GSKIP-Mediated Anchoring Increases Phosphorylation of Tau by PKA but Not by GSK3beta via cAMP/PKA/GSKIP/GSK3/Tau Axis Signaling in Cerebrospinal Fluid and iPS Cells in Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Transfection and RNA Interference
2.3. Cloning and DNA Sequencing
2.4. In Vitro Kinase Assay
2.5. Coimmunoprecipitation
2.6. Study Groups and CSF Samples
2.7. iPSC Lines Genotyping and Exome Sequencing
2.8. Generation and Culture of Human iPSC
2.8.1. Generation of Isogenic iPSC lines Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology
2.8.2. RNA isolation and RT-PCR
2.8.3. Karyotyping
2.8.4. In Vivo Teratoma Formation
2.8.5. In Vitro Embryoid Body (EB) Formation
2.8.6. Immunofluorescent Staining
2.8.7. Lentivirus Production and Infection
2.8.8. Generation of Induced Neurons from iPSC
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
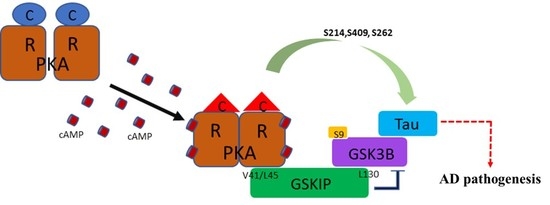
3.1. PKA, GSKIP, GSK3β, and Tau May Form a Local Working Complex
3.2. Knockdown Experiments Revealed that GSKIP and GSK3β Are Involved in cAMP/PKA/Tau Axis Signaling in SH-SY5Y Cells
3.3. Site-Specific Effects of Prephosphorylation of Tau by PKA on the Subsequent Phosphorylation by GSK3β and CaMKII
3.4. Total and Phosphorylated Tau of CSF in AD, NAD, and MCI Patients
3.5. Phosphorylation of Tau in AD-iPSC-Derived Neurons with CRISPR/Cas9
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Patient Consent for Publication
References
- Hundsrucker, C.; Skroblin, P.; Christian, F.; Zenn, H.M.; Popara, V.; Joshi, M.; Eichhorst, J.; Wiesner, B.; Herberg, F.W.; Reif, B.; et al. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta interaction protein functions as an A-kinase anchoring protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5507–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skroblin, P.; Grossmann, S.; Schafer, G.; Rosenthal, W.; Klussmann, E. Mechanisms of protein kinase A anchoring. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 283, 235–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.N.; Lo, C.W.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chen, C.T.; Sun, Y.C.; Hong, Y.R.; Yang, C.N. Prediction of the binding mode between GSK3β and a peptide derived from GSKIP using molecular dynamics simulation. Biopolymers 2011, 95, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howng, S.L.; Hwang, C.C.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hsu, M.Y.; Teng, C.Y.; Chou, C.H.; Lee, M.F.; Wu, C.H.; Chiou, S.J.; Lieu, A.S.; et al. Involvement of the residues of GSKIP, AxinGID, and FRATtide in their binding with GSK3beta to unravel a novel C-terminal scaffold-binding region. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 339, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Chou, C.H.; Howng, S.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hwang, C.C.; Wang, C.; Hsu, C.M.; Hong, Y.R. GSKIP, an inhibitor of GSKβ, mediates the N-cadherin/betacatenin pool in the differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 108, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.Y.; Howng, S.L.; Cheng, T.S.; Hsiao, Y.L.; Lieu, A.S.; Loh, J.K.; Hwang, S.L.; Lin, C.C.; Hsu, C.M.; Wang, C.; et al. GSKIP is homologous to the Axin GSK3beta interaction domain and functions as a negative regulator of GSK3β. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 11379–11389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.K.; Lin, C.C.; Yang, M.C.; Chou, C.H.; Chen, W.S.; Hong, M.C.; Cho, C.L.; Hsu, C.M.; Cheng, J.T.; Chou, A.K.; et al. GSKIP- and GSK3-mediated anchoring strengthens cAMP/PKA/Drp1 axis signaling in the regulation of mitochondrial elongation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dema, A.; Schroter, M.F.; Perets, E.; Skroblin, P.; Moutty, M.C.; Deak, V.A.; Birchmeier, W.; Klussmann, E. The A-Kinase Anchoring Protein (AKAP) Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3beta Interaction Protein (GSKIP) Regulates β-Catenin through Its Interactions with Both Protein Kinase A (PKA) and GSK3beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 19618–19630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.H.; Yang, M.C.; Hsiao, B.X.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, H.F.; Chiou, S.J.; Chuang, Y.C.; Yang, C.N.; Lieu, A.S.; Loh, J.K.; et al. The origin of GSKIP, a multifaceted regulatory factor in the mammalian Wnt pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, V.A.; Skroblin, P.; Dittmayer, C.; Knobeloch, K.P.; Bachmann, S.; Klussmann, E. The A-kinase Anchoring Protein GSKIP Regulates GSK3β Activity and Controls Palatal Shelf Fusion in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plo, I.; Bellanné-Chantelot, C.; Vainchenker, W. ATG2B and GSKIP: 2 new genes predisposing to myeloid malignancies. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 3, e1094564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saliba, J.; Saint-Martin, C.; Di Stefano, A.; Lenglet, G.; Marty, C.; Keren, B.; Pasquier, F.; Valle, V.D.; Secardin, L.; Leroy, G.; et al. Germline duplication of ATG2B and GSKIP predisposes to familial myeloid malignancies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattulainen-Collanus, S.; Akinrinade, O.; Li, M.; Koskenvuo, M.; Li, C.G.; Rao, S.P.; de Jesus Perez, V.; Yuan, K.; Sawada, H.; Koskenvuo, J.W.; et al. Loss of PPARγ in endothelial cells leads to impaired angiogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement 2016, 12, 459–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.-C.; Wu, Y.-T.; Prina, A.M.; Winblad, B.; Jönsson, L.; Liu, Z.; Prince, M. The worldwide costs of dementia 2015 and comparisons with 2010. Alzheimer’s Dement 2017, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T. Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.R.; Jonasson, E.M.; Alberico, E.O.; Li, C.; Scripture, J.P.; Miller, R.A.; Alber, M.S.; Goodson, H.V. Interactions between Tau and Different Conformations of Tubulin: Implications for Tau Function and Mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 1424–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Reddy, P.H. Structure Based Design and Molecular Docking Studies for Phosphorylated Tau Inhibitors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I.; Adlard, P.A. GSK-3 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 2011, 189246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, F.; Gomez de Barreda, E.; Fuster-Matanzo, A.; Lucas, J.J.; Avila, J. GSK3: A possible link between beta amyloid peptide and tau protein. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 223, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayapalan, S.; Natarajan, J. The role of CDK5 and GSK3B kinases in hyperphosphorylation of microtubule associated protein tau (MAPT) in Alzheimer’s disease. Bioinformation 2013, 9, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyllaert, D.; Kremer, A.; Jaworski, T.; Borghgraef, P.; Devijver, H.; Croes, S.; Dewachter, I.; Van Leuven, F. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β, or a link between amyloid and tau pathology? Genes Brain Behav. 2008, 7 (Suppl. 1), 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J. A hundred years of Alzheimer’s disease research. Neuron 2006, 52, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Bi, S.; Li, B. Processing of Mutant β-Amyloid Precursor Protein and the Clinicopathological Features of Familial Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.H.; Lee-Chen, G.J.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, J.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Wei, P.C.; Lo, Y.S.; Yao, C.F.; Kuo, M.W.; Chen, C.M. Modeling Alzheimer’s Disease by Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Carrying APP D678H Mutation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3972–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungenast, A.E.; Siegert, S.; Tsai, L.H. Modeling Alzheimer’s disease with human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 73, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seward, M.E.; Swanson, E.; Norambuena, A.; Reimann, A.; Cochran, J.N.; Li, R.; Roberson, E.D.; Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-beta signals through tau to drive ectopic neuronal cell cycle re-entry in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Cheng, J.T.; Yao, Y.C.; Juo Lo, Y.K.; Lin, C.H.; Ger, L.P.; Lu, P.J. Increased total TAU but not amyloid-β(42) in cerebrospinal fluid correlates with short-term memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2009, 18, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banito, A.; Rashid, S.T.; Acosta, J.C.; Li, S.; Pereira, C.F.; Geti, I.; Pinho, S.; Silva, J.C.; Azuara, V.; Walsh, M.; et al. Senescence impairs successful reprogramming to pluripotent stem cells. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 21349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.P.; Chen, P.H.; Hwu, W.L.; Chuang, C.Y.; Chien, Y.H.; Stone, L.; Chien, C.L.; Li, L.T.; Chiang, S.C.; Chen, H.F.; et al. Human Pompe disease-induced pluripotent stem cells for pathogenesis modeling, drug testing and disease marker identification. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4851–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.W.; Ko, H.J.; Chou, C.H.; Cheng, T.S.; Cheng, H.W.; Liang, Y.H.; Lai, Y.L.; Lin, C.Y.; Wang, C.; Loh, J.K.; et al. Thioridazine Enhances P62-Mediated Autophagy and Apoptosis Through Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Glioma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liang, Z.; Wegiel, J.; Hwang, Y.W.; Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Ramakrishna, N.; Gong, C.X. Overexpression of Dyrk1A contributes to neurofibrillary degeneration in Down syndrome. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 322433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, L.; Creighton, J.; Alexeyev, M.; Strada, S.J.; Stevens, T. Protein kinase A phosphorylation of tau-serine 214 reorganizes microtubules and disrupts the endothelial cell barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L493L501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.; Costa, M.; de Almeida, M.S.C.; da Cruz, E.S.O.A.B.; Henriques, A.G. Protein Phosphorylation is a Key Mechanism in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 953–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liang, Z.; Shi, J.; Yin, D.; El-Akkad, E.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Gong, C.X. PKA modulates GSK-3β- and cdk5-catalyzed phosphorylation of tau in site- and kinase-specific manners. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 6269–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Kinases and phosphatases and tau sites involved in Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.T.; Hong, C.J.; Lin, Y.T.; Chang, W.H.; Huang, H.T.; Liao, J.Y.; Chang, Y.J.; Hsieh, Y.F.; Cheng, C.Y.; Liu, H.C.; et al. Amyloid-beta (Abeta) D7H mutation increases oligomeric Abeta42 and alters properties of Abetazinc/copper assemblies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35807. [Google Scholar]
- Simic, G.; Babic Leko, M.; Wray, S.; Harrington, C.; Delalle, I.; Jovanov-Milosevic, N.; Bazadona, D.; Buee, L.; de Silva, R.; Di Giovanni, G.; et al. Tau Protein Hyperphosphorylation and Aggregation in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Tauopathies, and Possible Neuroprotective Strategies. Biomolecules 2016, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.Y.; Liu, J.S.; Wu, Y.S.; Peng, C.H.; Chang, Y.Y. A novel APP mutation (D678H) in a Taiwanese patient exhibiting dementia and cerebral microvasculopathy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, K.C.; Liao, J.Y.; Cheng, I.H. Differential regulation of amyloid precursor protein sorting with pathological mutations results in a distinct effect on amyloid-beta production. J. Neurochem. 2014, 131, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chiu, Y.J.; Yang, S.M.; Chen, C.M.; Huang, C.C.; Lee-Chen, G.J.; Lin, W.; Chang, K.H. Novel synthetic chalcone-coumarin hybrid for Aβ aggregation reduction. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safieh, M.; Korczyn, A.D.; Michaelson, D.M. ApoE4: An emerging therapeutic _target for Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanoiselee, H.M.; Nicolas, G.; Wallon, D.; Rovelet-Lecrux, A.; Lacour, M.; Rousseau, S.; Richard, A.C.; Pasquier, F.; Rollin-Sillaire, A.; Martinaud, O.; et al. APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 mutations in early-onset Alzheimer disease: A genetic screening study of familial and sporadic cases. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Run, X.; Liang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Gong, C.X. Developmental regulation of tau phosphorylation, tau kinases, and tau phosphatases. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 1480–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sergeant, N.; Bretteville, A.; Hamdane, M.; Caillet-Boudin, M.L.; Grognet, P.; Bombois, S.; Blum, D.; Delacourte, A.; Pasquier, F.; Vanmechelen, E.; et al. Biochemistry of Tau in Alzheimer’s disease and related neurological disorders. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2008, 5, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanger, D.P.; Anderton, B.H.; Noble, W. Tau phosphorylation: The therapeutic challenge for neurodegenerative disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Latypova, X.; Wilson, C.M.; Magnaudeix, A.; Perrin, M.L.; Yardin, C.; Terro, F. Tau protein kinases: Involvement in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeganathan, S.; von Bergen, M.; Mandelkow, E.M.; Mandelkow, E. The natively unfolded character of tau and its aggregation to Alzheimer-like paired helical filaments. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 10526–10539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, J.; Jiménez, J.S.; Sayas, C.L.; Bolós, M.; Zabala, J.C.; Rivas, G.; Hernández, F. Tau Structures. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blennow, K.; Vanmechelen, E.; Hampel, H. CSF total tau, Abeta42 and phosphorylated tau protein as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2001, 24, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Teipel, S.J.; Fuchsberger, T.; Andreasen, N.; Wiltfang, J.; Otto, M.; Shen, Y.; Dodel, R.; Du, Y.; Farlow, M.; et al. Value of CSF beta-amyloid1-42 and tau as predictors of Alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondragon-Rodriguez, S.; Basurto-Islas, G.; Santa-Maria, I.; Mena, R.; Binder, L.I.; Avila, J.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G.; Garcia-Sierra, F. Cleavage and conformational changes of tau protein follow phosphorylation during Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2008, 89, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondragón-Rodríguez, S.; Basurto-Islas, G.; Lee, H.-G.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X.; Castellani, R.J.; Smith, M.A. Causes versus effects: The increasing complexities of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2010, 10, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, J.; Jones, J.; Haggerty, T.; Duka, V.; Joyce, J.N.; Sidhu, A. Elevated tauopathy and alpha-synuclein pathology in postmortem Parkinson’s disease brains with and without dementia. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 225, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlyle, B.C.; Nairn, A.C.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.E.; Simen, A.A.; Ramos, B.P.; Bordner, K.A.; Craft, G.E.; Davies, P.; et al. cAMP-PKA phosphorylation of tau confers risk for degeneration in aging association cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5036–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.Y.; He, S.S.; Wang, X.; Duan, Q.H.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Wang, J. Levels of nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated tau in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients: An ultrasensitive bienzyme-substrate-recycle enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, R.J.; Wong, P.C. Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Kinase | Specific Phosphorylated Site for Tau | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| PKA | Ser214 Ser262 Ser409 | Liu et al., 2006 [35], Liu et al., 2008 [32], Zhu et al., 2010 [33], Oliveira et al., 2017 [34] |
| GSK3β | Ser181 Ser205 Ser231 Ser396 Ser400 Ser404 | Liu et al., 2006 [35], Wang et al., 2007 [36], Liu et al., 2008 [32], Oliveira et al., 2017 [34] |
| CaMKⅡ | Ser212 Ser214 Ser262 Ser356 Ser416 | Liu et al., 2006 [35], Wang et al., 2007 [36], Seward et al., 2013 [27], Oliveira et al., 2017 [34] |
| hiPSC Lines | Gender | Age at Biopsy | Genotype * | APOE Status | Clinical Diagnosis at Time of Biopsy | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Female | 45 | WT | ε4/ε4 | N/A | Unedited |
| APPWT/WT | Female | N/A | APPWT/WT | ε3/ε4 | N/A | CRISPR-edited |
| APPWT/D678H | Female | 63 | APPWT/D678H | ε3/ε4 | progressive memory and behavior problems | Unedited |
| APPD678H/D678H | Female | N/A | APPD678H/D678H | ε3/ε4 | N/A | CRISPR-edited |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ko, H.-J.; Chiou, S.-J.; Wong, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-H.; Lai, Y.-L.; Chou, C.-H.; Wang, C.; Loh, J.-K.; Lieu, A.-S.; Cheng, J.-T.; et al. GSKIP-Mediated Anchoring Increases Phosphorylation of Tau by PKA but Not by GSK3beta via cAMP/PKA/GSKIP/GSK3/Tau Axis Signaling in Cerebrospinal Fluid and iPS Cells in Alzheimer Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101751
Ko H-J, Chiou S-J, Wong Y-H, Wang Y-H, Lai Y-L, Chou C-H, Wang C, Loh J-K, Lieu A-S, Cheng J-T, et al. GSKIP-Mediated Anchoring Increases Phosphorylation of Tau by PKA but Not by GSK3beta via cAMP/PKA/GSKIP/GSK3/Tau Axis Signaling in Cerebrospinal Fluid and iPS Cells in Alzheimer Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(10):1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101751
Chicago/Turabian StyleKo, Huey-Jiun, Shean-Jaw Chiou, Yu-Hui Wong, Yin-Hsuan Wang, Yun-Ling Lai, Chia-Hua Chou, Chihuei Wang, Joon-Khim Loh, Ann-Shung Lieu, Jiin-Tsuey Cheng, and et al. 2019. "GSKIP-Mediated Anchoring Increases Phosphorylation of Tau by PKA but Not by GSK3beta via cAMP/PKA/GSKIP/GSK3/Tau Axis Signaling in Cerebrospinal Fluid and iPS Cells in Alzheimer Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 10: 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101751
APA StyleKo, H. -J., Chiou, S. -J., Wong, Y. -H., Wang, Y. -H., Lai, Y. -L., Chou, C. -H., Wang, C., Loh, J. -K., Lieu, A. -S., Cheng, J. -T., Lin, Y. -T., Lu, P. -J., Fann, M. -J., Huang, C. -Y., & Hong, Y. -R. (2019). GSKIP-Mediated Anchoring Increases Phosphorylation of Tau by PKA but Not by GSK3beta via cAMP/PKA/GSKIP/GSK3/Tau Axis Signaling in Cerebrospinal Fluid and iPS Cells in Alzheimer Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(10), 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101751