Functional Insights into the Sphingolipids C1P, S1P, and SPC in Human Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Proteomic Analysis
- PMID: 39125932
- PMCID: PMC11313292
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158363
Functional Insights into the Sphingolipids C1P, S1P, and SPC in Human Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Proteomic Analysis
Abstract
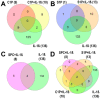
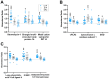
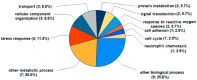
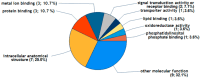
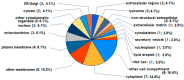
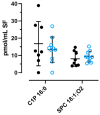
The (patho)physiological function of the sphingolipids ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P), sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), and sphingosylphosphorylcholine (SPC) in articular joints during osteoarthritis (OA) is largely unknown. Therefore, we investigated the influence of these lipids on protein expression by fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) from OA knees. Cultured human FLSs (n = 7) were treated with 1 of 3 lipid species-C1P, S1P, or SPC-IL-1β, or with vehicle. The expression of individual proteins was determined by tandem mass tag peptide labeling followed by high-resolution electrospray ionization (ESI) mass spectrometry after liquid chromatographic separation (LC-MS/MS/MS). The mRNA levels of selected proteins were analyzed using RT-PCR. The 3sphingolipids were quantified in the SF of 18 OA patients using LC-MS/MS. A total of 4930 proteins were determined using multiplex MS, of which 136, 9, 1, and 0 were regulated both reproducibly and significantly by IL-1β, C1P, S1P, and SPC, respectively. In the presence of IL-1ß, all 3 sphingolipids exerted ancillary effects. Only low SF levels of C1P and SPC were found. In conclusion, the 3 lipid species regulated proteins that have not been described in OA. Our results indicate that charged multivesicular body protein 1b, metal cation symporter ZIP14, glutamine-fructose-6-P transaminase, metallothionein-1F and -2A, ferritin, and prosaposin are particularly interesting proteins due to their potential to affect inflammatory, anabolic, catabolic, and apoptotic mechanisms.
Keywords: ceramide-1-phosphate; functions; inflammation; lysosphingomyelin; mass spectrometry; osteoarthritis; proteomics; sphingolipid; sphingosine-1-phosphate; sphingosylphosphorylcholine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Characterization of Lysophospholipids by Proteomic and Lipidomic Analysis of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes.Cells. 2023 Jun 29;12(13):1743. doi: 10.3390/cells12131743. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443777 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and biological functions of two phosphorylated sphingolipids, sphingosine 1-phosphate and ceramide 1-phosphate.Prog Lipid Res. 2007 Mar;46(2):126-44. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2007.03.001. Epub 2007 Mar 14. Prog Lipid Res. 2007. PMID: 17449104 Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate and ceramide-1-phosphate promote migration, pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic responses in retinal pigment epithelium cells.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Nov;224:109222. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.109222. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 36041511
-
Upregulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 on fibroblast-like synoviocytes is associated with the development of collagen-induced arthritis via increased interleukin-6 production.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 7;14(6):e0218090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218090. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31173610 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Ceramide-1-Phosphate in Inflammation and Cancer.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:4806541. doi: 10.1155/2017/4806541. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29269995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kosinska M.K., Ludwig T.E., Liebisch G., Zhang R., Siebert H.-C., Wilhelm J., Kaesser U., Dettmeyer R.B., Klein H., Ishaque B., et al. Articular Joint Lubricants during Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Display Altered Levels and Molecular Species. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0125192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125192. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sluzalska K.D., Liebisch G., Wilhelm J., Ishaque B., Hackstein H., Schmitz G., Rickert M., Steinmeyer J. Growth factors regulate phospholipid biosynthesis in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes obtained from osteoarthritic knees. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:13469. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14004-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

