A Data-Driven Review of the Genetic Factors of Pregnancy Complications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pregnancy Complications Included in the Study
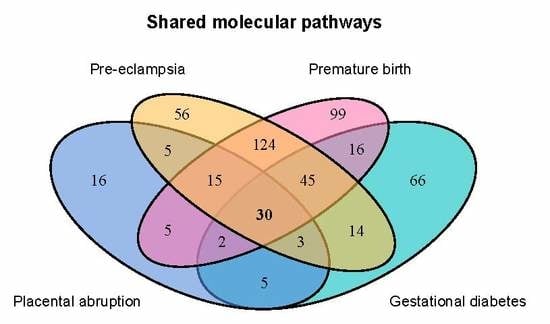
2.2. Genes Implicated in Pregnancy Complications

2.3. An Overview of the Genome-Wide Associations for Pregnancy-Related Traits
2.4. Genome-Wide Association Studies of Pregnancy-Related Traits in the UK Biobank Cohort
3. Discussion
3.1. Pregnancy Complications and Strategies for Their Genetic Analysis
3.2. The Genetic and Molecular Basis of Major Pregnancy Disorders
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APH | Antepartum haemorrhage |
| GDM | Gestational diabetes mellitus |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| PA | Placental abruption |
| PE | Preeclampsia |
| PTB | Preterm birth |
| UKB | UK Biobank |
References
- Zhao, Z.; Moley, K.H.; Gronowski, A.M. Diagnostic potential for miRNAs as biomarkers for pregnancy-specific diseases. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.; Ebbing, C.; Irgens, L.M. Predicting preeclampsia from a history of preterm birth. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monte, S. Biochemical markers for prediction of preclampsia: Review of the literature. J. Prenat. Med. 2011, 5, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winger, E.; Reed, J. Preterm birth, preeclampsia and miscarriage can be predicted from peripheral blood throughout the first trimester with high reliability. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 108, e391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Cui, L.; Tam, W.H.; Ma, R.C.; Wang, C.C. Genetic variants associated with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and subgroup analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth-Carson, S.J.; Lim, R.; Mitton, A.; Whitehead, C.; Rice, G.E.; Permezel, M.; Lappas, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are altered in pathologies of the human placenta: Gestational diabetes mellitus, intrauterine growth restriction and preeclampsia. Placenta 2010, 31, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissgerber, T.L.; Mudd, L.M. Preeclampsia and diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2015, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zdoukopoulos, N.; Zintzaras, E. Genetic risk factors for placental abruption: A HuGE review and meta-analysis. Epidemiol. (Camb. Mass.) 2008, 19, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, R.L.; Culhane, J.F.; Iams, J.D.; Romero, R. Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2008, 371, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bao, W.; Rong, Y.; Yang, H.; Bowers, K.; Yeung, E.; Kiely, M. Genetic variants and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2013, 19, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Srivastava, A.; Bacelis, J.; Juodakis, J.; Jacobsson, B.; Muglia, L.J. Genetic studies of gestational duration and preterm birth. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 52, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakoordeen, S.; Moodley, J.; Naicker, T. Candidate Gene, Genome-Wide Association and Bioinformatic Studies in Pre-eclampsia: A Review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Su, R.; Ao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, H. Genetic variants and clinical relevance associated with gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese women: A case-control study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Chagoya, A.; Vázquez-Cárdenas, P.; Moreno-Macías, H.; Tapia-Maruri, L.; Rodríguez-Guillén, R.; López-Vite, E.; García-Escalante, G.; Escobedo-Aguirre, F.; Parra-Covarrubias, A.; Cordero-Brieño, R.; et al. Genetic determinants for gestational diabetes mellitus and related metabolic traits in Mexican women. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearson, T.A.; Manolio, T.A. How to Interpret a Genome-wide Association Study. J. Am. Med Assoc. 2008, 299, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Clyne, M.; Khoury, M.J.; Gwinn, M. Phenopedia and genopedia: Disease-centered and gene-centered views of the evolving knowledge of human genetic associations. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buniello, A.; Macarthur, J.A.; Cerezo, M.; Harris, L.W.; Hayhurst, J.; Malangone, C.; McMahon, A.; Morales, J.; Mountjoy, E.; Sollis, E.; et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog of published genome-wide association studies, _targeted arrays and summary statistics 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1005–D1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naba, A.; Clauser, K.R.; Hoersch, S.; Liu, H.; Carr, S.A.; Hynes, R.O. The matrisome: In silico definition and in vivo characterization by proteomics of normal and tumor extracellular matrices. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2012, 11, M111.014647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.H.; O’dushlaine, C.; Thomas, B.; Purcell, S.M. INRICH: Interval-based enrichment analysis for genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1797–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, K.; Stringer, S.; Frei, O.; Umićević Mirkov, M.; de Leeuw, C.; Polderman, T.J.; van der Sluis, S.; Andreassen, O.A.; Neale, B.M.; Posthuma, D. A global overview of pleiotropy and genetic architecture in complex traits. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikov, A.E.; Skitchenko, R.K.; Predeus, A.V.; Barbitoff, Y.A. Phenome-wide functional dissection of pleiotropic effects highlights key molecular pathways for human complex traits. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reich, D.E.; Goldstein, D.B. Detecting association in a case-control study while correcting for population stratification. Genet. Epidemiol. 2001, 20, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadl, S.A.; Linnau, K.F.; Dighe, M.K. Placental abruption and hemorrhage—Review of imaging appearance. Emerg. Radiol. 2019, 26, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argraves, W.S.; Greene, L.M.; Cooley, M.A.; Gallagher, W.M. Fibulins: Physiological and disease perspectives. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, S.H.; Girard, S.L.; Hopfner, F.; Merner, N.D.; Bourassa, C.V.; Lorenz, D.; Clark, L.N.; Tittmann, L.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.I.; Klebe, S.; et al. Genome-wide association study in essential tremor identifies three new loci. Brain 2016, 139, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiensuu, H.; Haapalainen, A.M.; Karjalainen, M.K.; Pasanen, A.; Huusko, J.M.; Marttila, R.; Ojaniemi, M.; Muglia, L.J.; Hallman, M.; Rämet, M. Risk of spontaneous preterm birth and fetal growth associates with fetal SLIT2. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, K.R.; Sevilla, L.M.; Nishi, K.; DiColandrea, T.; Watt, F.M. Kazrin, a novel periplakin-interacting protein associated with desmosomes and the keratinocyte plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramasamy, S.; Saez, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ding, D.; Ahmed, A.M.; Chen, X.; Pucci, F.; Yamin, R.; Wang, J.; Pittet, M.J.; et al. Tle1 tumor suppressor negatively regulates inflammation in vivo and modulates NF-κB inflammatory pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1871–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tilli, T.M.; da Silva Castro, C.; Tuszynski, J.A.; Carels, N. A strategy to identify housekeeping genes suitable for analysis in breast cancer diseases. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolae, D.L. Association Tests for Rare Variants. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2016, 17, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.S.Q.; Tayade, C.; Smith, G.N. Maternal Circulating microRNAs and Pre-Eclampsia: Challenges for Diagnostic Potential. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 21, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lycoudi, A.; Mavreli, D.; Mavrou, A.; Papantoniou, N.; Kolialexi, A. miRNAs in pregnancy-related complications. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashukova, E.S.; Glotov, A.S.; Fedotov, P.V.; Efimova, O.A.; Pakin, V.S.; Mozgovaya, E.V.; Pendina, A.A.; Tikhonov, A.V.; Koltsova, A.S.; Baranov, V.S. Placental microRNA expression in pregnancies complicated by superimposed pre-eclampsia on chronic hypertension. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laganà, A.S.; Vitale, S.G.; Sapia, F.; Valenti, G.; Corrado, F.; Padula, F.; Rapisarda, A.M.C.; D’Anna, R. miRNA expression for early diagnosis of preeclampsia onset: Hope or hype? J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Lu, C.; Ji, X.; Miao, Z.; Long, W.; Ding, H.; Lv, M. Roles of microRNAs in preeclampsia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, C.; Desgagné, V.; Guérin, R.; Bouchard, L. MicroRNAs in Pregnancy and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Emerging Role in Maternal Metabolic Regulation. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Higashijima, A.; Murakami, Y.; Fuchi, N.; Tsukamoto, O.; Abe, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Miura, S.; Masuzaki, H. Circulating Levels of Pregnancy-Associated, Placenta-Specific microRNAs in Pregnant Women With Placental Abruption. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 24, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnowski, M.; Tkacz, M.; Dziedziejko, V.; Safranow, K.; Pawlik, A. COX2 and NOS3 gene polymorphisms in women with gestational diabetes. J. Gene Med. 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, L.V.C.; Javorski, N.; André Cavalcanti Brandão, L.; de Carvalho Lima, M.; Crovella, S.; Eickmann, S.H. Influence of MBL2 and NOS3 polymorphisms on spontaneous preterm birth in North East Brazil: genetics and preterm birth. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 33, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atay, A.E.; Akbas, H.; Tumer, C.; Sakar, M.N.; Esen, B.; Incebiyik, A.; Simsek, S.; Sit, D. The association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene G894T polymorphism and serum nitric oxide concentration with microalbuminuria in patients with gestational diabetes. Clin. Nephrol. 2014, 81, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Li, J.; Wu, G.; Miao, Z.; Lu, L.; Ren, G.; Wang, X. Upregulation of microRNA-335 and microRNA-584 contributes to the pathogenesis of severe preeclampsia through downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5383–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kadam, L.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Drewlo, S. The balancing act—PPAR-γ’s roles at the maternal-fetal interface. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2015, 61, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constância, M.; Hemberger, M.; Hughes, J.; Dean, W.; Ferguson-Smith, A.; Fundele, R.; Stewart, F.; Kelsey, G.; Fowden, A.; Sibley, C.; et al. Placental-specific IGF-II is a major modulator of placental and fetal growth. Nature 2002, 417, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Song, W. Role and mechanism of insulin-like growth factor 2 on the proliferation of human trophoblasts in vitro. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2016, 42, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhong, M.; Luo, Y.; Xiao, L.; Chen, X. The expression of imprinted genes IGF2 and PHLDA2 in mid-pregnancy have predictive values for the development of pre-eclampsia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 8934–8941. [Google Scholar]
- Vadillo-Ortega, F.; Estrada-Gutiérrez, G. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in preterm labour. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2005, 112 (Suppl. 1), 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, S.E.Y.; Flores-Pliego, A.; Espejel-Nuñez, A.; Medina-Bastidas, D.; Vadillo-Ortega, F.; Zaga-Clavellina, V.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G. New Insights into the Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Preeclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, R.; Liu, X.M.; Xiang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Guo, F.; Liu, Z.W.; Fan, J.X. Altered Matrix Metalloproteinases Expression in Placenta from Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, H.Y.; Dendrou, C.A. Pregnancy Immunogenetics and Genomics: Implications for Pregnancy-Related Complications and Autoimmune Disease. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2019, 20, 73–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulchenko, Y.S.; Ripke, S.; Isaacs, A.; van Duijn, C.M. GenABEL: An R library for genome-wide association analysis. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1294–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turner, S.D. qqman: An R package for visualizing GWAS results using Q-Q and manhattan plots. bioRxiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Richardson, T.G.; Millard, L.A.; Hemani, G.; Elsworth, B.L.; Raistrick, C.A.; Vilhjalmsson, B.; Neale, B.M.; Haycock, P.C.; Smith, G.D.; et al. PhenoSpD: An integrated toolkit for phenotypic correlation estimation and multiple testing correction using GWAS summary statistics. GigaScience 2018, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinform. (Oxf. Engl.) 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Lead SNP Location | Lead SNP ID | Lead SNP Gene | Genes in Locus * | Trait ** | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2:113052585 | rs371385421 | ZC3H6 | AC115115.2, AC115115.3, AC115115.4, FBLN7, RGPD8, TTL, ZC3H6, ZC3H8, snoU13 | i9_HYP | |
| 4:5427052 | rs59654075 | STK32B | RN7SKP275, STK32B, Y_RNA | O69 | |
| 7:152604776 | rs10241971 | ACTR3B | ACTR3B | O46 | |
| X:121644980 | rs151100704 | n.a. | n.a. | O26 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbitoff, Y.A.; Tsarev, A.A.; Vashukova, E.S.; Maksiutenko, E.M.; Kovalenko, L.V.; Belotserkovtseva, L.D.; Glotov, A.S. A Data-Driven Review of the Genetic Factors of Pregnancy Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093384
Barbitoff YA, Tsarev AA, Vashukova ES, Maksiutenko EM, Kovalenko LV, Belotserkovtseva LD, Glotov AS. A Data-Driven Review of the Genetic Factors of Pregnancy Complications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093384
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbitoff, Yury A., Alexander A. Tsarev, Elena S. Vashukova, Evgeniia M. Maksiutenko, Liudmila V. Kovalenko, Larisa D. Belotserkovtseva, and Andrey S. Glotov. 2020. "A Data-Driven Review of the Genetic Factors of Pregnancy Complications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093384
APA StyleBarbitoff, Y. A., Tsarev, A. A., Vashukova, E. S., Maksiutenko, E. M., Kovalenko, L. V., Belotserkovtseva, L. D., & Glotov, A. S. (2020). A Data-Driven Review of the Genetic Factors of Pregnancy Complications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093384