The Mechanistic Link Between Tau-Driven Proteotoxic Stress and Cellular Senescence in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 39596399
- PMCID: PMC11595124
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252212335
The Mechanistic Link Between Tau-Driven Proteotoxic Stress and Cellular Senescence in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
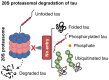
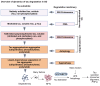
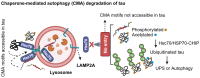
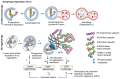
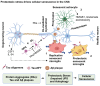
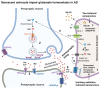
In Alzheimer's disease (AD), tau dissociates from microtubules (MTs) due to hyperphosphorylation and misfolding. It is degraded by various mechanisms, including the 20S proteasome, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), 26S proteasome, macroautophagy, and aggrephagy. Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) form upon the impairment of aggrephagy, and eventually, the ubiquitin chaperone valosin-containing protein (VCP) and heat shock 70 kDa protein (HSP70) are recruited to the sites of NFTs for the extraction of tau for the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS)-mediated degradation. However, the impairment of tau degradation in neurons allows tau to be secreted into the extracellular space. Secreted tau can be monomers, oligomers, and paired helical filaments (PHFs), which are seeding competent pathological tau that can be endocytosed/phagocytosed by healthy neurons, microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs), and oligodendrocytes, often causing proteotoxic stress and eventually triggers senescence. Senescent cells secrete various senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factors, which trigger cellular atrophy, causing decreased brain volume in human AD. However, the molecular mechanisms of proteotoxic stress and cellular senescence are not entirely understood and are an emerging area of research. Therefore, this comprehensive review summarizes pertinent studies that provided evidence for the sequential tau degradation, failure, and the mechanistic link between tau-driven proteotoxic stress and cellular senescence in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; aggrephagy; autophagy; cellular senescence; nucleophagy; proteotoxic stress; senolytic drugs; tau; tauopathy; ubiquitin–proteasome system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Protein tau phosphorylation in the proline rich region and its implication in the progression of Alzheimer's disease.Exp Neurol. 2025 Jan;383:115049. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.115049. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Exp Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39522802
-
Unlocking data: Decision-maker perspectives on cross-sectoral data sharing and linkage as part of a whole-systems approach to public health policy and practice.Public Health Res (Southampt). 2024 Nov 20:1-30. doi: 10.3310/KYTW2173. Online ahead of print. Public Health Res (Southampt). 2024. PMID: 39582242
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of _targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin for endometrial hyperplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5(5):CD012214. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012214.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38695827 Review.
References
-
- Ghetti B., Oblak A.L., Boeve B.F., Johnson K.A., Dickerson B.C., Goedert M. Invited review: Frontotemporal dementia caused by microtubule-associated protein tau gene (MAPT) mutations: A chameleon for neuropathology and neuroimaging. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2015;41:24–46. doi: 10.1111/nan.12213. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

