Changes in Haematological Parameters and Lipid Profiles in Diabetes Mellitus: A Literature Review
- PMID: 39130996
- PMCID: PMC11310571
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.64201
Changes in Haematological Parameters and Lipid Profiles in Diabetes Mellitus: A Literature Review
Abstract
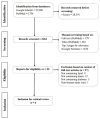
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose that has sequelae on cellular, haematological, and metabolic parameters, including lipid profile disturbed homeostasis, which manifest in alterations in haematological parameters and lipid profiles. These changes in haematological parameters and lipid profiles have been reported by previous research; however, the pattern of these changes and their correlation have not been elucidated. This review aims to assess these changes and investigate the degree of correlation between haematological parameters and lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The method adopted was a traditional review approach that included a narrative of concepts and a critical assessment of a few selected articles. Findings highlight that haematological parameters and lipid profiles show varied alterations and correlations in T2DM. For instance, statistical significances at p < 0.05 are reported for WBC count (r = -0.75) showing negative correlations (p < 0.001), where RBC count (r = 0.56) showed correlation with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC), whereas anaemia (packed cell volume: r = -0.51) and RBC indices (mean corpuscular volume: r = -0.75; mean corpuscular haemoglobin: r = -089) show negative correlations with total cholesterol (TC). The specific haematological parameters, namely, RBC and WBC with differential and platelet counts, as well as indices, showed varied changes and correlation with lipid profiles, namely, HDLC, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, TC, and triglyceride, in the six reviewed articles. Diabetes is characterized by changes in haematological parameters and lipid profiles. A better understanding of the negative and positive correlating changes could be utilized in routine evaluation of subjects with prediabetes as well as managing complications in diabetes. Correlation between haematological parameters and lipid profiles over the course of diabetes progression using HbA1c as an index of glucose control is necessary for additional empirical data and updates.
Keywords: cardiovascular complications; correlation; dyslipidaemia; haematology; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2024, Mbah et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Haematological parameters and lipid profile abnormalities among patients with Type-2 diabetes mellitus in Ghana.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Dec 13;17(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0926-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30545361 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Hypolipidaemic and haematological evaluation of the hydromethanolic extract of Ficus glumosa stem bark in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.J Complement Integr Med. 2014 Dec;11(4):259-64. doi: 10.1515/jcim-2014-0029. J Complement Integr Med. 2014. PMID: 25294718
-
Beneficial effects of probiotic and synbiotic supplementation on some cardiovascular risk factors among individuals with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A grade-assessed systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized clinical trials.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Aug;182:106288. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106288. Epub 2022 Jun 6. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 35680009 Review.
-
Nigella sativa supplementation improves cardiometabolic indicators in population with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Nutr. 2022 Aug 11;9:977756. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.977756. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36034891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lipids and lipoproteins in patients with type 2 diabetes. Krauss RM. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1496–1504. - PubMed
-
- Usefulness of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as predictors of cardiovascular disease in Chinese. Gu X, Yang X, Li Y, et al. Am J Cardiol. 2015;116:1063–1070. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources