Recent Advances and Prospects of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for Anti-Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 39407665
- PMCID: PMC11477775
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29194737
Recent Advances and Prospects of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for Anti-Cancer Therapy
Abstract
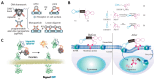
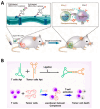
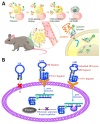
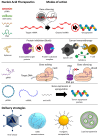
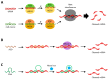
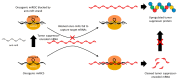
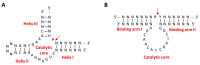
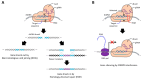
Nucleic acid therapeutics are promising alternatives to conventional anti-cancer therapy, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy. While conventional therapies have limitations, such as high side effects, low specificity, and drug resistance, nucleic acid therapeutics work at the gene level to eliminate the cause of the disease. Nucleic acid therapeutics treat diseases in various forms and using different mechanisms, including plasmid DNA (pDNA), small interfering RNA (siRNA), anti-microRNA (anti-miR), microRNA mimics (miRNA mimic), messenger RNA (mRNA), aptamer, catalytic nucleic acid (CNA), and CRISPR cas9 guide RNA (gRNA). In addition, nucleic acids have many advantages as nanomaterials, such as high biocompatibility, design flexibility, low immunogenicity, small size, relatively low price, and easy functionalization. Nucleic acid therapeutics can have a high therapeutic effect by being used in combination with various nucleic acid nanostructures, inorganic nanoparticles, lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), etc. to overcome low physiological stability and cell internalization efficiency. The field of nucleic acid therapeutics has advanced remarkably in recent decades, and as more and more nucleic acid therapeutics have been approved, they have already demonstrated their potential to treat diseases, including cancer. This review paper introduces the current status and recent advances in nucleic acid therapy for anti-cancer treatment and discusses the tasks and prospects ahead.
Keywords: RNA interference (RNAi); anti-cancer therapy; aptamer; gene therapy; nucleic acid delivery; nucleic acid therapeutics (NATs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent advances in delivery of drug-nucleic acid combinations for cancer treatment.J Control Release. 2013 Dec 10;172(2):589-600. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.04.010. Epub 2013 Apr 25. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23624358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects for nucleic acid-based therapeutics against hepatitis C virus.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Dec 21;19(47):8949-62. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8949. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24379620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theranostic Nanoparticles for RNA-Based Cancer Treatment.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Jun 18;52(6):1496-1506. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00101. Epub 2019 May 28. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31135134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery approaches of immunomodulatory nucleic acids for cancer therapy.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2024 Oct;89:103182. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2024.103182. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39178725 Review.
-
Current status of nucleic acid therapy and its new progress in cancer treatment.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;142(Pt B):113157. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113157. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39288629 Review.
References
-
- Gopal S., Sivaram S., Rajaraman P., Trimble E.L. Think globally about cancer. Nat. Med. 2019;25:351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

