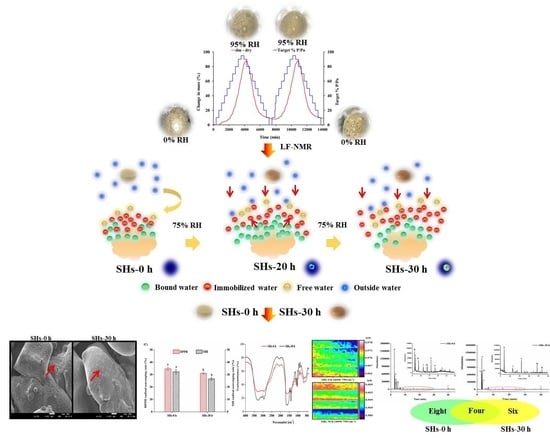
Proton Dynamics of Water Diffusion in Shrimp Hydrolysates Flour and Effects of Moisture Absorption on Its Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Shrimp Hydrolysate (SHs) Flour by Alcalase
2.3. Dynamic Vapor Sorption (DVS) Measurements in RH from 0% to 95%
2.4. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Test
2.5. Detection of Morphological of SHs-0 h and SHs-30 h Flour by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Detection of Radicals of SHs-0 h and SHs-30 Flour by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR)
2.7. Mid-Infrared (MIR) Spectroscopy Analysis of SHs-0 h and SHs-30 Flour
2.8. Infrared Microscopic Imaging of SHs-0 h and SHs-30 Flour
2.9. Identification and Quantification of the Volatile Compounds of SHs-0 h and SHs-30 h Flour by PT-GC-MS
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Vapor Sorption Analyses of SHs Flour in RH from 0% to 95%
3.2. Water Distribution of SHs Flour Monitored by LF-NMR during Process of Storage
3.3. Effects of Moisture Absorption on Morphological Changes of SHs Flour
3.4. Effects of Moisture Absorption on Radicals Scavenging Activity of SHs Flour
3.5. Changes of Functional Groups after Moisture Absorption
3.6. Effects of Moisture Adsorption on Volatile Compounds of SHs Flour
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Hu, C.A.; Kovacs-Nolan, J.; Mine, Y. Bioactive dietary peptides and amino acids in inflammatory bowel disease. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2127–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberio, M.S.; Joanitti, G.A.; Fontes, W.; Castro, M.S. Anticancer peptides and proteins: A panoramic view. Protein Peptide Lett. 2013, 20, 380–391. [Google Scholar]
- Thaha, A.; Wang, B.; Chang, Y.; Hsia, S.; Huang, T.; Shiau, C.Y.; Hwang, D.; Chen, T. Food-derived bioactive peptides with antioxidative capacity, Xanthine Oxidase and Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity. Xanthine Oxidase Tyrosinase Inhib. Act. 2021, 9, 747. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Wijesekara, I. Development and biological activities of marine-derived bioactive peptides: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Argyropoulos, D.; Nagle, M.; Khan, M.T.; Müller, J. Combination of digital images and laser light to predict moisture content and color of bell pepper simultaneously during drying. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovnya, R.V. Investigation of organic bases in the specific odour of casein and coprecipitate during storage. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 26, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Feng, C.; Zhang, M. Dynamics of water mobility and distribution in soybean antioxidant peptide powders monitored by LF-NMR. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Lin, S. Water Dynamics in Egg White Peptide, Asp-His-Thr-Lys-Glu, Powder Monitored by Dynamic Vapor Sorption and LF-NMR. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Lin, S.; Chen, F. Moisture-absorption and water dynamics in the powder of egg albumen peptide, Met-Pro-Asp-Ala-His-Leu. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Xue, P.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Chen, F. Water dynamics of Ser-His-Glu-Cys-Asn powder and effects of moisture absorption on its chemical properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 97, 3124–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyropoulos, D.; Alex, R.; Müller, J. Equilibrium moisture contents of a medicinal herb (Melissa officinalis) and a medicinal mushroom (Lentinula edodes) determined by dynamic vapour sorption. Procedia Food Sci. 2010, 1, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agudelo-Laverde, L.M.; Schebor, C.; Buera, M.D.P. Proton mobility for the description of dynamic aspects of freeze-dried fruits. J. Food Eng. 2014, 125, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiff, K.; Fuentes, A.; Aursand, I.G.; Erikson, U.; Masot, R.; Alcañiz, M.; Barat, J.M. Innovative nondestructive measurements of water activity and the content of salts in low-salt hake minces. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, R.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Tan, M. Assessment of water mobility in surf clam and soy protein system during gelation using lf-nmr technique. Foods 2020, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, N.; Li, Y.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, C.; Lin, S. Effects of electron beam irradiation (EBI) on structure characteristics and thermal properties of walnut protein flour. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, P.M.; Edge, S.; Staniforth, J.N.; Steele, D.F.; Price, R. Dynamic vapor sorption properties of sodium starch glycolate disintegrants. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2005, 10, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Liang, R.; Yang, Y.; Sun, N.; Lin, S. Optimization of pea protein hydrolysate preparation and purification of antioxidant peptides based on an in silico analytical approach-ScienceDirect. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 123, 109126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, P.; Pang, Y.; Ye, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Jones, G. Optimized antioxidant peptides fractions preparation and secondary structure analysis by MIR. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonwell, E.S.; Wetzel, D.L. Innovative FT-IR Imaging of Protein Film Secondary Structure before and after Heat Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10067–10072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PozoBayón, M.Á.; MartínÁlvarez, P.J.; Reineccius, G.A. Monitoring changes in the volatile profile of cheese crackers during storage using GC-MS and PTR-MS. Flavour Fragr. J. 2010, 24, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamblin, S.L.; Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Water vapor sorption by peptides, proteins and their formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, H.A.; Schebor, C.; Buera, M.P.; Chirife, J. Sorption isotherm and calorimetric behavior of amorphous/crystalline raffinose-water systems. J. Food Sci. 2010, 65, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Tu, C.; Rui, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, M. Study of water dynamics in the soaking, steaming, and solid-state fermentation of glutinous rice by LF-NMR: A novel monitoring approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Lin, Z.; Zu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Cheng, S. Effect of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on the quality of instant sea cucumber: Emphatically on water status of by LF-NMR and MRI. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Song, Y.; Kamal, T.L.; Xia, K.; Lin, Z.; Qi, L.; Cheng, S.; Zhu, B.; Tan, M. A non-invasive method based on low-field NMR to analyze the quality changes in caviar from hybrid sturgeon (Huso dauricus, Acipenser schrenckiid). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.Y.; Shao, J.H.; Liu, D.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. The distribution of water in pork meat during wet-curing as studied by low-field NMR. Food Sci. Technol. Int. Tokyo 2014, 20, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, R.; Sun, N.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, S.; Lin, S. The formation pattern of off-flavor compounds induced by water migration during the storage of sea cucumber peptide powders (SCPPs). Food Chem. 2019, 274, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, H.C.; Donstrup, S.; Karlsson, A.H.; Andersen, H.J. Continuous distribution analysis of T2 relaxation in meat-an approach in the determination of water-holding capacity. Meat Sci. 2002, 60, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.B.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhou, G.H.; Xu, X.L.; Qi, J.; Shi, P.L.; Xia, T.L. Meat quality and cooking attributes of thawed pork with different low field NMR T 21. Meat Sci. 2002, 92, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Yong, L.; Cheng, S.; Dong, X.; Kamal, T.; Zhou, D. Changes in body wall of sea cucumber (stichopus japonicus ) during a two-step heating process assessed by rheology, lf-nmr, and texture profile analysis. Food Biophys. 2016, 11, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, H.C.; Karlsson, A.H.; Andersen, H.J. The significance of cooling rate on water dynamics in porcine muscle from heterozygote carriers and non-carriers of the halothane gene-a low-field NMR relaxation study. Meat Sci. 2003, 65, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Cheng, S.; Wang, H.; Tan, M. Freezing-induced proton dynamics in tofu evaluated by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2007, 11, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Tang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Song, Y.; Tan, M. An approach for monitoring the dynamic states of water in shrimp during drying process with lf-nmr and mri. Dry. Technol. 2018, 36, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacios, L.F. Distinct molecular surfaces and hydrophobicity of amino acid residues in proteins. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2001, 41, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Neuroprotective effects of different molecular weight peptide fractions obtained from beef by hydrolysis with commercial enzymes in SH-SY5Y cells. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, D.J.; Thielmann, F.; Sokoloski, T.; Brum, J. Investigating the moisture-induced crystallization kinetics of spray-dried lactose. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 313, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sun, N.; Li, D.; Cheng, S.; Liang, R.; Lin, S. Enzyme-controlled hygroscopicity and proton dynamics in sea cucumber (stichopus japonicus) ovum peptide powders. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yang, R.; Cheng, S.; Wang, K.; Qin, L. Decreased quality and off-flavour compound accumulation of 3–10kDa fraction of pine nut (Pinus koraiensis) peptide during storage. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liang, R.; Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, S. Effect of structure changes on hydrolysis degree, moisture state, and thermal denaturation of egg white protein treated by electron beam irradiation. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 77, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Jin, Z.; Li, D.; Yin, H.; Lin, S. An exploration of the calcium-binding mode of egg white peptide, Asp-His-Thr-Lys-Glu, and in vitro calcium absorption studies of peptide-calcium complex. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9782–9789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.; Giacomelli, C.; Soldi, V. Thermal stability of films formed by soy protein isolate-sodium dodecyl sulfate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 87, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Wei, Y. Effect of mixing time on the structural characteristics of noodle dough under vacuum. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinzawa, H.; Turner, B.; Mizukado, J.; Kazarian, S. Protein hydrations in living cell probed by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopic imaging. Analyst 2017, 142, 2475–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, C.R.; Ruggeri, G.; De Paoli, M.-A. Synthesis in pilot plant scale and physical properties of sulfonated polystyrene. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haris, P.I.; Chapman, D. The conformational analysis of peptides using Fourie transform IR spectroscopy. Biopolymers 1995, 37, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baianu, I.C.; Costescu, D.; You, T.; Lozano, P.R.; Hofmann, N.E.; Korban, S.S.; Luthria, D.L. Near infrared microspectroscopy, fluorescence microspectroscopy, infrared chemical imaging and high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of soybean seeds embryos and single cells. Nat. Preced. 2011, 1, 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Liang, R.; Li, X.; Xing, J.; Yuan, Y. Effect of pulsed electric field (PEF) on structures and antioxidant activity of soybean source peptides-SHCMN. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, H.; Hagen, B.F.; Pedersen, B.O.; Holck, A.L.; Axelsson, L.; Næs, H. Accelerated production of dry fermented sausage. Meat Sci. 1996, 43S1, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, R.; Lin, S.; Ye, H.; Chen, F. Identification of key volatiles responsible for aroma changes of egg white antioxidant peptides during storage by HS-SPME-GC-MS and sensory evaluation. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Peak No. | Time | Compounds Volatile | CAS | Molecule Fomula | RIa | RIb | Characteristic Fragment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 2.494 | 2-Methoxy-ethanol | 109-86-4 | C3H8O2 | 621.9 | 624 | 14, 11, 29, 57 |
| b | 2.785 | 4-Penten-2-ol | 625-31-0 | C5H10O | 643.4 | 647 | 45 |
| c | 2.922 | 2-Nitro-ethanol | 625-48-9 | C2H5NO3 | 653.9 | 658 | 43, 45 |
| d | 3.128 | 1-Methoxy-2-propanol | 107-98-2 | C4H10O2 | 669.5 | 661 | 43, 45, 47 |
| e | 3.226 | 3-Methyl-2-butanol | 598-75-4 | C5H12O | 676.6 | 674 | 45, 55, 73 |
| f | 3.779 | 2-Pentanol | 6032-29-7 | C5H12O | 709.2 | 703 | 43, 45 |
| g | 4.892 | Paraldehyde | 123-63-7 | C6H12O3 | 753.8 | 755 | 43 |
| h | 6.365 | Butanoic acid | 107-92-6 | C4H8O2 | 809.6 | 805 | 41, 60 |
| i | 6.763 | Hexanal | 66-25-1 | C6H12O | 821.6 | 800 | 44, 56, 72 |
| j | 6.999 | 2,4-Dimtthyl-heptane | 2213-23-2 | C9H20 | 829.1 | 821 | 43, 57, 71 |
| k | 8.677 | o-Xylene | 95-47-6 | C8H10 | 881.1 | 887 | 91, 106 |
| l | 11.409 | Benzaldehyde | 100-52-7 | C7H6O | 965.2 | 962 | 51, 77, 106 |
| m | 13.692 | 2-Ethyl-1-hexanol | 104-76-7 | C8H18O | 1035.3 | 1030 | 41, 57, 70 |
| n | 16.000 | Nonanal | 124-19-6 | C9H18O | 1106.4 | 1104 | 41, 57, 70 |
| o | 18.329 | Naphthalene | 91-20-3 | C10H8 | 1184.1 | 1182 | 102, 128 |
| p | 24.277 | Tetradecane | 629-59-4 | C14H3O | 1400.5 | 1400 | 43, 57, 71 |
| q | 26.769 | 2-hexyl-1-decanol | 2425-77-6 | C16H34O | 1500.5 | 1504 | 43, 57, 71, 85 |
| r | 40.022 | Oleic acid | 112-80-1 | C18H34O2 | 2141.1 | 2141 | 43, 55, 69, 83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Lin, S.; Yang, R.; Chen, D.; Sun, N. Proton Dynamics of Water Diffusion in Shrimp Hydrolysates Flour and Effects of Moisture Absorption on Its Properties. Foods 2021, 10, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051137
Zhao Y, Lin S, Yang R, Chen D, Sun N. Proton Dynamics of Water Diffusion in Shrimp Hydrolysates Flour and Effects of Moisture Absorption on Its Properties. Foods. 2021; 10(5):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yue, Songyi Lin, Ruiwen Yang, Dong Chen, and Na Sun. 2021. "Proton Dynamics of Water Diffusion in Shrimp Hydrolysates Flour and Effects of Moisture Absorption on Its Properties" Foods 10, no. 5: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051137
APA StyleZhao, Y., Lin, S., Yang, R., Chen, D., & Sun, N. (2021). Proton Dynamics of Water Diffusion in Shrimp Hydrolysates Flour and Effects of Moisture Absorption on Its Properties. Foods, 10(5), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051137