Liu Jun Zi Tang—A Potential, Multi-Herbal Complementary Therapy for Chemotherapy-Induced Neurotoxicity
Abstract
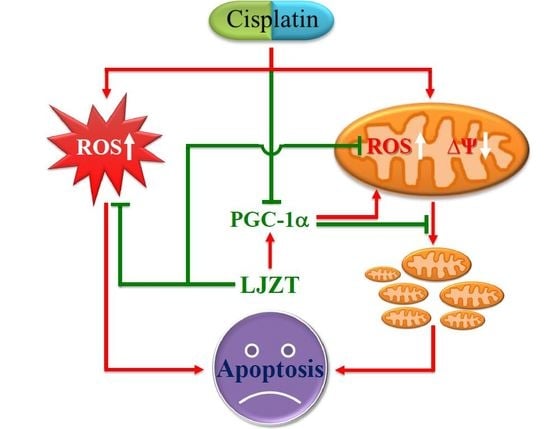
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LJZT Prevented Cisplatin-Induced Thermal Hyperalgesia in Mice and Apoptosis in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells
2.2. LJZT Prevented Cisplatin-Induced Cytosolic Free Radical Formation
2.3. LJZT Attenuated Cisplatin-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction
2.4. LJZT Attenuated Cisplatin-Induced Mitochondrial Pro-Apoptotic Factor Release
2.5. LJZT Reversed the Cisplatin-Induced Decreased Expression of PGC-1α
2.6. Silencing of PGC-1α Gene Attenuated the Protection of LJZT
3. Discussion
3.1. LJZT Prevented Cisplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity
3.2. LJZT Attenuated Cisplatin-Induced Cytosolic and Mitochondrial Free Radical Formation
3.3. LJZT Attenuated Cisplatin-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and PGC-1α Down-Regulation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. LJZT Preparation
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Survival Assays
4.5. Cisplatin-Induced Neuropathy and Tail Flick Assay
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Measurement of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species
4.8. Measurement of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Membrane Potential
4.9. Transient PGC-1α Gene Silencing
4.10. Transient Transfection, Luminescence, and Image Detections
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Huang, H.; Zhu, L.J. Introduction to Formulae of Traditional Chinese Medicine. In World Century Compendium to TCM; World Centry Publishing Corporation: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yu, K.Q.; Ouyang, M.Z.; Luo, R.; Zhao, X.S. Chinese herbal medicine liu jun zi tang and xiang sha liu jun zi tang for functional dyspepsia: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 936459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, S.; Takeda, H. Herbal medicines for the treatment of cancer chemotherapy-induced side effects. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T.H.; Fu, P.K.; Chang, C.H.; Chang, S.N.; Chiahung Mao, F.; Lin, C.H.; Evidence-based Chinese Medicine Research Group. Prescription patterns of Chinese herbal products for post-surgery colon cancer patients in Taiwan. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.; Bussom, S.; Guan, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gullen, E.A.; Liu, S.H.; Cheng, Y.C. The four-herb Chinese medicine PHY906 reduces chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal toxicity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 45ra59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, B.; Li, A.; Wang, Z.; Han, J. The advantages of using traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy in the whole course of cancer treatment instead of only terminal stage of cancer. Biosci. Trends 2015, 9, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, H.; Muto, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Ohnishi, S.; Sadakane, C.; Saegusa, Y.; Nahata, M.; Hattori, T.; Asaka, M. Rikkunshito as a ghrelin enhancer. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 514, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, M. Modern Study of the Medical Formulae in Traditional Chinese Medicine; Beijing Xue Yuan Press: Beijing, China, 1997; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Esin, E.; Yalcin, S. Neuropathic cancer pain: What we are dealing with? How to manage it? Onco_targets Ther. 2014, 7, 599–618. [Google Scholar]
- Starobova, H.; Vetter, I. Pathophysiology of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippard, S.J. New chemistry of an old molecule: Cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]. Science 1982, 218, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.; Lippard, S.J. Direct cellular responses to platinum-induced DNA damage. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 1387–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastman, A. Activation of programmed cell death by anticancer agents: Cisplatin as a model system. Cancers Cells 1990, 2, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Barabas, K.; Milner, R.; Lurie, D.; Adin, C. Cisplatin: A review of toxicities and therapeutic applications. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2008, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasawa, T.; Steyger, P.S. An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 237, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Schumaker, L.M.; Egorin, M.J.; Zuhowski, E.G.; Guo, Z.; Cullen, K.J. Cisplatin preferentially binds mitochondrial DNA and voltage-dependent anion channel protein in the mitochondrial membrane of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Possible role in apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5817–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, E.S.; Windebank, A.J. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis of DRG neurons involves bax redistribution and cytochrome c release but not fas receptor signaling. Neurobiol. Dis. 2002, 9, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregg, R.W.; Molepo, J.M.; Monpetit, V.J.; Mikael, N.Z.; Redmond, D.; Gadia, M.; Stewart, D.J. Cisplatin neurotoxicity: The relationship between dosage, time, and platinum concentration in neurologic tissues, and morphologic evidence of toxicity. J. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 10, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carozzi, V.A.; Canta, A.; Chiorazzi, A. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: What do we know about mechanisms? Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 596, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareyson, D.; Piscosquito, G.; Moroni, I.; Salsano, E.; Zeviani, M. Peripheral neuropathy in mitochondrial disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, P.S.; Govindaraju, C.; Sonam, K.; Nagappa, M.; Chiplunkar, S.; Kumar, R.; Gayathri, N.; Bharath, M.M.; Arvinda, H.R.; Sinha, S.; et al. Peripheral neuropathy in genetically characterized patients with mitochondrial disorders: A study from south India. Mitochondrion 2016, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, S.; Meyer-Hamme, G.; Friedemann, T. Treatment of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy: The role of medicinal herbs. Forum Immunopathol. Dis. Ther. 2012, 3, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, J.; Colosimo, M.; Vitetta, L. Herbal Medicines and Chemotherapy Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN): A Critical Literature Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheat, J.; Currie, G. Herbal medicine for cancer patients: An evidence based review. Int. J. Alt. Med. 2008, 5, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas Abad, A.N.; Kayate Nouri, M.H.; Gharjanie, A.; Tavakoli, F. Effect of matricaria chamomilla hydroalcoholic extract on cisplatin-induced neuropathy in mice. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2011, 9, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kono, T.; Hata, T.; Morita, S.; Munemoto, Y.; Matsui, T.; Kojima, H.; Takemoto, H.; Fukunaga, M.; Nagata, N.; Shimada, M.; et al. Goshajinkigan oxaliplatin neurotoxicity evaluation (GONE): A phase 2, multicenter, randomized, doubleblind, placebocontrolled trial of goshajinkigan to prevent oxaliplatininduced neuropathy. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 72, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Hosokawa, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Yagi, N.; Kokura, S.; Naito, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; Kokuba, Y.; Otsuji, E.; Kuroboshi, H.; et al. Efficacy of goshajinkigan for oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer patients. J. Oncol. 2013, 2013, 139740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Yang, J. Immune enhancing effect of modified sijunzi decoction on patients with colorectal cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2011, 31, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, B.; Wang, Y. Functional _targets of Chinese herbal medicine. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2010, 8, 1190–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Xuan, Z.R. Progress in research on applying Sijunzi Decoction in treating digestive malignant tumor. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2007, 13, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ta, L.E.; Low, P.A.; Windebank, A.J. Mice with cisplatin and oxaliplatin-induced painful neuropathy develop distinct early responses to thermal stimuli. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donzelli, E.; Carfi, M.; Miloso, M.; Strada, A.; Galbiati, S.; Bayssas, M.; Griffon-Etienne, G.; Cavaletti, G.; Petruccioli, M.G.; Tredici, G. Neurotoxicity of platinum compounds: Comparison of the effects of cisplatin and oxaliplatin on the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. J. Neurooncol. 2004, 67, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cece, R.; Barajon, I.; Tredici, G. Cisplatin induces apoptosis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line. Anticancer Res. 1995, 15, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; Baillie, G.J.; Vetter, I. Neuronal cell lines as model dorsal root ganglion neurons: A transcriptomic comparison. Mol. Pain 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, R.N. Biomolecular _targets for platinum antitumor drugs. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amptoulach, S.; Tsavaris, N. Neurotoxicity caused by the treatment with platinum analogues. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 843019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.L.; Chao, C.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Lu, M.K.; Cheng, J.J.; Yang, Y.C.; Wang, V.C.; Chang, W.C.; Huang, N.K. Paraquat Induces Cell Death Through Impairing Mitochondrial Membrane Permeability. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2169–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altun, Z.S.; Gunes, D.; Aktas, S.; Erbayraktar, Z.; Olgun, N. Protective effects of acetyl-l-carnitine on cisplatin cytotoxicity and oxidative stress in neuroblastoma. Neurochem. Res. 2010, 35, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casares, C.; Ramirez-Camacho, R.; Trinidad, A.; Roldan, A.; Jorge, E.; Garcia-Berrocal, J.R. Reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induced by cisplatin: Review of physiopathological mechanisms in animal models. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 269, 2455–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, H.; Tanaka, T.; Takahama, U. Cisplatin generates superoxide anion by interaction with DNA in a cell-free system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 203, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandic, A.; Hansson, J.; Linder, S.; Shoshan, M.C. Cisplatin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and nucleus-independent apoptotic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9100–9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Terazawa, R.; Kojima, K.; Nakane, K.; Deguchi, T.; Ando, M.; Tsukamasa, Y.; Ito, M.; Nozawa, Y. Cisplatin induces production of reactive oxygen species via NADPH oxidase activation in human prostate cancer cells. Free Radic. Res. 2011, 45, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruidering, M.; Van de Water, B.; de Heer, E.; Mulder, G.J.; Nagelkerke, J.F. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in porcine proximal tubular cells: Mitochondrial dysfunction by inhibition of complexes I to IV of the respiratory chain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marullo, R.; Werner, E.; Degtyareva, N.; Moore, B.; Altavilla, G.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Doetsch, P.W. Cisplatin induces a mitochondrial-ROS response that contributes to cytotoxicity depending on mitochondrial redox status and bioenergetic functions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujitsuka, N.; Uezono, Y. Rikkunshito, a ghrelin potentiator, ameliorates anorexia-cachexia syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, H.; Sadakane, C.; Hattori, T.; Katsurada, T.; Ohkawara, T.; Nagai, K.; Asaka, M. Rikkunshito, an herbal medicine, suppresses cisplatin-induced anorexia in rats via 5-HT2 receptor antagonism. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 2004–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, Z.B.; Liu, Z.W.; Walllingford, N.; Erion, D.M.; Borok, E.; Friedman, J.M.; Tschop, M.H.; Shanabrough, M.; Cline, G.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. UCP2 mediates ghrelin’s action on NPY/AgRP neurons by lowering free radicals. Nature 2008, 454, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietri, M.; Schneider, B.; Mouillet-Richard, S.; Ermonval, M.; Mutel, V.; Launay, J.M.; Kellermann, O. Reactive oxygen species-dependent TNF-α converting enzyme activation through stimulation of 5-HT2B and alpha1D autoreceptors in neuronal cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raha, S.; Robinson, B.H. Mitochondria, oxygen free radicals, and apoptosis. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 106, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santin, G.; Piccolini, V.M.; Barni, S.; Veneroni, P.; Giansanti, V.; dal Bo, V.; Bernocchi, G.; Bottone, M.G. Mitochondrial fusion: A mechanism of cisplatin-induced resistance in neuroblastoma cells? Neurotoxicology 2013, 34, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, N.M.; Santos, N.A.; Curti, C.; Bianchi, M.L.; Santos, A.C. Cisplatin induces mitochondrial oxidative stress with resultant energetic metabolism impairment, membrane rigidification and apoptosis in rat liver. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podratz, J.L.; Knight, A.M.; Ta, L.E.; Staff, N.P.; Gass, J.M.; Genelin, K.; Schlattau, A.; Lathroum, L.; Windebank, A.J. Cisplatin induced mitochondrial DNA damage in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zsengeller, Z.K.; Ellezian, L.; Brown, D.; Horvath, B.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Parikh, S.M.; Karumanchi, S.A.; Stillman, I.E.; Pacher, P. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity involves mitochondrial injury with impaired tubular mitochondrial enzyme activity. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2012, 60, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, F.; Dong, Z. Mitochondrial dysregulation and protection in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Gonzalez, P.D.; Lopez-Hernandez, F.J.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M.; Morales, A.I. An integrative view of the pathophysiological events leading to cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2011, 41, 803–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabla, N.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: Mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portilla, D.; Dai, G.; McClure, T.; Bates, L.; Kurten, R.; Megyesi, J.; Price, P.; Li, S. Alterations of PPARalpha and its coactivator PGC-1 in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldelli, S.; Aquilano, K.; Ciriolo, M.R. PGC-1alpha buffers ROS-mediated removal of mitochondria during myogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloh, R.H. Mitochondrial dynamics and peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscientist 2008, 14, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajic, M. Mitochondrial dynamics in peripheral neuropathies. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, A.; Vital, C. Mitochondria and peripheral neuropathies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J. Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathic pain. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2014, 67, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilkens, P.H.; ven den Bent, M.J. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 1997, 2, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quasthoff, S.; Hartung, H.P. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avan, A.; Postma, T.J.; Ceresa, C.; Avan, A.; Cavaletti, G.; Giovannetti, E.; Peters, G.J. Platinum-induced neurotoxicity and preventive strategies: Past, present, and future. Oncologist 2015, 20, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Martinez, S.M.; Prieto-Garcia, L.; Prieto, M.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M.; Lopez-Hernandez, F.J. Subcellular _targets of cisplatin cytotoxicity: An integrated view. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunji, S.; Ueda, S.; Yoshida, M.; Kanai, M.; Terajima, H.; Takabayashi, A. Effects of rikkunshito, a kampo medicine, on quality of life after proximal gastrectomy. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 185, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, S.; Beckmann, K.; Franconi, G.; Meyer-Hamme, G.; Friedemann, T.; Greten, H.J.; Rostock, M.; Efferth, T. Can medical herbs stimulate regeneration or neuroprotection and treat neuropathic pain in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy? Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 423713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.L.; Liu, H.Q.; Wang, Q.; Huo, J.G.; Wang, X.N.; Cao, P. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity and complementary and alternative medicines: Progress and perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchart, D.; Hager, S.; Albrecht, S.; Dai, J.; Weidenhammer, W.; Teschke, R. Herbal Traditional Chinese Medicine and suspected liver injury: A prospective study. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenzel, C.; Teschke, R. Herbal Hepatotoxicity: Clinical Characteristics and Listing Compilation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Zhang, L.; Long, H.; Schwarzenboeck, A.; Schmidt-Taenzer, W.; Genthner, A.; Wolff, A.; Frenzel, C.; Schulze, J.; Eickhoff, A. Traditional Chinese Medicine and herbal hepatotoxicity: A tabular compilation of reported cases. Ann. Hepatol. 2015, 14, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, G.; del Peso, A.; Zurita, J.L. Neutral red uptake assay for the estimation of cell viability/cytotoxicity. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.L.; Lee, Y.C.; Yang, Y.C.; Kuo, T.Y.; Huang, N.K. Minocycline prevents paraquat-induced cell death through attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 209, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajjel Nayebi, A.; Sharifi, H.; Ramadzani, M.; Rezazadeh, H. Effect of acute and chronic administration of carbamazepine on Cisplatin-induced hyperalgesia in rats. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2012, 7, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.K.; Lin, Y.W.; Huang, C.L.; Messing, R.O.; Chern, Y. Activation of protein kinase A and atypical protein kinase C by A2A adenosine receptors antagonizes apoptosis due to serum deprivation in PC12 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 13838–13846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Chinese Name | Botanical Name | Common Name | Weight (g) | Part Used or Processed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bai Zhu | Atractylodes mocrocephala Kioidz. | Atractylodes Mocrocephala Rhizoma | 5.0 | Rhizome |
| Ban Xia | Pinellia ternate (Thunb.) Breit. | Pinelliae Rhizoma | 5.0 | Rhizome Gingered |
| Chen Pi | Citrus reticulate Blanco | Tangerine Peel | 2.5 | Peel |
| Da Zao | Ziziphus jujube Mill. | Jujubae Fructus | 2.5 | Fruit |
| Fu Ling | Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf | Poria | 5.0 | Sclerotium |
| Gan Cao | Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch | Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma | 2.5 | Root and Rhizome |
| Ren Shen | Panax jinseng C.A. Mey | Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma | 5.0 | Root and Rhizome |
| Sheng Jiang | Zingiber officinale Rosc. | Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens | 2.5 | Rhizome |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiou, C.-T.; Wang, K.-C.; Yang, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-L.; Yang, S.-H.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Huang, N.-K. Liu Jun Zi Tang—A Potential, Multi-Herbal Complementary Therapy for Chemotherapy-Induced Neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041258
Chiou C-T, Wang K-C, Yang Y-C, Huang C-L, Yang S-H, Kuo Y-H, Huang N-K. Liu Jun Zi Tang—A Potential, Multi-Herbal Complementary Therapy for Chemotherapy-Induced Neurotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041258
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiou, Chun-Tang, Kaw-Chen Wang, Ying-Chen Yang, Chuen-Lin Huang, Sien-Hung Yang, Yao-Haur Kuo, and Nai-Kuei Huang. 2018. "Liu Jun Zi Tang—A Potential, Multi-Herbal Complementary Therapy for Chemotherapy-Induced Neurotoxicity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041258
APA StyleChiou, C.-T., Wang, K.-C., Yang, Y.-C., Huang, C.-L., Yang, S.-H., Kuo, Y.-H., & Huang, N.-K. (2018). Liu Jun Zi Tang—A Potential, Multi-Herbal Complementary Therapy for Chemotherapy-Induced Neurotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041258