Structural requirements for biological activity of the ninth and tenth FIII domains of human fibronectin
- PMID: 9045628
- PMCID: PMC1626579
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.272.10.6159
Structural requirements for biological activity of the ninth and tenth FIII domains of human fibronectin
Abstract
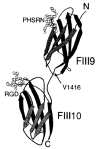
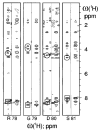
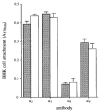
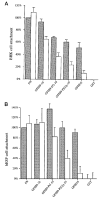
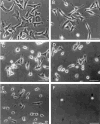
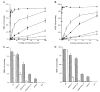
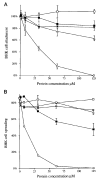
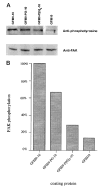
The ninth and tenth type III domains of fibronectin each contain specific cell binding sequences, RGD in FIII10 and PHSRN in FIII9, that act synergistically in mediating cell adhesion. We investigated the relationship between domain-domain orientation and synergistic adhesive activity of the FIII9 and FIII10 pair of domains. The interdomain interaction of the FIII9-10 pair was perturbed by introduction of short flexible linkers between the FIII9 and FIII10 domains. Incremental extensions of the interdomain link between FIII9 and FIII10 reduced the initial cell attachment, but had a much more pronounced effect on the downstream cell adhesion events of spreading and phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase. The extent of disruption of cell adhesion depended upon the length of the interdomain linker. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the wild type and mutant FIII9-10 proteins demonstrated that the structure of the RGD-containing loop is unaffected by domain-domain interactions. We conclude that integrin-mediated cell adhesion to the central cell binding domain of fibronectin depends not only upon specific interaction sites, but also on the relative orientation of these sites. These data have implications for the molecular mechanisms by which integrin-ligand interactions are achieved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential activation of focal adhesion kinase, Rho and Rac by the ninth and tenth FIII domains of fibronectin.J Cell Sci. 1999 Sep;112 (Pt 17):2937-46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.112.17.2937. J Cell Sci. 1999. PMID: 10444388
-
The eighth FIII domain of human fibronectin promotes integrin alpha5beta1 binding via stabilization of the ninth FIII domain.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 19;276(42):38885-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105868200. Epub 2001 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11500513
-
The role of the ninth and tenth type III domains of human fibronectin in cell adhesion.FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 7;340(3):197-201. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80137-1. FEBS Lett. 1994. PMID: 8131845
-
Integrins in cell adhesion and signaling.Hum Cell. 1996 Sep;9(3):181-6. Hum Cell. 1996. PMID: 9183647 Review.
-
Cell adhesion and tumor metastasis.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994;24:99-105. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994. PMID: 8983067 Review.
Cited by
-
Extra-domain B in oncofetal fibronectin structurally promotes fibrillar head-to-tail dimerization of extracellular matrix protein.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 18;287(21):17578-17588. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.303131. Epub 2012 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22442152 Free PMC article.
-
Guiding epithelial cell phenotypes with engineered integrin-specific recombinant fibronectin fragments.Tissue Eng Part A. 2011 Jan;17(1-2):139-50. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2010.0199. Epub 2010 Dec 12. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011. PMID: 20695776 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin α3β1 Binding to Fibronectin Is Dependent on the Ninth Type III Repeat.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 16;290(42):25534-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.656702. Epub 2015 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26318455 Free PMC article.
-
Using self-assembled monolayers to understand α8β1-mediated cell adhesion to RGD and FEI motifs in nephronectin.ACS Chem Biol. 2011 Oct 21;6(10):1078-86. doi: 10.1021/cb200186j. Epub 2011 Aug 12. ACS Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21790180 Free PMC article.
-
The fibronectin synergy site re-enforces cell adhesion and mediates a crosstalk between integrin classes.Elife. 2017 Jan 16;6:e22264. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22264. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28092265 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

