random forests, these techniques often lack transparency and interpretability, limiting their practical application in clinical settings. To address this challenge, this research introduces EPFHD-RARMING, an innovative approach designed to enhance the understanding and predictability of heart disease through the discovery of rare and meaningful patterns. EPFHD-RARMING utilizes rare association rule mining to uncover hidden and unexpected rules that identify critical factors contributing to heart disease. This method is particularly adept at identifying high-risk patterns in individuals who appear healthy but may develop heart disease under certain conditions, thus facilitating early intervention and preventive measures. By integrating these insights with established feature engineering techniques, EPFHD-RARMING enhances its practical utility, enabling medical professionals to proactively manage patient care and tailor interventions to individual risk profiles. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of EPFHD-RARMING in providing a deeper, actionable understanding of the complex dynamics of heart disease. The model's ability to identify and interpret rare patterns holds significant promise for advancing medical analytics and improving patient outcomes. Moreover, the applicability of EPFHD-RARMING extends beyond the healthcare domain, offering valuable insights in various fields where the discovery of rare patterns is critical, such as finance, marketing, and cybersecurity. This study conducts a comprehensive evaluation, which demonstrates the superior performance of EPFHD-RARMING compared to traditional predictive models in identifying key factors contributing to heart disease, in terms of interestingness, explainability, and comprehensiveness of insights. The results underscore the potential of this innovative approach to revolutionize our understanding and prediction of heart disease, ultimately contributing to more effective and personalized healthcare solutions. This research emphasizes the importance of rare association rule mining in medical analytics and paves the way for future studies to explore and utilize these techniques across diverse domains.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk factors; Early detection; Frequent association rules; Heart disease; Interesting rules; Rare association rules.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
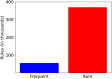



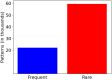
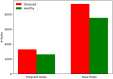
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition of temporal patterns from electronic health records: an application to multimorbid patients.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Sep 19;23(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02287-0. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37726756 Free PMC article.
-
Using Visual Analytic Methods to Identify Patient Groups [Internet].Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 Jun. Washington (DC): Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI); 2021 Jun. PMID: 38781405 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence, the Digital Surgeon: Unravelling Its Emerging Footprint in Healthcare - The Narrative Review.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Aug 15;17:4011-4022. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S482757. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39165254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (2021).
-
- Addressing Cardiovascular Disease - A Global Employer’s Approach to Non Communicable Diseases, vol. All Days of SPE International Conference and Exhibition on Health, Safety, Environment, and Sustainability. 10.2118/156849-MS.
-
- Chen, Y., Xia, R., Yang, K. & Zou, K. Dnnam: Image inpainting algorithm via deep neural networks and attention mechanism. Appl. Soft Comput.154, 111392 (2024).10.1016/j.asoc.2024.111392 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

