Carbohydrate Counting: A Bibliometric Analysis with a Focus on Research
- PMID: 39408216
- PMCID: PMC11478275
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16193249
Carbohydrate Counting: A Bibliometric Analysis with a Focus on Research
Abstract
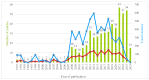
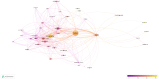
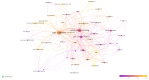
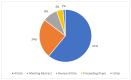
Diabetes is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia due to impaired insulin secretion, activity, or both. Carbohydrate counting, known for optimal metabolic control, plays in the therapeutic strategy in diabetes. In the last decade, an increasing amount of research has been conducted on carbohydrate counting, and the literature on this topic has been published in academic journals. This bibliometric analysis aimed to comprehensively review and analyze publications from this period, shedding light on trends, developments, and key contributors. The Expanded Science Citation Index published by the Institute for Scientific Information Web of Science, which covers English-language articles published from 1993 to 2024, was used. We selected "carbohydrate counting", "carbohydrate count", "carbohydrate counts", "carbohydrate counts", and similar words as "TOPIC" to search for related articles. All basic information about each article were collected, including authors, countries, citations, and keywords. The findings emphasized the need for continued research in this area and to learn more about studies showing the relationship between carbohydrate counting and the pathophysiology of diabetes, treatment, complications, and technologies. This analysis summarizes the general trends and key findings of research on carbohydrate counting over the past years and provides guidance for future research.
Keywords: carb counting; diet; medical nutrition therapy; type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Global Trends in LADA Type Diabetes Research: A Bibliometric Analysis of Publications from Web of Science and Scopus, 1994-2024.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Oct 14;2024:4960075. doi: 10.1155/2024/4960075. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 39435133 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trends in the Effect of Caffeine Intake on Fat Oxidation: A Bibliometric and Visual Analysis.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 10;15(20):4320. doi: 10.3390/nu15204320. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37892395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research trends in regulating gut microbiome to improve type 2 diabetes mellitus: bibliometrics and visual analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 3;15:1401070. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1401070. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38887274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research situation, hot spots, and global trends of melasma therapy: Bibliometric insights and visual analysis from 2000 to 2023.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024 Nov;23(11):3667-3683. doi: 10.1111/jocd.16438. Epub 2024 Jun 25. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38925583
-
Seven decades of Ramadan intermittent fasting research: Bibliometrics analysis, global trends, and future directions.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022 Aug;16(8):102566. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2022.102566. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 35872466
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation IDF Diabetes Atlas Eighth Edition 2017. [(accessed on 20 June 2024)]. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/upload/resources/previous/files/8/IDF_DA_8e-EN....
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

