Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Glycemia Risk Index in Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39526203
- PMCID: PMC11550701
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S482824
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Glycemia Risk Index in Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Purpose: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a prevalent chronic complication of diabetes which is linked to chronic hyperglycemia and glycemic variability. This study aimed to investigate the association between the glycemia risk index (GRI) and DPN in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data.
Patients and methods: From 2019 to 2023, 862 adults diagnosed with T2DM were enrolled at a tertiary care diabetes center in Ningbo, China. The medical history and laboratory parameters were recorded. Neurophysiological examinations were performed to evaluate DPN. The CGM data were recorded for 14 days, and the GRI was calculated based on these data. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to assess the odds ratio (OR) for DPN with an increased GRI.
Results: The prevalence of DPN in the ascending GRI quartiles was 41.6%, 47.9%, 49.1%, and 59.5%, respectively (P for trend < 0.001). In the multivariable logistic analysis, the highest GRI quartile exhibited a 63% greater risk of DPN (OR 1.631, 95% CI: 1.071 to 2.484, P = 0.023) than the lowest quartile after adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, diabetes duration, blood pressure, creatinine, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio, lipid profile and glycated hemoglobin.
Conclusion: High GRI levels, as measured by CGM, were associated with a greater likelihood of DPN in T2DM patients.
Keywords: continuous glucose monitoring; diabetic peripheral neuropathy; glycemia risk index; microvascular complications.
© 2024 Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
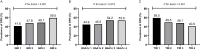
Similar articles
-
Association between glycemia risk index and arterial stiffness in type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Investig. 2024 May;15(5):614-622. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14153. Epub 2024 Jan 22. J Diabetes Investig. 2024. PMID: 38251792 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index With Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-sectional Study.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024 Oct 14:19322968241288579. doi: 10.1177/19322968241288579. Online ahead of print. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39397773 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2023 Oct;25(10):726-735. doi: 10.1089/dia.2023.0165. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37335748
-
The Emerging Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Management of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Narrative Review.Diabetes Ther. 2022 May;13(5):931-952. doi: 10.1007/s13300-022-01257-5. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Diabetes Ther. 2022. PMID: 35394566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review of the prevalence, risk factors and screening tools for autonomic and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in children, adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes.Acta Diabetol. 2022 Mar;59(3):293-308. doi: 10.1007/s00592-022-01850-x. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Acta Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35089443 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

