Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) levels in pre-treatment plasma identifying breast cancer: A case control study
- PMID: 39359441
- PMCID: PMC11444118
- DOI: 10.22088/cjim.15.4.706
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) levels in pre-treatment plasma identifying breast cancer: A case control study
Abstract
Background: Diabetes (primarily type 2) is linked to a higher risk of breast cancer. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) is one of the most important factors that affects mitosis and thus inhibits apoptosis. The purpose of this study was to compare the pre-treatment insulin-like growth factor (IGF) levels in breast cancer against normal population.
Methods: In this case-control study, 60 patients with breast cancer and 60 healthy controls were enrolled in 2017 and 2018 at Tehran's Shahid-Modarres Hospital. In this study, the blood sugar of the patients was examined before entering the study, and the age of the patients was also within the age limit of 18 to 70 years. They were studied to determine the relationship between insulin-like growth factor (ELISA method) and breast cancer.
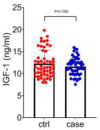
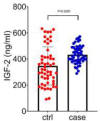
Results: Both groups have similar IGF-1 levels (Ctrl and Case) (P= 0.188). But, IGF-2 levels were significantly higher in breast cancer patients (373.4 vs. 317.3 ng/ml), (P=0.0001).
Conclusion: According to our study, IGF-2 may serve as a prognostic biomarker and potential therapeutic _target for breast cancer. However, further investigation is needed to validate this claim.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Diabetes; ELISA; IGF-1; IGF-2.
© The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) received no financial support for the research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors associated with circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in 740 women at risk for breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004 Nov;88(1):63-73. doi: 10.1007/s10549-004-0746-9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004. PMID: 15538047
-
Relationships between critical period of estrogen exposure and circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) in breast cancer: evidence from a case-control study.Int J Cancer. 2010 Jan 15;126(2):508-14. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24722. Int J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19585556
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I, its binding proteins (IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-3), and growth hormone and breast cancer risk in The Nurses Health Study II.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006 Jun;13(2):583-92. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01149. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16728584
-
[Plasma insulin, IGF-I and breast cancer].Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2001 Mar;29(3):185-91. doi: 10.1016/s1297-9589(00)00047-3. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2001. PMID: 11300043 Review. French.
-
The potential clinical applications of insulin-like growth factor-1 ligand in human breast cancer.Anticancer Res. 2007 May-Jun;27(3B):1617-24. Anticancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17595785 Review.
References
-
- Khodadadi E, Ataei N, Mofid MR. The effect and mechanism of action of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in human breast cancer; A systematic review. J Isfahan Med Sch. 2013;31:1560–7.
-
- Key T, Appleby P, Barnes I, Reeves G. Endogenous Hormones and Breast Cancer Collaborative Group Endogenous sex hormones and breast cancer in postmenopausal women: reanalysis of nine prospective studies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:606–16. - PubMed
-
- Espelund U, Cold S, Frystyk J, Ørskov H, Flyvbjerg A. Elevated free IGF2 levels in localized, early-stage breast cancer in women. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;159:595. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous