Silencing of Two Insulin Receptor Genes Disrupts Nymph-Adult Transition of Alate Brown Citrus Aphid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Two Insulin Receptor Genes in A. citricidus
2.2. Expression Profiles of AcInR1 and AcInR2 at Different Developmental Stages
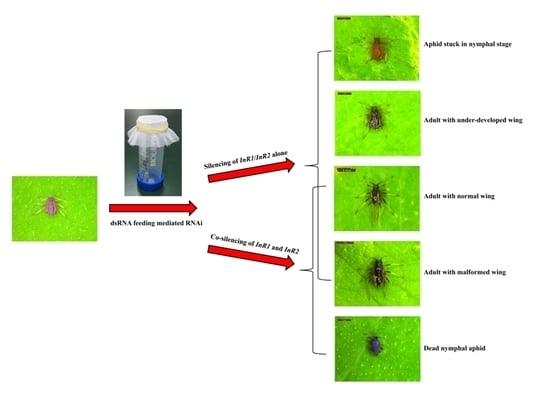
2.3. Silencing of AcInR1 and AcInR2 by RNAi Showed Clear Phenotypes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Culture
4.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. cDNA Cloning
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.6. RNAi
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.B.; Yang, W.J.; Xie, Y.F.; Xu, K.K.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, G.R.; Wang, J.J. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of BdFoxO gene in the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). Gene 2015, 578, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, T.X. Insulin-related peptide 5 is involved in regulating embryo development and biochemical composition in pea aphid with wing polyphenism. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.K.; Yang, W.J.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.B.; Wang, J.J. Insulin signaling pathway in the oriental fruit fly: The role of insulin receptor substrate in ovarian development. Gen. Comp. Endocr. 2014, 216, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.D.; Busto, M.; Suster, M.L.; So, A.K.C.; Ben-Shahar, Y.; Leevers, S.J.; Sokolowski, M.B. Natural variation in Drosophila melanogaster diapause due to the insulin-regulated PI3-kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15911–15915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, C.; Denlinger, D.L. Insulin signaling and FOXO regulate the overwintering diapause of the mosquito Culex pipiens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6777–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.J.; Xue, J.; Lu, B.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhuo, J.C.; He, S.F.; Ma, X.F.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Fan, H.W.; Xu, J.Y.; et al. Two insulin receptors determine alternative wing morphs in planthoppers. Nature 2015, 519, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, M.; Li, C.j.; Wu, W.; Li, B. Identification and evolution of two insulin receptor genes involved in Tribolium castaneum development and reproduction. Gene 2016, 585, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nässel, D.R.; Broeck, J.V. Insulin/IGF signaling in Drosophila and other insects: Factors that regulate production, release and post-release action of the insulin-like peptides. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantley, L.C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogiolo, W.; Stocker, H.; Ikeya, T.; Rintelen, F.; Fernandez, R.; Hafen, E. An evolutionarily conserved function of the Drosophila insulin receptor and insulin-like peptides in growth control. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, S.; Hafen, E. Insulin/IGF and _target of rapamycin signaling: A TOR de force in growth control. Trends Cell Biol. 2003, 13, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Brown, M.R. Signaling and function of insulin-like peptides in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, R.S. Genetic analysis of insulin signaling in Drosophila. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 13, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R.; Neuenschwander, S.; Brown, M.; Ackermann, U. Insulin-mediated secretion of ecdysteroids from mosquito ovaries and molecular cloning of the insulin receptor homologue from ovaries of bloodfed Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol. Biol. 1997, 6, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullbright, G.; Lacy, E.R.; Büllesbach, E.E. The prothoracicotropic hormone bombyxin has specific receptors on insect ovarian cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 245, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrisqueta, M.; Sueren Castillo, S.; Maestro, J.L. Insulin receptor-mediated nutritional signalling regulates juvenile hormone biosynthesis and vitellogenin production in the German cockroach. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavine, L.C.; Hahn, L.L.; Warren, I.A.; Garczynski, S.F.; Dworkin, I.; Emlen, D.J. Cloning and characterization of an mrna encoding an insulin receptor from the horned scarab beetle Onthophagus nigriventris (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. 2013, 82, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Azevedo, S.V.; Hartfelder, K. The insulin signaling pathway in honey bee (Apis mellifera) caste development—Differential expression of insulin-like peptides and insulin receptors in queen and worker larvae. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.L.; Pietrantonio, P.V. Insect insulin receptors: Insights from sequence and caste expression analyses of two cloned hymenopteran insulin receptor cdnas from the fire ant. Insect Mol. Biol. 2011, 20, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Jack, J.; Garofalo, R.S. The Drosophila insulin receptor is required for normal growth. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Yu, N.; Smagghe, G. Insulin receptor regulates food intake through sulfakinin signaling in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Peptides 2016, 80, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Teng, X.L.; Chen, M.H.; Li, F. Orthologs of human disease associated genes and RNAi analysis of silencing insulin receptor gene in Bombyx mori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18102–18116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatar, M.; Kopelman, A.; Epstein, D.; Tu, M.P.; Yin, C.M.; Garofalo, R.S. A mutant Drosophila insulin receptor homolog that extends life-span and impairs neuroendocrine function. Science 2001, 292, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braendle, C.; Davis, G.K.; Brisson, J.A.; Stern, D.L. Wing dimorphism in aphids. Heredity 2006, 97, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, D.G.; Brisson, J.A. Aphids: A model for polyphenism and epigenetics. Genet. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 431531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, A.; Hongo, S.; Miura, T. Morphological and histological examination of polyphenic wing formation in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera, hexapoda). Zoomorphology 2008, 127, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Gotoh, H.; Abe, T.; Miura, T. Juvenile hormone titer and wing-morph differentiation in the vetch aphid Megoura crassicauda. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K.; Miura, T. Aphid polyphenisms: Trans-generational developmental regulation through viviparity. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, I.A.G. Genome sequence of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000313. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, P.; Ambr, O.S.; Albiach Martí, M.R.; Guerri, J.; Pena, L. Citrus tristeza virus: A pathogen that changed the course of the citrus industry. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2008, 9, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, W.B.; Dang, P.M.; Bausher, M.; Chaparro, J.X.; McKendree, W.; Shatters, R.G., Jr.; McKenzie, C.L.; Sinisterra, X.H. Aphid biology: Expressed genes from alate Toxoptera citricida, the brown citrus aphid. J. Insect Sci. 2003, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, J.P. Colony density and wing development in Toxoptera citricida (Homoptera, aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2001, 30, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbert, S.E.; Brown, L.G. Toxoptera Citricida (Kirkaldy), Brown Citrus Aphid-Identification, Biology, And Management Strategies. In Entomology Circular; Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services—Division of Plant Industry: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, S.J.; Nickerson, M.L.; Dean, M.; Song, Y.; Hoyt, P.R.; Rhee, H.; Kim, C.; Puterka, G.J. The genome of Diuraphis noxia, a global aphid pest of small grains. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisson, J.A.; Ishikawa, A.; Miura, T. Wing development genes of the pea aphid and differential gene expression between winged and unwinged morphs. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Xia, W.K.; Wei, D.D.; Wei, D.; Wang, J.J. Identification, characterization and functional analysis of a chitin synthase gene in the brown citrus aphid, Toxoptera citricida (Hemiptera, aphididae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiaens, O.; Swevers, L.; Smagghe, G. DsRNA degradation in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) associated with lack of response in RNAi feeding and injection assay. Peptides 2014, 53, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.B.; Ghanim, M.; Liu, S.S.; Czosnek, H. Silencing the ecdysone synthesis and signaling pathway genes disrupts nymphal development in the whitefly. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, F.; Ding, B.Y.; Xiong, Y.; Dou, W.; Wei, D.; Jiang, H.B.; Wei, D.D.; Wang, J.J. Differential expression of genes in the alate and apterous morphs of the brown citrus aphid, Toxoptera citricida. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P.; Whittaker, J. Structural biology of insulin and IGF1 receptors: Implications for drug design. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. Insulin and its receptor: Structure, function and evolution. Bioessays 2004, 26, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganassi, S.; Signa, G.; Mola, L. Development of the wing buds in Megoura viciae: A morphological study. Bull. Insectol. 2005, 58, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Bertuso, A.G.; Morooka, S.; Tojo, S. Sensitive periods for wing development and precocious metamorphosis after precocene treatment of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. J. Insect Physiol. 2002, 48, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.B.; Williams, I.S.; Hardie, J. The role of nutrition, crowding and interspecific interactions in the development of winged aphids. Ecol. Entomol. 2001, 26, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ma, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Sheng, Z.T.; Jiang, R.J.; Bendena, W.G.; Li, S. Transcriptional regulation of the insulin signaling pathway genes by starvation and 20-hydroxyecdysone in the Bombyx fat body. J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanning, C.N.T.; Eynde, B.V.; Yu, N.; Ma, S.; Smagghe, G. CRISPR/Cas9 in insect: Applications, best practices and biosafety concerns. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 98, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, F.; Wei, D.D.; Jiang, X.Z.; Wei, D.; Shen, G.M.; Feng, Y.C.; Li, T.; Wang, J.J. Reference gene validation for quantitative PCR under various biotic and abiotic stress conditions in Toxoptera citricida (Hemiptera, aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellemans, J.; Mortier, G.; de Paepe, A.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. Qbase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Comparison | Presented Phenotype | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Presented Phenotypes | Adult Stage | Nymph Stage | ||||
| Normal Wing (b in Figure 4A) versus Others | Malformed Wing (c in Figure 4A) versus Others | Underdeveloped Wing (d in Figure 4A) versus Others | Alive (e in Figure 4A) versus Others | Dead (f in Figure 4A) versus Others | ||
| dsInR1 versus dsGFP | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) | * (p = 0.026) | *** (p = 0.000) | - |
| dsInR2 versus dsGFP | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) | * (p = 0.045) | *** (p = 0.000) | - |
| dsInR1 + dsInR2 versus dsGFP’ | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) | - | - | *** (p = 0.000) |
| dsInR1 versus dsInR2 | NS (p = 0.292) | NS (p = 0.056) | NS (p = 0.658) | NS (p = 0.756) | NS (p = 0.183) | - |
| dsInR1 versus dsInR1 + dsInR2 | *** (p = 0.000) | * (p = 0.012) | NS (p = 0.712) | * (p = 0.027) | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) |
| dsInR2 versus dsInR1 + dsInR2 | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) | NS (p = 0.442) | * (p = 0.047) | *** (p = 0.000) | *** (p = 0.000) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, B.-Y.; Shang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, Q.; Niu, J.-Z.; Smagghe, G.; Wang, J.-J. Silencing of Two Insulin Receptor Genes Disrupts Nymph-Adult Transition of Alate Brown Citrus Aphid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020357
Ding B-Y, Shang F, Zhang Q, Xiong Y, Yang Q, Niu J-Z, Smagghe G, Wang J-J. Silencing of Two Insulin Receptor Genes Disrupts Nymph-Adult Transition of Alate Brown Citrus Aphid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020357
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Bi-Yue, Feng Shang, Qiang Zhang, Ying Xiong, Qun Yang, Jin-Zhi Niu, Guy Smagghe, and Jin-Jun Wang. 2017. "Silencing of Two Insulin Receptor Genes Disrupts Nymph-Adult Transition of Alate Brown Citrus Aphid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020357
APA StyleDing, B.-Y., Shang, F., Zhang, Q., Xiong, Y., Yang, Q., Niu, J.-Z., Smagghe, G., & Wang, J.-J. (2017). Silencing of Two Insulin Receptor Genes Disrupts Nymph-Adult Transition of Alate Brown Citrus Aphid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020357