In Silico Screening of Novel α1-GABAA Receptor PAMs towards Schizophrenia Based on Combined Modeling Studies of Imidazo [1,2-a]-Pyridines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
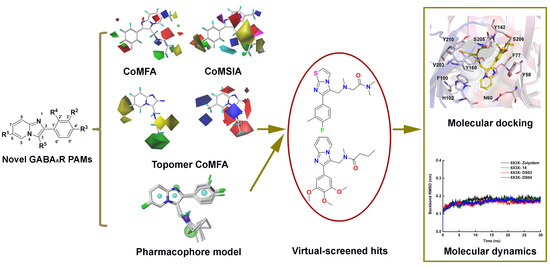
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Statistical Analysis of the 3D-QSAR Models
2.2. 3D-QSAR Contour Map Analysis
2.3. Molecular Docking
2.4. Pharmacophore Model
2.5. Virtual Screening Analysis
2.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Molecular Construction and Structure Optimization
3.2. 3D-QSAR Model Generation and Alignment
3.3. Analysis and Validation of the QSAR Model
3.4. Molecular Docking
3.5. Pharmacophore Model
3.6. Virtual Screening
3.7. Molecular Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Legge, S.E.; Santoro, M.L.; Periyasamy, S.; Okewole, A.; Arsalan, A.; Kowalec, K. Genetic architecture of schizophrenia: A review of major advancements. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percelay, S.; Billard, J.-M.; Freret, T.; Andrieux, A.; Boulouard, M.; Bouet, V. Functional Dysregulations in CA1 Hippocampal Networks of a 3-Hit Mouse Model of Schizophrenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerman, S.; Schulte, P.; Haan, L.D. Treatment for negative symptoms in schizophrenia: A comprehensive review. Drugs. 2017, 77, 1423–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, P.; Wierońska, J.M. Regulation of Glutamatergic Activity via Bidirectional Activation of Two Select Receptors as a Novel Approach in Antipsychotic Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucht, S.; Davis, J.M. Schizophrenia, primary negative symptoms, and soft outcomes in psychiatry. Lancet 2017, 389, 1077–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, C.Z.; Harvey, P.D.; Patterson, T.L.; Twamley, E.W. Neurocognitive insight and objective cognitive functioning in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 171, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hjorthøj, C.; Stürup, A.E.; McGrath, J.J.; Nordentoft, M. Years of potential life lost and life expectancy in schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiat. 2017, 4, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ved, H.S.; Doshi, G.M. A Review on Emerging Drug _targets in Treatment of Schizophrenia. Curr. Drug _targets 2020, 21, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Che, T.; Levit, A.; Shoichet, B.K.; Wacker, D.; Roth, B.L. Structure of the D2 dopamine receptor bound to the atypical antipsychotic drug risperidone. Nature 2018, 555, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Xu, P.; Mao, C.; Wang, L.; Krumm, B.; Zhou, X.E.; Huang, S.; Liu, H.; Cheng, X.; Huang, X.P.; et al. Structural insights into the human D1 and D2 dopamine receptor signaling complexes. Cell 2021, 184, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preda, A. Review: Antipsychotic drugs improve symptoms, with different levels of side effects, in schizophrenia. ACP J. Club 2013, 159, JC7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servonnet, A.; Uchida, H.; Samaha, A.N. Continuous versus extended antipsychotic dosing in schizophrenia: Less is more. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 401, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.S.; Adams, D.H.; Kinon, B.J. Discontinuation of treatment of schizophrenic patients is driven by poor symptom response: A pooled post-hoc analysis of four atypical antipsychotic drugs. BMC. Med. 2005, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenschein, S.F.; Grace, A. Emerging therapeutic _targets for schizophrenia: A framework for novel treatment strategies for psychosis. Expert Opin. Ther. Tar. 2020, 25, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E. An hypothesis suggesting that there is a defect in the GABA system in schizophrenia. Neurosci. Res. Program. Bull. 1972, 10, 468–482. [Google Scholar]
- Spiering, M.J. The discovery of GABA in the brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 19159–19160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, P.S.; Aricescu, A.R. Crystal structure of a human GABAA receptor. Nature 2014, 512, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ju, X.; Ozoe, Y. Potential of Competitive Antagonists of Insect Ionotropic γ-Aminobutyric Acid Receptors as Insecticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4760–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.W. GABAA receptor: Positive and negative allosteric modulators. Neuropharmacology 2018, 136, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, B.P.; Mann, J.J. The GABAergic system in schizophrenia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002, 5, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoftman, G.D.; Volk, D.W.; Bazmi, H.H.; Li, S.; Sampson, A.R.; Lewis, D.A. Altered Cortical Expression of GABA-Related Genes in Schizophrenia: Illness Progression vs. Developmental Disturbance. Schizophr. Bulletin. 2015, 41, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiones, G.M.; Mayeli, A.; Yushmanov, V.E.; Hetherington, H.P.; Ferrarelli, F. Reduced GABA/glutamate in the thalamus of individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierzejewski, P.; Kolaczkowski, M.; Marcinkowska, M.; Wesolowska, A.; Samochowiec, J.; Pawlowski, M.; Bienkowski, P. Antipsychotic-like effects of zolpidem in Wistar rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 773, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierzejewski, P.; Kolaczkowski, M.; Marcinkowska, M.; Wesolowska, A.; Samochowiec, J.; Pawlowski, M.; Bienkowski, P. Pharmacological characteristics of zolpidem-induced catalepsy in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 556, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, T.; Inada, K.; Matsui, Y.K.; Iwata, N.K. Z-drug for schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 256, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska, M.; Kolaczkowski, M.; Kamiński, K.; Bucki, A.; Pawłowski, M.; Siwek, A.; Karcz, T.; Starowicz, G.; Słoczyńska, K.; Pękala, E.; et al. 3-Aminomethyl Derivatives of 2-Phenylimidazo[1,2-a]-pyridine as Positive Allosteric Modulators of GABAA Receptor with Potential Antipsychotic Activity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska, M.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Kamiński, K.; Bucki, A.; Pawłowski, M.; Siwek, A.; Karcz, T.; Mordyl, B.; Starowicz, G.; Kubowicz, P.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of fluorinated imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives with potential antipsychotic activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnick, P. Anxioselective anxiolytics: On a quest for the Holy Grail. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trabanco, A.A.; Tresadern, G.; Macdonald, G.J.; Vega, J.A.; Lucas, A.I.D.; Matesanz, E.; García, A.; Linares, M.L.; Diego, A.A.A.D.; Alonso, J.M.; et al. Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines: Orally active positive allosteric modulators of the metabotropic glutamate 2 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 2688–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, T.A.; Rassokhina, I.V.; Kondrakhin, E.A.; Fedosov, M.A.; Bukanova, J.V.; Rossokhin, A.V.; Sharonova, I.N.; Kovalev, G.I.; Zavarzin, I.V.; Volkova, Y.A. Development of 1,3-Thiazole Analogues of Imidazopyridines as Potent Positive Allosteric Modulators of GABAA Receptors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 94, 103334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noormandi, A.; Shahrokhi, M.; Khalili, H. Potential benefits of zolpidem in disorders of consciousness. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Gharpure, A.; Teng, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Hibbs, R.E. Shared structural mechanisms of general anaesthetics and benzodiazepines. Nature 2020, 585, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, D.V.; Spasov, A.A.; Yakovlev, D.S.; Vassiliev, P.M.; Morkovnik, A.S. Searching for new anxiolytic agents among derivatives of 11-dialkylaminoethyl-2, 3, 4, 5-tetrahydrodiazepino [1,2-a] benzimidazole. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 161, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.M.; Morlock, E.V.; Satyshur, K.A.; Czajkowski, C. Structural requirements for eszopiclone and zolpidem binding to the γ-Aminobutyric acid type-A (GABAA) receptor are different. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7243–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jankowska, A.; Sataa, G.; Partyka, A.; Wesolowska, A.; Bojarski, A.J.; Pawlowski, M.; Chłoń-Rzepa, G. Discovery and Development of Non-Dopaminergic Agents for the Treatment of Schizophrenia: Overview of the Preclinical and Early Clinical Studies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 4885–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Y.; Luo, X.; Ju, X.; Liu, G. In silico study of 3-hydroxypyrimidine-2,4-diones as inhibitors of HIV RT-associated RNase H using molecular docking, molecular dynamics, 3D-QSAR, and pharmacophore models. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 17004–17017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.; Blundell, T.L.; Ascher, D.B. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and toxicity properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, R.; Lynn, A. g_mmpbsa—A GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Gu, S.; Ju, X.; Liu, G. In silico studies of diarylpyridine derivatives as novel HIV-1 NNRTIs using docking-based 3D-QSAR, molecular dynamics, and pharmacophore modeling approaches. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 40529–40543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Wan, Y.; Ju, X.; Gu, S. Application of 3D-QSAR, pharmacophore, and molecular docking in the molecular design of diarylpyrimidine derivatives as HIV-1 nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halim, S.A.; Haqa, Z.U. Structure based 3D-QSAR studies of Interleukin-2 inhibitors: Comparing the quality and predictivity of 3D-QSAR models obtained from different alignment methods and charge calculations. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2015, 238, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdizadeha, R.; Heidarianb, E.; Hadizadehc, F.; Abdizadeh, T. Investigation of pyrimidine analogues as xanthine oxidase inhibitors to treat of hyperuricemia and gout through combined QSAR techniques, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 113, 72–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, S.; Gan, Y.; Han, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, J. Combined HQSAR, topomer CoMFA, homology modeling and docking studies on triazole derivatives as SGLT2 inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zięba, A.; Laitinen, T.; Patel, J.Z.; Poso, A.; Kaczor, A.A. Docking-Based 3D-QSAR Studies for 1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-one Derivatives as FAAH Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, N.J.; Abrams, C.A.; Wolohan, P.; Abrahamian, E.; Willett, P.; Clark, R.D. GALAHAD: 1. Pharmacophore identification by hypermolecular alignment of ligands in 3D. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2006, 20, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Pei, J.; Liu, G. Exploring the interaction mechanism of desmethyl-broflanilide in insect GABA receptors and screening potential antagonists by in silico simulations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14768–14780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, F.; Luo, X.; Ju, X.; Liu, G. Computationally exploring novel xanthine oxidase inhibitors using docking-based 3D-QSAR, molecular dynamics, and virtual screening. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 19276–19287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhshani, H.; Dehghanian, E.; Rahati, A. Enhanced GROMACS: Toward a better numerical simulation framework. J. Mol. Model. 2019, 25, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| No. | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | Ki(nM) | Actual pKi | CoMFA | CoMSIA | Topomer CoMFA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pred. pKi | Residual | Pred. pKi | Residual | Pred. pKi | Residual | ||||||||
| 1 | CH3 | H | F | H |  | 60.0 | 7.222 | 7.240 | 0.018 | 7.269 | 0.047 | 7.190 | −0.032 |
| 2 a | F | H | CH3 | H |  | 25.0 | 7.602 | 7.494 | −0.108 | 7.529 | −0.073 | 7.490 | −0.112 |
| 3 | F | H | H | H |  | 130.0 | 6.886 | 6.941 | 0.055 | 6.937 | 0.051 | 7.020 | 0.134 |
| 4 | F | F | H | H |  | 140.0 | 6.854 | 6.854 | 0 | 6.935 | 0.081 | 6.920 | 0.066 |
| 5 a | F | H | F | F |  | 180.0 | 6.745 | 6.843 | 0.098 | 6.916 | 0.171 | 6.920 | 0.175 |
| 6 | F | H | CF3 | H |  | 68.0 | 7.167 | 7.154 | −0.013 | 7.162 | −0.005 | 7.170 | 0.003 |
| 7 | CF3 | H | F | H |  | 510.0 | 6.292 | 6.324 | 0.032 | 6.327 | 0.035 | 6.330 | 0.038 |
| 8 | CF3 | H | F | F |  | 830.0 | 6.081 | 6.080 | −0.001 | 6.080 | −0.001 | 6.090 | 0.009 |
| 9 | CF3 | H | CF3 | H |  | 487.0 | 6.312 | 6.324 | 0.012 | 6.316 | 0.004 | 6.320 | 0.008 |
| 10 | F | H | F | H |  | 56.0 | 7.252 | 7.150 | −0.102 | 7.165 | −0.087 | 7.180 | −0.072 |
| 11 | F | F | F | H |  | 58.0 | 7.237 | 7.278 | 0.041 | 7.158 | −0.079 | 7.220 | −0.017 |
| 12 | CF3 | F | H | H |  | 730.0 | 6.137 | 6.094 | −0.043 | 6.100 | −0.037 | 6.080 | −0.057 |
| 13 | CH3 | H | F | H |  | 78.4 | 7.106 | 7.159 | 0.053 | 7.172 | 0.066 | 7.230 | 0.124 |
| 14 # | CH3 | H | F | H |  | 27.2 | 7.565 | 7.447 | −0.118 | 7.415 | −0.150 | 7.460 | −0.105 |
| 15 a | CH3 | H | F | H |  | 364.0 | 6.439 | 6.307 | −0.132 | 6.539 | 0.100 | 6.420 | −0.019 |
| 16 | CH3 | H | F | H |  | 116.0 | 6.936 | 6.982 | 0.046 | 6.981 | 0.045 | 7.030 | 0.094 |
| 17 # | F | H | CH3 | H |  | 44.0 | 7.357 | 7.405 | 0.048 | 7.409 | 0.052 | 7.380 | 0.023 |
| 18 # | F | H | CH3 | H |  | 36.5 | 7.438 | 7.389 | −0.049 | 7.547 | 0.109 | 7.580 | 0.142 |
| 19 a | F | H | CH3 | H |  | 87.5 | 7.058 | 7.253 | 0.195 | 7.268 | 0.210 | 7.310 | 0.252 |
| 20 | F | H | CH3 | H |  | 55.1 | 7.259 | 7.214 | −0.045 | 7.216 | −0.043 | 7.220 | −0.039 |
| 21 # | F | H | F | H |  | 43.0 | 7.367 | 7.306 | −0.061 | 7.342 | −0.025 | 7.320 | −0.047 |
| 22 # | F | H | F | H |  | 37.0 | 7.432 | 7.546 | 0.114 | 7.573 | 0.141 | 7.480 | 0.048 |
| 23 a | F | H | F | H |  | 308.7 | 6.510 | 6.651 | 0.141 | 6.419 | −0.091 | 6.540 | 0.030 |
| 24 a, # | F | H | F | H |  | 20.9 | 7.680 | 7.663 | −0.017 | 7.657 | −0.023 | 7.740 | 0.060 |
| 25 | F | F | F | H |  | 39.0 | 7.409 | 7.372 | −0.037 | 7.369 | −0.040 | 7.410 | 0.001 |
| 26 # | F | F | F | H |  | 24.0 | 7.620 | 7.626 | 0.006 | 7.628 | 0.008 | 7.560 | −0.060 |
| 27 | F | F | F | H |  | 72.0 | 7.143 | 7.177 | 0.034 | 7.209 | 0.066 | 7.170 | 0.027 |
| 28 a,# | F | F | F | H |  | 22.8 | 7.642 | 7.568 | −0.074 | 7.594 | −0.048 | 7.390 | −0.252 |
| 29 | F | H | CF3 | H |  | 62.7 | 7.203 | 7.199 | −0.004 | 7.150 | −0.053 | 7.160 | −0.043 |
| 30 # | F | H | CF3 | H |  | 48.0 | 7.319 | 7.347 | 0.028 | 7.399 | 0.08 | 7.260 | −0.059 |
| 31 | F | H | CF3 | H |  | 86.3 | 7.064 | 7.029 | −0.035 | 6.999 | −0.065 | 6.970 | −0.094 |
| 32 a | F | H | CF3 | H |  | 67.0 | 7.174 | 7.191 | 0.017 | 7.195 | 0.021 | 7.070 | −0.104 |
| Zolpidem # | CH3 | H | CH3 | H |  | 44.0 | 7.357 | 7.359 | 0.002 | 7.349 | −0.008 | 7.260 | −0.097 |
| Model a | q2 | ONC | SEE | R2 | F | rpre2 | Field Contribution (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | E | H | D | A | ||||||||
| Topomer CoMFA | S+E | 0.857 | 7 | 0.092 | 0.978 | 74.312 | 0.879 | |||||
| CoMFA | S+E | 0.808 | 15 | 0.084 | 0.987 | 44.347 | 0.935 | 0.373 | 0.627 | |||
| CoMSIA | S+E+H+D+A | 0.862 | 13 | 0.093 | 0.980 | 40.610 | 0.927 | 0.078 | 0.180 | 0.168 | 0.407 | 0.167 |
| S+E+H+D | 0.839 | 13 | 0.106 | 0.980 | 41.865 | 0.852 | 0.086 | 0.215 | 0.184 | 0.516 | ||
| S+E+H+A | 0.823 | 10 | 0.088 | 0.967 | 40.690 | 0.876 | 0.157 | 0.339 | 0.340 | 0.164 | ||
| E+H+D+A | 0.870 | 12 | 0.091 | 0.978 | 46.769 | 0.926 | 0.188 | 0.224 | 0.411 | 0.176 | ||
| S+E+H | 0.815 | 10 | 0.109 | 0.965 | 38.265 | 0.839 | 0.186 | 0.410 | 0.404 | |||
| E+H+A | 0.839 | 12 | 0.099 | 0.975 | 39.391 | 0.892 | 0.326 | 0.296 | 0.378 | |||
| S+E+D | 0.864 | 13 | 0.092 | 0.980 | 41.944 | 0.929 | 0.202 | 0.242 | 0.556 | |||
| E+H+D | 0.867 | 11 | 0.097 | 0.974 | 44.741 | 0.921 | 0.250 | 0.325 | 0.425 | |||
| S+H | 0.817 | 10 | 0.105 | 0.967 | 41.551 | 0.823 | 0.205 | 0.705 | ||||
| E+H | 0.820 | 11 | 0.111 | 0.966 | 33.460 | 0.845 | 0.448 | 0.552 | ||||
| H+A | 0.805 | 12 | 0.094 | 0.973 | 44.556 | 0.814 | 0.492 | 0.508 | ||||
| Validation Parameters | RMSE | r2 | r02 | r0′2 | (r2 − r0′2)/r2 | k | k′ | rm2 | rm′2 | ∆rm2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topomer CoMFA | 0.156 | 0.882 | 0.881 | 0.856 | 0.0296 | 0.9974 | 1.0022 | 0.856 | 0.739 | 0.116 | 0.798 |
| CoMFA | 0.114 | 0.936 | 0.935 | 0.927 | 0.0099 | 0.9973 | 1.0019 | 0.912 | 0.846 | 0.065 | 0.878 |
| CoMSIA(S+E+H+D+A) | 0.121 | 0.944 | 0.943 | 0.938 | 0.0051 | 0.9863 | 1.0132 | 0.942 | 0.871 | 0.026 | 0.884 |
| Name | SPECIFICITY | N_HITS | FEATS | PARETO | ENERGY | STERICS | HBOND | MOL_QRY |
| MODEL_1 | 5.015 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 25.5 | 421.9 | 35.8 | 33.85 |
| MODEL_2 | 5.028 | 10 | 6 | 0 | 111.93 | 445.9 | 35.9 | 33.1 |
| MODEL_3 | 5.022 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 69.9 | 469.5 | 33.9 | 31.02 |
| MODEL_4 | 5.019 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 14,028.0703 | 450.9 | 36.8 | 33.57 |
| MODEL_5 | 5.020 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 50.97 | 426.7 | 32.2 | 30.02 |
| MODEL_6 | 5.019 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 13,991.6396 | 411.9 | 36.3 | 34.27 |
| MODEL_7 | 5.024 | 7 | 6 | 0 | 21.15 | 363 | 34.7 | 27.14 |
| MODEL_8 | 5.025 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 13.94 | 366.6 | 31.1 | 28.9 |
| MODEL_9 | 4.255 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 20.15 | 396.4 | 30.4 | 19.84 |
| MODEL_10 | 5.023 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 25.47 | 416.8 | 25.8 | 21.04 |
| MODEL_11 | 5.018 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 34.75 | 353.9 | 36.5 | 13.55 |
| MODEL_12 | 5.026 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 10.92 | 328.5 | 29.8 | 15.6 |
| MODEL_13 | 4.982 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 39.63 | 413.9 | 31 | 26.93 |
| MODEL_14 | 4.398 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 46.68 | 386.8 | 31.2 | 26.14 |
| MODEL_15 | 5.021 | 9 | 6 | 1 | 55.91 | 383.1 | 32.9 | 25.61 |
| MODEL_16 | 4.394 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 36.53 | 380.1 | 29.5 | 27.07 |
| MODEL_17 | 5.017 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 39.23 | 374.4 | 30.4 | 24.03 |
| MODEL_18 | 5.008 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 55.91 | 393.9 | 32.3 | 17.77 |
| MODEL_19 | 5.025 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 14.13 | 339.4 | 27.9 | 25.46 |
| MODEL_20 | 5.012 | 9 | 6 | 1 | 65.33 | 382.1 | 33.2 | 16.91 |
| Parameter | Compound | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS01 | DS02 | DS03 | DS04 | Zolpidem | 14 | ||
| Molecular properties | MW (g/mol) | 364.42 | 390.94 | 376.91 | 377.47 | 307.39 | 311.36 |
| logP | 2.861 | 3.853 | 3.540 | 3.785 | 3.248 | 3.475 | |
| Fraction Csp3 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.22 | |
| rotatable bonds | 5 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 4 | |
| TPSA (Å2) | 69.09 | 69.09 | 69.09 | 69.09 | 37.61 | 46.40 | |
| Absorption | Water solubility | −3.076 | −3.091 | −3.094 | −3.357 | −3.586 | −3.405 |
| Caco2 permeability (log Papp in 10−6 cm/s) | 1.217 | 1.008 | 1.003 | 1.445 | 0.977 | 1.321 | |
| Intestinal absorption (human) (% Absorbed) | 94.438 | 95.073 | 94.320 | 96.052 | 95.252 | 94.089 | |
| Skin permeability (log Kp) | −2.725 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | −2.735 | |
| GI absorption | High | High | High | High | High | High | |
| P-gp substrate | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| Distribution | BBB permeant (log BB) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| CNS permeant (log PS) | −1.054 | −1.035 | −1.307 | −1.295 | −1.125 | −1.265 | |
| Metabolism | CYP2D6 substrate | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| CYP3A4 substrate | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| Excretion | Total clearance (log mL/min/kg) | 0.762 | 0.842 | 0.848 | 0.894 | 0.722 | 0.886 |
| Renal OCT2 substrate | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | |
| Toxicity | hERG I inhibitor | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Skin sensitization | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| Drug-likeness | Lipinski violations | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Synthetic accessibility | 3.24 | 3.46 | 3.35 | 3.27 | 2.93 | 2.72 | |
| Compound | Structure | Docking Score | Predicted pKi |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 |  | 6.910 | 7.460 |
| DS01 |  | 9.035 | 7.643 |
| DS02 |  | 9.036 | 7.645 |
| DS03 |  | 9.776 | 7.689 |
| DS04 |  | 9.262 | 7.678 |
| Complex | ΔEvdW (kJ/mol) | ΔEele (kJ/mol) | ΔGPB (kJ/mol) | ΔGSA (kJ/mol) | ΔGbinding (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6X3X-zolpidem | −166.722 ± 2.866 | −12.403 ± 5.571 | 102.850 ± 2.345 | −18.907 ± 0.636 | −95.181 ± −6.696 |
| 6X3X-14 | −185.718 ± 5.400 | −33.782 ± 4.775 | 117.687 ± 6.308 | −18.241 ± 0.582 | −120.055 ± 6.238 |
| 6X3X-DS03 | −187.731 ± 10.951 | −14.533 ± 4.779 | 94.581 ± 4.630 | −18.692 ± 0.655 | −126.376 ± 11.440 |
| 6X3X-DS04 | −183.268 ± 8.895 | −45.446 ± 6.257 | 116.936 ± 7.296 | −19.729 ± 0.823 | −131.507 ± 10.246 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Wang, C.; Zhai, N.; Luo, X.; Liu, G.; Ju, X. In Silico Screening of Novel α1-GABAA Receptor PAMs towards Schizophrenia Based on Combined Modeling Studies of Imidazo [1,2-a]-Pyridines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179645
Zheng X, Wang C, Zhai N, Luo X, Liu G, Ju X. In Silico Screening of Novel α1-GABAA Receptor PAMs towards Schizophrenia Based on Combined Modeling Studies of Imidazo [1,2-a]-Pyridines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(17):9645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179645
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xiaojiao, Chenchen Wang, Na Zhai, Xiaogang Luo, Genyan Liu, and Xiulian Ju. 2021. "In Silico Screening of Novel α1-GABAA Receptor PAMs towards Schizophrenia Based on Combined Modeling Studies of Imidazo [1,2-a]-Pyridines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 17: 9645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179645
APA StyleZheng, X., Wang, C., Zhai, N., Luo, X., Liu, G., & Ju, X. (2021). In Silico Screening of Novel α1-GABAA Receptor PAMs towards Schizophrenia Based on Combined Modeling Studies of Imidazo [1,2-a]-Pyridines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(17), 9645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22179645