The Value of PHQ-9 and GAD-7 for Screening Emotional Disorders in IBS-D and the Specificity of the Gut Flora Associated with Emotional Comorbidity: Preliminary Findings
- PMID: 39564595
- PMCID: PMC11573876
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S486784
The Value of PHQ-9 and GAD-7 for Screening Emotional Disorders in IBS-D and the Specificity of the Gut Flora Associated with Emotional Comorbidity: Preliminary Findings
Abstract
Background: To identify irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) combined with anxiety and/or depression through a psychological screening tool and to further explore the relationships between patients with comorbidities and gut microbiota.
Methods: The GAD-7, SAS, PHQ-9 and SDS were administered to evaluate anxiety and depression. Faeces were subsequently collected from 44 patients with emotional disorders (IBS-EDs), 22 patients without emotional disorders (IBS-nEDs) and 18 healthy controls (HCs) via 16S rRNA sequencing, depending on the participants' wishes. The differences in gut microbiota among different groups were analysed. Spearman analysis was conducted at the genus level and was based on psychological assessment scores. Patients with IBS-D were recruited from December 2020 to November 2022.
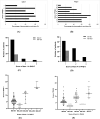
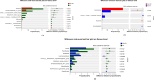
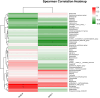
Results: This study included 124 outpatients with IBS-D. According to the GAD-7 and SAS scores, 40.3% and 19.3% of the participants, respectively, had anxiety (P < 0.05). Similarly, a significantly greater percentage of participants had depression according to the PHQ-9 than according to the SDS (61.3% vs 33.1%) (P < 0.05). Overall, approximately 66.1% of the participants had emotional disorders (anxiety and/or depression) according to the GAD-7 and PHQ-9. Correlation analysis revealed that the abundances of Eubacterium_hallii_group, Monoglobus and Lachnoclostridium were closely related to the PHQ-9 scores and that the abundances of Subdoligranulum and Holdemanella were closely related to the GAD-7 scores.
Conclusion: In comparison to the SAS and SDS, both the GAD-7 and PHQ-9 identified a greater number of individuals with emotional disorders within the IBS-D population. Furthermore, our findings demonstrated that Lachnoclostridium is not only a biomarker for IBS-ED patients but also that its abundance changes are related to PHQ-9 scores, which may provide insights for further brain gut investigations.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; IBS-D; anxiety; depression.
© 2024 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Value of Chinese Version GAD-7 and PHQ-9 to Screen Anxiety and Depression in Chinese Outpatients with Atypical Chest Pain.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021 May 18;17:423-431. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S305623. eCollection 2021. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2021. PMID: 34040380 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial and metabolomic profiles in correlation with depression and anxiety co-morbidities in diarrhoea-predominant IBS patients.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Jun 17;20(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01841-4. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32552668 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the optimal cutoff values of HADS, PHQ-9 and GAD-7 as screening instruments for depression and anxiety in irritable bowel syndrome.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Dec;33(12):e14161. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14161. Epub 2021 May 3. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. PMID: 33938601 Free PMC article.
-
Feeling down? A systematic review of the gut microbiota in anxiety/depression and irritable bowel syndrome.J Affect Disord. 2020 Apr 1;266:429-446. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.01.124. Epub 2020 Jan 22. J Affect Disord. 2020. PMID: 32056910 Review.
-
A Systematic Review: Fecal Bacterial Profile in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Analyzed with the GA-Map Dysbiosis Test Based on the 16S rRNA Gene of Bacterial Species or Groups.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr 17;17:109-120. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S451675. eCollection 2024. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38646157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhao J, Li X, Yang J, et al. Prevalence of and factors associated with symptoms consistent with a diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome among resident physicians in standardised training in China: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2023;13(12):e079874. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2023-079874 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palsson OS, Whitehead WE, van Tilburg MAL, et al. Development and validation of the Rome IV diagnostic questionnaire for adults. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1481–1491. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.014 - DOI
-
- Jin L, Qian C, Xuan Z. Changes of gastrointestinal hormones in diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome treated by Tongxie Sishen decoction and its clinical significance. World Chin Med. 2020;15(1):71–75. In Chinese.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

