Emerging therapeutic strategies _targeting extracellular histones for critical and inflammatory diseases: an updated narrative review
- PMID: 39206200
- PMCID: PMC11349558
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1438984
Emerging therapeutic strategies _targeting extracellular histones for critical and inflammatory diseases: an updated narrative review
Abstract
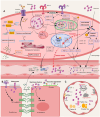
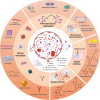
Extracellular histones are crucial damage-associated molecular patterns involved in the development and progression of multiple critical and inflammatory diseases, such as sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, acute liver failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, vasculitis and arthritis. During the past decade, the physiopathologic mechanisms of histone-mediated hyperinflammation, endothelial dysfunction, coagulation activation, neuroimmune injury and organ dysfunction in diseases have been systematically elucidated. Emerging preclinical evidence further shows that anti-histone strategies with either their neutralizers (heparin, heparinoids, nature plasma proteins, small anion molecules and nanomedicines, etc.) or extracorporeal blood purification techniques can significantly alleviate histone-induced deleterious effects, and thus improve the outcomes of histone-related critical and inflammatory animal models. However, a systemic evaluation of the efficacy and safety of these histone-_targeting therapeutic strategies is currently lacking. In this review, we first update our latest understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms of histone-induced hyperinflammation, endothelial dysfunction, coagulopathy, and organ dysfunction. Then, we summarize the latest advances in histone-_targeting therapy strategies with heparin, anti-histone antibodies, histone-binding proteins or molecules, and histone-affinity hemoadsorption in pre-clinical studies. Finally, challenges and future perspectives for improving the clinical translation of histone-_targeting therapeutic strategies are also discussed to promote better management of patients with histone-related diseases.
Keywords: blood purification; damage-associated molecular patterns; extracellular histones; heparin; histone-neutralization; inflammation.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Peng, Zhang, Chen, Liu, Jiang, Jin, Han, Su and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
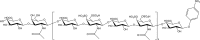
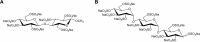
Similar articles
-
_targeting circulating high mobility group box-1 and histones by extracorporeal blood purification as an immunomodulation strategy against critical illnesses.Crit Care. 2023 Feb 28;27(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04382-0. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 36855150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular histones in lung dysfunction: a new biomarker and therapeutic _target?Pulm Circ. 2020 Nov 10;10(4):2045894020965357. doi: 10.1177/2045894020965357. eCollection 2020 Oct-Dec. Pulm Circ. 2020. PMID: 33240489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Histones Are Major Mediators of Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome in Acute Critical Illnesses.Crit Care Med. 2019 Aug;47(8):e677-e684. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003839. Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 31162199
-
Circulating Histones in Sepsis: Potential Outcome Predictors and Therapeutic _targets.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 24;12:650184. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.650184. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular histones are clinically relevant mediators in the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome.Respir Res. 2017 Sep 2;18(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12931-017-0651-5. Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 28865478 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

