In Vitro Investigation of the Anti-Fibrotic Effects of 1-Phenyl-2-Pentanol, Identified from Moringa oleifera Lam., on Hepatic Stellate Cells
- PMID: 39201682
- PMCID: PMC11354330
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25168995
In Vitro Investigation of the Anti-Fibrotic Effects of 1-Phenyl-2-Pentanol, Identified from Moringa oleifera Lam., on Hepatic Stellate Cells
Abstract
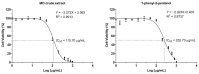
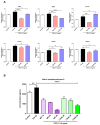
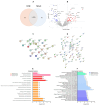
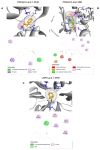
Liver fibrosis, characterized by excessive extracellular matrix deposition, is driven by activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Due to the limited availability of anti-fibrotic drugs, the research on therapeutic agents continues. Here we have investigated Moringa oleifera Lam. (MO), known for its various bioactive properties, for anti-fibrotic effects. This study has focused on 1-phenyl-2-pentanol (1-PHE), a compound derived from MO leaves, and its effects on LX-2 human hepatic stellate cell activation. TGF-β1-stimulated LX-2 cells were treated with MO extract or 1-PHE, and the changes in liver fibrosis markers were assessed at both gene and protein levels. Proteomic analysis and molecular docking were employed to identify potential protein _targets and signaling pathways affected by 1-PHE. Treatment with 1-PHE downregulated fibrosis markers, including collagen type I alpha 1 chain (COL1A1), collagen type IV alpha 1 chain (COL4A1), mothers against decapentaplegic homologs 2 and 3 (SMAD2/3), and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2), and reduced the secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). Proteomic analysis data showed that 1-PHE modulates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, providing a possible mechanism for its effects. Our results suggest that 1-PHE inhibits the TGF-β1 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways and HSC activation, indicating its potential as an anti-liver-fibrosis agent.
Keywords: 1-phenyl-2-pentanol; Moringa oleifera Lam.; hepatic stellate cell; liver fibrosis; molecular docking analysis; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigating the Antifibrotic Effects of β-Citronellol on a TGF-β1-Stimulated LX-2 Hepatic Stellate Cell Model.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 5;14(7):800. doi: 10.3390/biom14070800. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062514 Free PMC article.
-
Phillygenin Inhibits TGF-β1-induced Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Inflammation: Regulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 and Wnt/β-catenin Pathways.Inflammation. 2024 Aug;47(4):1403-1422. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-01984-w. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 38393550
-
Physalin D attenuates hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad and YAP signaling.Phytomedicine. 2020 Nov;78:153294. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153294. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32771890
-
Advancements in Plant-Based Therapeutics for Hepatic Fibrosis: Molecular Mechanisms and Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 28;25(17):9346. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179346. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Products in Liver Fibrosis Management: A Five-year Review.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(31):5061-5082. doi: 10.2174/0109298673288458240203064112. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38362686 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

