Correlative ultrastructural distribution of neurotensin receptor proteins and binding sites in the rat substantia nigra
- PMID: 9763490
- PMCID: PMC6792847
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-20-08473.1998
Correlative ultrastructural distribution of neurotensin receptor proteins and binding sites in the rat substantia nigra
Abstract
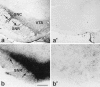
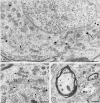
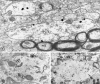
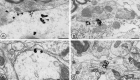
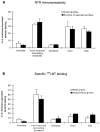
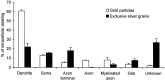
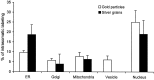
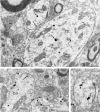
Neurotensin (NT) produces various stimulatory effects on dopaminergic neurons of the rat substantia nigra. To gain insight into the subcellular substrate for these effects, we compared by electron microscopy the distribution of immunoreactive high-affinity NT receptor proteins (NTRH) with that of high-affinity 125I-NT binding sites in this region of rat brain. Quantitative analysis showed a predominant association of immunogold and radioautographic labels with somata and dendrites of presumptive dopaminergic neurons, and a more modest localization in myelinated and unmyelinated axons and astrocytic leaflets. The distributions of immunoreactive NTRH and 125I-NT binding sites along somatodendritic plasma membranes were highly correlated and homogeneous, suggesting that membrane-_targeted NTRH proteins were functional and predominantly extrasynaptic. Abundant immunocytochemically and radioautographically labeled receptors were also detected inside perikarya and dendrites. Within perikarya, these were found in comparable proportions over membranes of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, suggesting that newly synthesized receptor proteins already possess the molecular and conformational properties required for effective ligand binding. By contrast, dendrites showed a proportionally higher concentration of immunolabeled than radiolabeled intracellular receptors. A fraction of these immunoreactive receptors were found in endosomes, suggesting that they had undergone ligand-induced internalization and were under a molecular conformation and/or in a physical location that precluded their recognition by and/or access to exogenous ligand. Our results provide the first evidence that electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of the NT receptor identifies sites for both the binding and trafficking of NT in the substantia nigra.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complementarity of radioautographic and immunohistochemical techniques for localizing neuroreceptors at the light and electron microscopy level.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1998 Feb;31(2):215-23. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x1998000200005. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1998. PMID: 9686144 Review.
-
Light and electron microscopic localization of retrogradely transported neurotensin in rat nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons.Neuroscience. 1992 Sep;50(2):269-82. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90422-x. Neuroscience. 1992. PMID: 1279459
-
Predominant surface distribution of neurokinin-3 receptors in non-dopaminergic dendrites in the rat substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area.Neuroscience. 2007 Feb 23;144(4):1393-408. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.10.058. Epub 2006 Dec 29. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17197098
-
Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of neurotensin and the dopamine D2 receptor in the rat nucleus accumbens.J Comp Neurol. 1996 Aug 5;371(4):552-66. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960805)371:4<552::AID-CNE5>3.0.CO;2-3. J Comp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8841909
-
Morphological substrate for neurotensin-dopamine interactions in the rat midbrain tegmentum.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992;668:173-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27349.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992. PMID: 1361112 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Role of calcium in neurotensin-evoked enhancement in firing in mesencephalic dopamine neurons.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 10;24(10):2566-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5376-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15014132 Free PMC article.
-
Normal biogenesis and cycling of empty synaptic vesicles in dopamine neurons of vesicular monoamine transporter 2 knockout mice.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jan;16(1):306-15. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0559. Epub 2004 Oct 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15496457 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotensin in reward processes.Neuropharmacology. 2020 May 1;167:108005. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108005. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32057800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic stress differentially alters mRNA expression of opioid peptides and receptors in the dorsal hippocampus of female and male rats.J Comp Neurol. 2021 Jul 1;529(10):2636-2657. doi: 10.1002/cne.25115. Epub 2021 Feb 8. J Comp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33483980 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic immobilization stress primes the hippocampal opioid system for oxycodone-associated learning in female but not male rats.Synapse. 2019 May;73(5):e22088. doi: 10.1002/syn.22088. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Synapse. 2019. PMID: 30632204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baude A, Nusser Z, Roberts JDB, Mulvihill E, McIlhinney RAJ, Somogyi P. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1α) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron. 1993;11:771–787. - PubMed
-
- Bayer VE, Towle AC, Pickel VM. Ultrastructural localization of neurotensin-like immunoreactivity within dense core vesicles in perikarya, but not terminals, colocalizing tyrosine hydroxylase in the rat ventral tegmental area. J Comp Neurol. 1991;311:179–196. - PubMed
-
- Beaudet A. Autoradiographic localization of receptors at the electron microscopic level. In: Wharton J, Polak JM, editors. Receptor autoradiography. Principles and practices. Oxford UP; Oxford: 1993. pp. 135–158.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
