Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Suppressed Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induced by Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase
- PMID: 39420979
- PMCID: PMC11483118
- DOI: 10.14740/cr1705
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Suppressed Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induced by Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase
Abstract
Background: Previous investigations have established the anti-inflammatory properties of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21). However, the specific mechanism through which FGF21 mitigates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury by inhibiting neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) remains unclear.
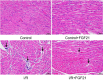
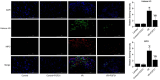
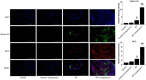
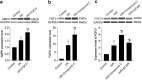
Methods: A mice model of myocardial I/R injury was induced, and myocardial tissue was stained with immunofluorescence to assess NETs. Serum NETs levels were quantified using a PicoGreen kit. In addition, the expression levels of adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and FGF21 were evaluated by Wes fully automated protein blotting quantitative analysis system. Moreover, a hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) model was established using AMPK inhibitor and agonist pretreated H9c2 cells to further explore the relationship between FGF21 and AMPK.
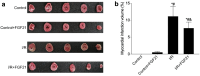
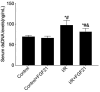
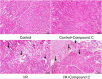
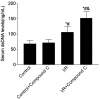
Results: Compared with the control group, serum NETs levels were significantly higher in I/R mice, and a large number of NETs were formed in myocardial tissues (97.63 ± 11.45 vs. 69.65 ± 3.33, P < 0.05). However, NETs levels were reversed in FGF21 pretreated mice (P < 0.05). Further studies showed that FGF21 enhanced AMPK expression, which was significantly increased after inhibition of AMPK and decreased after promotion of AMPK (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: FGF21 may exert cardioprotective effects by inhibiting I/R injury-induced NETs via AMPK.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; Neutrophil extracellular traps.
Copyright 2024, Gu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Activation of AMPK/p38/Nrf2 is involved in resveratrol alleviating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats as an endogenous antioxidant stress feedback.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Aug;10(16):890. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3789. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36111006 Free PMC article.
-
FGF21 protects myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through reduction of miR-145-mediated autophagy.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Nov 15;10(11):3677-3688. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30662618 Free PMC article.
-
Schizandrin B attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in H9c2 cells by activating the AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Mar;21(3):220. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9651. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33603829 Free PMC article.
-
Roflumilast reduces myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro by activating the AMPK signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2023 May 9;25(6):302. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12001. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37229319 Free PMC article.
-
Role of angiopoietin-2 in the cardioprotective effect of fibroblast growth factor 21 on ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in H9c2 cardiomyocytes.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jul;14(1):771-779. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4564. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28672998 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
