Atypical sphingosine-1-phosphate metabolites-biological implications of alkyl chain length
- PMID: 39297971
- PMCID: PMC11582160
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-024-03018-8
Atypical sphingosine-1-phosphate metabolites-biological implications of alkyl chain length
Abstract
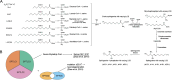
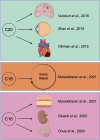
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a bioactive lipid signaling molecule with pleiotropic implications by both auto- and paracrine signaling. Signaling occurs by engaging five G protein-coupled receptors (S1P1-5) or intracellular pathways. While the extensively studied S1P with a chain length of 18 carbon atoms (d18:1 S1P) affects lymphocyte trafficking, immune cell survival and inflammatory responses, the biological implication of atypical S1Ps such as d16:1 or d20:1 remains elusive. As S1P lipids have far-reaching implications in health and disease states in mammalian organisms, the previous contrasting results may be attributed to differences in S1P's alkyl chain length. Current research is beginning to appreciate these less abundant atypical S1P moieties. This review provides an up-to-date foundation of recent findings on the biological implications of atypical S1P chain lengths and offers a perspective on future research endeavors on S1P alkyl chain length-influenced signaling and its implications for drug discovery.
Keywords: Chain lengths; Myristoyl CoA; Palmitoyl CoA; Serine palmitoyl transferase; Sphingolipids; Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P); Stearoyl CoA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The contribution of the sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling pathway to chronic kidney diseases: recent findings and new perspectives.Pflugers Arch. 2024 Dec;476(12):1845-1861. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-03029-5. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 39384640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of _targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Genedrive kit for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism m.1555A>G in neonates and their mothers: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(75):1-75. doi: 10.3310/TGAC4201. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39487741 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lipid signaling: facets of a versatile cell communication strategy in health and disease.Pflugers Arch. 2024 Dec;476(12):1777-1778. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-03034-8. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 39527143 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The contribution of the sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling pathway to chronic kidney diseases: recent findings and new perspectives.Pflugers Arch. 2024 Dec;476(12):1845-1861. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-03029-5. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 39384640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- A treatise on the chemical constitution of the brain : based throughout upon original researches / by J. L. W. Thudichum. In: Wellcome Collection. https://wellcomecollection.org/works/zcf2rr7p. Accessed 27 Aug 2024
-
- Allende ML, Yamashita T, Proia RL (2003) G-protein-coupled receptor S1P1 acts within endothelial cells to regulate vascular maturation. Blood 102:3665–3667. 10.1182/blood-2003-02-0460 - PubMed
-
- Borup A, Donkin I, Boon MR, Frydland M, Martinez-Tellez B, Loft A, Keller SH, Kjaer A, Kjaergaard J, Hassager C, Barrès R, Rensen PCN, Christoffersen C (2022) Association of apolipoprotein M and sphingosine-1-phosphate with brown adipose tissue after cold exposure in humans. Sci Rep 12:18753. 10.1038/s41598-022-21938-2 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, Billich A, Baumruker T, Heining P, Schmouder R, Francis G, Aradhye S, Burtin P (2010) Fingolimod (FTY720): discovery and development of an oral drug to treat multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:883–897. 10.1038/nrd3248 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

