Modulation of miR-205 expression using a Cheiranthus cheiri phyto-nano hybrid as a potential therapeutic agent against breast cancer
- PMID: 39575377
- PMCID: PMC11580155
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra03069a
Modulation of miR-205 expression using a Cheiranthus cheiri phyto-nano hybrid as a potential therapeutic agent against breast cancer
Abstract
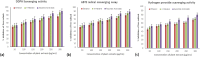
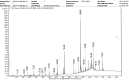
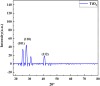
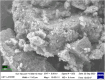
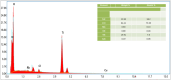
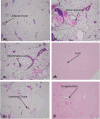
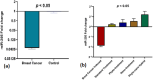
Breast cancer is the fifth major cause of fatalities associated with cancer worldwide and in Pakistan, 34 066 female breast cancer cases were recorded in 2018. This study was designed to understand extracts of Cheiranthus cheiri (C. cheiri) and to evaluate the epigenetic modulation of microRNA expression for breast cancer therapy using a selected phyto-nanohybrid treatment. The phytochemical screening revealed the presence of potential phytochemicals and antioxidant scavenging activity in the C. cheiri extracts with a DPPH (2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydroxyl) assay giving an IC50 value of 20.63 μg mL-1. GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy) analysis of the C. cheiri n-hexane extract detected 42 phytocompounds. Titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles were synthesized and characterized using XRD (X-ray diffraction), SEM (scanning electron microscopy) and EDX (energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry) to confirm the synthesis of anatase (tetragonal) TiO2. The prepared nanoparticles were conjugated with the selected plant i.e., C. cheiri. The resulting phyto-nanohybrid was used for the subsequent treatment of breast cancer induced in a female rat model. The treatment groups were as follows: doxorubicin as the standard treatment, C. cheiri, TiO2 and the phyto-nano hybrid treatment. After 8 weeks of treatment, the groups induced to exhibit breast cancer (with and without treatment) and the control groups were dissected and analysed for histopathological, haematological and microRNA expression. Histopathological examination revealed chronic inflammation in the dilated ducts and tumour embolus formation, thus confirming the presence of breast cancer in the DMBA-induced female rat model. MicroRNA expression analysis showed a statistically significant decrease in levels of miR-205 in the plasma of the breast cancer rat model compared to the control (p < 0.05). After treatment with the phyto-nano hybrid, a statistically significant increase in the expression of miR-205 was observed in the rat models induced to exhibit breast cancer compared to the rat model without any treatment (p < 0.05). The downregulation of miR-205 in the plasma of the breast cancer exhibiting model, as compared to the control, and its upregulation after treatment with the selected phyto-nano hybrid indicated its diagnostic and prognostic significance. It is concluded that the phyto-nano hybrid used in this study is effective against breast cancer induced female rat model. All the results support the finding that the selected phyto-nano hybrid has great potential as a possible therapeutic agent for the treatment of breast cancer.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GC/MS Analysis and Phyto-synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Amygdalus spinosissima Extract: Antibacterial, Antioxidant Effects, Anticancer and Apoptotic Effects.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2022 Jul-Sep;14(3):223-232. doi: 10.18502/ajmb.v14i3.9829. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36061132 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesised TiO2 Nanoparticles-Mediated Terenna asiatica: Evaluation of Their Role in Reducing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Human Breast Cancer Proliferation.Molecules. 2023 Jun 29;28(13):5126. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135126. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446788 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the molecular mechanism, cytotoxic, and anticancer activities of phyto-reduced silver nanoparticles in MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines.Microsc Res Tech. 2024 Jul;87(7):1627-1639. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24540. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Microsc Res Tech. 2024. PMID: 38450823
-
Phyto-Engineered Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) with Potential Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Wound Healing Activities Under in vitro and in vivo Conditions.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 7;15:7553-7568. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S257499. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33116487 Free PMC article.
-
Nano-pesticidal potential of Cassia fistula (L.) leaf synthesized silver nanoparticles (Ag@CfL-NPs): Deciphering the phytopathogenic inhibition and growth augmentation in Solanum lycopersicum (L.).Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 26;13:985852. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.985852. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36090121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F. Ferlay J. Soerjomataram I. Siegel R. L. Torre L. A. Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Torre L. Islami F. Siegel R. L. Ward E. Jemal A. Global cancer in women: burden and trends. Cancer Epidemiol., Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26(4):444–457. - PubMed
-
- Anwa D. M. El-Sayed M. Reda A. Fang J. Y. Khattab S. N. Elzoghby A. O. Recent advances in herbal combination nanomedicine for cancer: delivery technology and therapeutic outcomes. Expert Opin. Drug Delivery. 2021;2(11):1609–1625. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed F. Ijaz B. Ahmad Z. Farooq N. Sarwar M. B. Husnain T. Modification of miRNA Expression through plant extracts and compounds against breast cancer: mechanism and translational significance. Phytomedicine. 2020;68:153168. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

