Activation of the complement classical pathway (C1q binding) by mesophilic Aeromonas hydrophila outer membrane protein
- PMID: 9673268
- PMCID: PMC108428
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.8.3825-3831.1998
Activation of the complement classical pathway (C1q binding) by mesophilic Aeromonas hydrophila outer membrane protein
Abstract
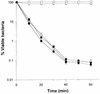
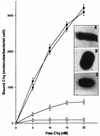
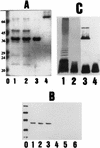
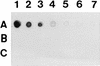
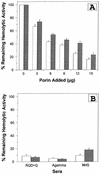
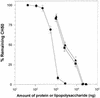
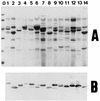
The mechanism of killing of Aeromonas hydrophila serum-sensitive strains in nonimmune serum by the complement classical pathway has been studied. The bacterial cell surface component that binds C1q more efficiently was identified as a major outer membrane protein of 39 kDa, presumably the porin II described by D. Jeanteur, N. Gletsu, F. Pattus, and J. T. Buckley (Mol. Microbiol. 6:3355-3363, 1992), of these microorganisms. We have demonstrated that the purified form of porin II binds C1q and activates the classical pathway in an antibody-independent manner, with the subsequent consumption of C4 and reduction of the serum total hemolytic activity. Activation of the classical pathway has been observed in human nonimmune serum and agammaglobulinemic serum (both depleted of factor D). Binding of C1q to other components of the bacterial outer membrane, in particular to rough lipopolysaccharide, could not be demonstrated. Activation of the classical pathway by this lipopolysaccharide was also much less efficient than activation by the outer membrane protein. The strains possessing O-antigen lipopolysaccharide bind less C1q than the serum-sensitive strains, because the outer membrane protein is less accessible, and are resistant to complement-mediated killing. Finally, a similar or identical outer membrane protein (presumably porin II) that binds C1q was shown to be present in strains from the most common mesophilic Aeromonas O serogroups.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C1q binding and activation of the complement classical pathway by Klebsiella pneumoniae outer membrane proteins.Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):852-60. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.852-860.1993. Infect Immun. 1993. PMID: 8432605 Free PMC article.
-
A C1q-binding 40 kDa porin from Aeromonas salmonicida: cloning, sequencing, role in serum susceptibility and fish immunoprotection.Microb Pathog. 2005 May-Jun;38(5-6):227-37. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2005.02.006. Microb Pathog. 2005. PMID: 15885977
-
Antibody-independent binding of complement component C1q by Legionella pneumophila.Infect Immun. 1995 Dec;63(12):4939-43. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.12.4939-4943.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7591161 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of fluid phase C1/C1q and macrophage membrane-associated C1q with gram-negative bacteria.Behring Inst Mitt. 1989 Jul;(84):236-54. Behring Inst Mitt. 1989. PMID: 2552981 Review.
-
[Immune and nonimmune complement activation].Rev Clin Esp. 1996 Mar;196 Spec No:3-6. Rev Clin Esp. 1996. PMID: 9206805 Review. Spanish. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of a glucose-inhibited division gene, gidA, that regulates cytotoxic enterotoxin of Aeromonas hydrophila.Infect Immun. 2004 Feb;72(2):1084-95. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.2.1084-1095.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 14742556 Free PMC article.
-
Reptiles as a source of Salmonella O48--clinically important bacteria for children: the relationship between resistance to normal cord serum and outer membrane protein patterns.Microb Ecol. 2011 Jan;61(1):41-51. doi: 10.1007/s00248-010-9677-7. Epub 2010 May 18. Microb Ecol. 2011. PMID: 20480364
-
Molecular and functional characterization of a ToxR-regulated lipoprotein from a clinical isolate of Aeromonas hydrophila.Infect Immun. 2006 Jul;74(7):3742-55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00402-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16790746 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Outer Membrane Proteins from Salmonella Enteritidis Strains with Different Sensitivity to Human Serum.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 3;11(10):e0164069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164069. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27695090 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of wboA enhances activation of the lectin pathway of complement in Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis.Infect Immun. 2001 Jul;69(7):4407-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4407-4416.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11401980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcolea J M, Antón C, Marqués G, Sánchez-Corral P, Vivanco F. Formation of covalent complexes between the fourth component of human complement and IgG immune aggregates. Complement. 1987;4:21–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

