Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Climate change and its influence on water systems increases the cost of electricity system decarbonization
Climate change and its influence on water systems increases the cost of electricity system decarbonization
The authors link water and electricity system models to evaluate how the electric grid can both adapt to climate change impacts and decarbonize, while also accounting for dependencies and climate vulnerabilities of the closely coupled water sector.
- Julia K. Szinai
- , David Yates
- & Patricia Hidalgo-Gonzalez
-
Article
| Open Access The role of farm subsidies in changing India’s water footprint
The role of farm subsidies in changing India’s water footprint
The study shows that India’s agricultural subsidies have driven significant groundwater depletion by incentivizing overproduction of water-intensive crops like rice and wheat. This impact is evident in both Punjab’s alluvial aquifers and Madhya Pradesh’s hard rock aquifers.
- Shoumitro Chatterjee
- , Rohit Lamba
- & Esha D. Zaveri
-
Article
| Open Access Resilient water infrastructure partnerships in institutionally complex systems face challenging supply and financial risk tradeoffs
Resilient water infrastructure partnerships in institutionally complex systems face challenging supply and financial risk tradeoffs
Hamilton and colleagues demonstrate critical water supply risks and financial tradeoffs for California utilities investing in cooperative infrastructure projects and develops computational methods for designing more resilient partnerships under uncertainty.
- A. L. Hamilton
- , P. M. Reed
- & G. W. Characklis
-
Article
| Open Access Self-reported anticipated harm from drinking water across 141 countries
Self-reported anticipated harm from drinking water across 141 countries
Perceptions of drinking water safety influence how people use and value water. Here, the authors find that 52.3% of adults across 141 countries self-report anticipating harm from drinking water.
- Joshua D. Miller
- , Chad Staddon
- & Sera L. Young
-
Article
| Open Access Timing the first emergence and disappearance of global water scarcity
Timing the first emergence and disappearance of global water scarcity
This research explores the emergence and resolution of water scarcity. The results indicate that water scarcity is likely to become predominant in Africa by 2090. Conversely, China might experience alleviation from water scarcity post-2050, attributed to its declining population.
- Junguo Liu
- , Delong Li
- & Philippe Ciais
-
Article
| Open Access How urban form impacts flooding
How urban form impacts flooding
A statistical mechanics approach unveils how urban layout influences flood hazards linking flood risk to factors like ground slope, porosity, building arrangement symmetry, and chord length, offering a scalable model applicable worldwide.
- Sarah K. Balaian
- , Brett F. Sanders
- & Mohammad Javad Abdolhosseini Qomi
-
Comment
| Open Access Can continental transboundary compacts hold water?
Can continental transboundary compacts hold water?
The growing number of threats facing continental-scale transboundary water treaties warrants contemporary evaluation of not only the political and climatological conditions under which they were constructed, but also of how different management strategies for accommodating changes in those conditions can lead to treaty success or failure. We assess these threats by highlighting key attributes and vulnerabilities of water treaties across North America that frame a diverse set of future water management priorities. While these threats are ubiquitous globally, they are particularly pronounced in North America where water-abundant basins along the border between the United States (US) and Canada contrast with arid basins along the border between the US and Mexico. We propose addressing these needs through a three-step call to action for management agencies, politicians, and the public at large to embrace a holistic perspective on transboundary water agreements.
- Andrew Gronewold
- , Jenna Bednar
- & Jon Allan
-
Article
| Open Access Water quality management could halve future water scarcity cost-effectively in the Pearl River Basin
Water quality management could halve future water scarcity cost-effectively in the Pearl River Basin
Future water scarcity is expected to increase up to fourfold in most parts of the Pearl Basin by 2050, driven by changes in both water quantity and quality. Water quality management options could cost-effectively half future water scarcity.
- Safa Baccour
- , Gerwin Goelema
- & Maryna Strokal
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis indicates better climate adaptation and mitigation performance of hybrid engineering-natural coastal defence measures
Meta-analysis indicates better climate adaptation and mitigation performance of hybrid engineering-natural coastal defence measures
This meta-analysis compares the performance of hard, hybrid, soft and natural coastal defence measures. Results show that all measures have a positive economic return over 20 years yet hybrid measures perform best for climate adaptation and mitigation.
- Lam Thi Mai Huynh
- , Jie Su
- & Alexandros Gasparatos
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodiffusive desalination
Thermodiffusive desalination
Current desalination technologies are energy intensive and suffer from membrane degradation and fouling. Here, authors propose and explore the potential of thermodiffusion as a means of membrane-free, single-phase thermal desalination. A pathway towards a feasible thermodiffusive desalination is provided.
- Shuqi Xu
- , Alice J. Hutchinson
- & Juan F. Torres
-
Article
| Open Access Imprint of urbanization on snow precipitation over the continental USA
Imprint of urbanization on snow precipitation over the continental USA
This study shows that urban areas in the continental US are associated with decreased snowfall likelihood and frequency, in large part due to surface albedo contrasts with neighboring areas. They also see a faster decline in snow precipitation frequency with time.
- Kaustubh Anil Salvi
- & Mukesh Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Light-responsive and ultrapermeable two-dimensional metal-organic framework membrane for efficient ionic energy harvesting
Light-responsive and ultrapermeable two-dimensional metal-organic framework membrane for efficient ionic energy harvesting
With porous structure and photothermal conversion performance, Cu-porphyrin framework membranes exhibit high efficiency in the extraction of electrical energy from salt solutions, opening avenues for renewable energy.
- Jin Wang
- , Zeyuan Song
- & Lei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Global and regional ocean mass budget closure since 2003
Global and regional ocean mass budget closure since 2003
This study shows that ice loss and human water use models explain global and regional satellite-observed ocean mass changes since 2003 and thereby pinpoint the main cause of sea level rise, with a negligible role coming from natural variability.
- Carsten Bjerre Ludwigsen
- , Ole Baltazar Andersen
- & Matt A. King
-
Article
| Open Access A triple increase in global river basins with water scarcity due to future pollution
A triple increase in global river basins with water scarcity due to future pollution
Here the authors find one third of global sub-basins will face severe clean water scarcity in 2050. Nitrogen pollution aggravates water scarcity in >2,000 sub-basins thus 3 billion more people will be posed with severe water scarcity in 2050.
- Mengru Wang
- , Benjamin Leon Bodirsky
- & Maryna Strokal
-
Article
| Open Access An artificial intelligence-based model for optimal conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources
An artificial intelligence-based model for optimal conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources
Towards optimizing the conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources in arid and semi-arid regions, here the authors propose a hybrid method involving moth-swarm and symbiotic organism search algorithms and artificial neural networks and demonstrate it for the HalīlRood basin.
- Saeid Akbarifard
- , Mohamad Reza Madadi
- & Mohammad Zounemat-Kermani
-
Article
| Open Access Managing urban development could halve nitrogen pollution in China
Managing urban development could halve nitrogen pollution in China
Here the authors demonstrate how managed urbanization in China could halve reactive nitrogen pollution to both the atmosphere and water resources. Investing 61 billion USD could provide 245 billion USD in benefits, while contributing to multiple SDG goals.
- Ouping Deng
- , Sitong Wang
- & Baojing Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Higher emissions scenarios lead to more extreme flooding in the United States
Higher emissions scenarios lead to more extreme flooding in the United States
This paper assesses future changes in flood magnitude across the conterminous United States based on multiple climate change scenarios. The results suggest that annual maximum peak discharge is projected to become more extreme under higher emission scenarios.
- Hanbeen Kim
- & Gabriele Villarini
-
Article
| Open Access A super liquid-repellent hierarchical porous membrane for enhanced membrane distillation
A super liquid-repellent hierarchical porous membrane for enhanced membrane distillation
Membrane distillation is an emerging desalination technology to obtain freshwater from saline based on low-grade energy. Here the authors report on novel superhydrophobic hierarchical porous membranes with enhanced distillation flux suitable for desalination or wastewater treatment.
- Youmin Hou
- , Prexa Shah
- & Hans-Jürgen Butt
-
Article
| Open Access Dual water-electricity cooperation improves economic benefits and water equality in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin
Dual water-electricity cooperation improves economic benefits and water equality in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin
Li and colleagues develop a dual water-electricity cooperation (DWEC) framework that combines water and electricity trading to meet the often-conflicting demands of participating countries in the Lancang-Mekong river basin. They discuss the potential of this framework for application in other transboundary river systems.
- Bingyao Zhang
- , Yu Li
- & Ximing Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainably developing global blue carbon for climate change mitigation and economic benefits through international cooperation
Sustainably developing global blue carbon for climate change mitigation and economic benefits through international cooperation
Sustainable development of blue carbon has increased globally over the past two decades. Global cooperation could enable countries to improve blue carbon sustainable development, increase carbon sequestration, and generate up to $136.34 million in 2030 in economic benefits.
- Cuicui Feng
- , Guanqiong Ye
- & Zhenci Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Global land and water limits to electrolytic hydrogen production using wind and solar resources
Global land and water limits to electrolytic hydrogen production using wind and solar resources
This study composes a country-specific analysis of land and water requirements for electrolytic hydrogen production, revealing nations constrained in achieving self-sufficiency in hydrogen supply and nations who can become hydrogen exporters.
- Davide Tonelli
- , Lorenzo Rosa
- & Francesco Contino
-
Article
| Open Access Stakeholder integration predicts better outcomes from groundwater sustainability policy
Stakeholder integration predicts better outcomes from groundwater sustainability policy
This paper shows that integrating diverse stakeholders into management plans results in better protection, especially for those most vulnerable to the impacts of natural resource depletion.
- Debra Perrone
- , Melissa M. Rohde
- & E. J. Remson
-
Article
| Open Access Food demand displaced by global refugee migration influences water use in already water stressed countries
Food demand displaced by global refugee migration influences water use in already water stressed countries
While minimal in most host countries, the water needed to produce the food consumed by refugees can have a large effect on water stress in vulnerable countries. Small changes to food trade and refugee resettlement policies can alleviate this unequal burden.
- Leonardo Bertassello
- , Marc F. Müller
- & Michèle C. Müller-Itten
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable and switchable CO2-responsive membranes with high wettability for separation of various oil/water systems
Scalable and switchable CO2-responsive membranes with high wettability for separation of various oil/water systems
Smart membranes with responsive wettability show promise for controllably separating oil/water mixtures but it remains challenging to fabricate responsive and stable scalable membranes. Here, the authors develop a capillary force-driven self-assembling strategy to construct a scalable and stable CO2-responsive membrane for the smart separation of various oil/water systems.
- Yangyang Wang
- , Shaokang Yang
- & Xiaowei Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Groundwater depletion in California’s Central Valley accelerates during megadrought
Groundwater depletion in California’s Central Valley accelerates during megadrought
Liu et al. used the NASA GRACE/FO missions to show that since 2019, groundwater depletion in California’s Central Valley has accelerated by 31% compared to recent droughts, and has increased by a nearly a factor of 5 compared to the 60-year average.
- Pang-Wei Liu
- , James S. Famiglietti
- & Matthew Rodell
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional open architecture enabling salt-rejection solar evaporators with boosted water production efficiency
Three-dimensional open architecture enabling salt-rejection solar evaporators with boosted water production efficiency
Conventional salt-rejection evaporators typically exhibit low evaporation rate due to large heat loss. Here, authors demonstrate a solar evaporator featuring vertically aligned mass transfer bridges that takes advantage of the conductive heat to enable optimized water transport and salt backflow.
- Kaijie Yang
- , Tingting Pan
- & Yu Han
-
Article
| Open Access Split westerlies over Europe in the early Little Ice Age
Split westerlies over Europe in the early Little Ice Age
A new stalagmite record from northern Italy and other published data from Europe and northern Africa reveals a split in the climatological westerlies during the early LIA, possibly attributed to sea ice melting.
- Hsun-Ming Hu
- , Chuan-Chou Shen
- & Robert Korty
-
Article
| Open Access Inequality of household water security follows a Development Kuznets Curve
Inequality of household water security follows a Development Kuznets Curve
A new study considering data from 7603 households across 28 sites in 22 low- and middle-income countries show that inequality of household water security follows a Development Kuznets Curve.
- Feng Mao
- , Joshua D. Miller
- & Zeina Jamaluddine
-
Article
| Open Access Global analysis and prediction of fluoride in groundwater
Global analysis and prediction of fluoride in groundwater
A global fluoride hazard prediction map was created using machine learning and over 400,000 fluoride measurements, this shows ~180 million people are potentially affected by chronic fluoride exposure worldwide, mostly in Asia and Africa.
- Joel Podgorski
- & Michael Berg
-
Article
| Open Access Accounting for interactions between Sustainable Development Goals is essential for water pollution control in China
Accounting for interactions between Sustainable Development Goals is essential for water pollution control in China
The UN’s 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are highly interrelated. This study finds 319 interactions between SDGs for the case of water pollution in China. Results show that effective pollution control requires accounting for these interactions.
- Mengru Wang
- , Annette B. G. Janssen
- & Carolien Kroeze
-
Article
| Open Access Hotspots for social and ecological impacts from freshwater stress and storage loss
Hotspots for social and ecological impacts from freshwater stress and storage loss
This work identifies the world’s most vulnerable basins to social and ecological impacts from freshwater stress and storage loss: a set of 168 hotspot basins for global prioritization that encompass 1.5 billion people, 17% of global food crops, 13% of global GDP, and hundreds of significant wetlands.
- Xander Huggins
- , Tom Gleeson
- & James S. Famiglietti
-
Article
| Open Access From calibration to parameter learning: Harnessing the scaling effects of big data in geoscientific modeling
From calibration to parameter learning: Harnessing the scaling effects of big data in geoscientific modeling
Much effort is invested in calibrating model parameters for accurate outputs, but established methods can be inefficient and generic. By learning from big dataset, a new differentiable framework for model parameterization outperforms state-of-the-art methods, produce more physically-coherent results, using a fraction of the training data, computational power, and time. The method promotes a deep integration of machine learning with process-based geoscientific models.
- Wen-Ping Tsai
- , Dapeng Feng
- & Chaopeng Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Collaborative management of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam increases economic benefits and resilience
Collaborative management of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam increases economic benefits and resilience
Integrating river system and economy-wide models in a dynamic, iterative, bidirectional fashion allows assessing some economic impacts of interventions in river systems. Here the authors use this framework to compare water resources management strategies for the Nile in a quest for efficient use of the river’s limited and stressed water resources.
- Mohammed Basheer
- , Victor Nechifor
- & Julien J. Harou
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable irrigation based on co-regulation of soil water supply and atmospheric evaporative demand
Sustainable irrigation based on co-regulation of soil water supply and atmospheric evaporative demand
Irrigation is the most important use of water. A newly developed irrigation management scheme leads to a significant reduction in water use and increase in economic gains while maintaining crop yields, presenting opportunities for real-world impacts under current and future climate conditions.
- Jingwen Zhang
- , Kaiyu Guan
- & Grace L. Miner
-
Article
| Open Access Future global urban water scarcity and potential solutions
Future global urban water scarcity and potential solutions
This paper quantifies global urban water scarcity in 2016 and 2050 and explores potential solutions. One third to nearly half of the global urban population is projected to face water scarcity problems.
- Chunyang He
- , Zhifeng Liu
- & Brett A. Bryan
-
Article
| Open Access The widespread and unjust drinking water and clean water crisis in the United States
The widespread and unjust drinking water and clean water crisis in the United States
Proper water and sanitation access remains an issue for many in the United States. Here the authors estimate and map the full scope of water hardship, including both incomplete plumbing and water quality across the country.
- J. Tom Mueller
- & Stephen Gasteyer
-
Article
| Open Access Protecting local water quality has global benefits
Protecting local water quality has global benefits
Clean water is a fundamental resource, yet the economic impacts of pollution, drinking water availability, and greenhouse gas emissions from freshwaters are unknown. Here the authors combine models with economic assessments and find trillions of dollars in savings by mitigating lake methane emissions.
- John A. Downing
- , Stephen Polasky
- & Stephen C. Newbold
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-strong polymeric hollow fiber membranes for saline dewatering and desalination
Ultra-strong polymeric hollow fiber membranes for saline dewatering and desalination
Osmotically assisted reverse osmosis can overcome limitations of the reverse osmosis process but a strong membrane which can withstand a high hydraulic pressure is crucial. Here, the authors develop strong polymer thin film composite hollow fiber membranes with exceptionally high hydraulic burst pressures of up to 110 bar, while maintaining high water permeance and salt rejection.
- Can Zeng Liang
- , Mohammad Askari
- & Tai-Shung Chung
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Oxic methanogenesis is only a minor source of lake-wide diffusive CH4 emissions from lakes
Oxic methanogenesis is only a minor source of lake-wide diffusive CH4 emissions from lakes
- F. Peeters
- & H. Hofmann
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding and managing new risks on the Nile with the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam
Understanding and managing new risks on the Nile with the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam
Several dams and reservoirs exist along the Nile, most notably the HAD (Egypt) and GERD (Ethiopia) dams. Due to the lack of strategies, the authors here explore potential risks and solutions how to use both dams simultaneously.
- Kevin G. Wheeler
- , Marc Jeuland
- & Dale Whittington
-
Article
| Open Access A nature-inspired hydrogen-bonded supramolecular complex for selective copper ion removal from water
A nature-inspired hydrogen-bonded supramolecular complex for selective copper ion removal from water
Heavy metals and metalloids pose major threats to health and environmental ecosystems, thus systems for low-cost remediation are needed. Here the authors report the scalable design of a hydrogen-bonded organic–inorganic framework for selective removal of trace heavy metal ions from water.
- Ngoc T. Bui
- , Hyungmook Kang
- & Jeffrey J. Urban
-
Article
| Open Access South-to-North Water Diversion stabilizing Beijing’s groundwater levels
South-to-North Water Diversion stabilizing Beijing’s groundwater levels
The authors here address water sustainability in the greater area of Beijing, China. Specifically, the positive effects towards Beijing groundwater levels via water diversion from the Yangtze River to the North are shown.
- Di Long
- , Wenting Yang
- & Yoshihide Wada
-
Article
| Open Access Preserving nanoscale features in polymers during laser induced graphene formation using sequential infiltration synthesis
Preserving nanoscale features in polymers during laser induced graphene formation using sequential infiltration synthesis
High temperatures induced during lasing can deform the substrate polymer used for fabrication of electrically conductive membranes. Here, the authors show that sequential infiltration synthesis of alumina stabilizes polyethersulfone (PES) membranes against deformation above the polymers’ glass transition temperature.
- David S. Bergsman
- , Bezawit A. Getachew
- & Jeffrey C. Grossman
-
Article
| Open Access Ion sieving by a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx alginate lamellar membrane with stable interlayer spacing
Ion sieving by a two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx alginate lamellar membrane with stable interlayer spacing
Two dimensional lamellar membranes are attractive for anomalous water and ion transfer, but performance is hindered by swelling. Here, the authors stabilize a MXene membrane laminar architecture with fixed nanochannels, achieving highly selective acid recovery from iron-based wastewater.
- Jin Wang
- , Zhijie Zhang
- & Lei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Gainers and losers of surface and terrestrial water resources in China during 1989–2016
Gainers and losers of surface and terrestrial water resources in China during 1989–2016
The authors of this study compile data on spatial and temporal dynamics of surface water bodies across China, covering a time span from 1989 – 2016. The study describes hot-spot areas with strongly decreasing trends in surface water area and terrestrial water storage in North China and discusses implications of water resources and security in China.
- Xinxin Wang
- , Xiangming Xiao
- & Bo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Groundwater level observations in 250,000 coastal US wells reveal scope of potential seawater intrusion
Groundwater level observations in 250,000 coastal US wells reveal scope of potential seawater intrusion
The authors here investigate in the susceptibility of coastal aquifers to seawater intrusion. Based on 20 years’ worth of observational data, the study finds that 15% of the US coastline is affected by landward hydraulic gradients conducive to seawater intrusion.
- Scott Jasechko
- , Debra Perrone
- & James W. Kirchner
-
Article
| Open Access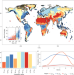 Climate change will affect global water availability through compounding changes in seasonal precipitation and evaporation
Climate change will affect global water availability through compounding changes in seasonal precipitation and evaporation
Adequate water availability is key to human and ecosystem sustainability. Here, the authors show that seasonally variable regimes become more variable, and the combined influence of seasonality and magnitude of climate variables will affect future water availability.
- Goutam Konapala
- , Ashok K. Mishra
- & Michael E. Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Drought and climate change impacts on cooling water shortages and electricity prices in Great Britain
Drought and climate change impacts on cooling water shortages and electricity prices in Great Britain
The impacts of power plant water shortage during drought on electricity prices are understudied. Here the authors show that on extreme days, almost 50% (7 GWe) of the freshwater thermal capacity is unavailable in the Great Britain and annualized cumulative costs on electricity prices are in the range of £29-95m per year.
- Edward A. Byers
- , Gemma Coxon
- & Jim W. Hall
-
Article
| Open Access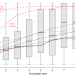 New insights into US flood vulnerability revealed from flood insurance big data
New insights into US flood vulnerability revealed from flood insurance big data
Economic estimates of flood damages rely on depth–damage functions that are inadequately verified. Here, the authors assessed flood vulnerability in the US and found that current depth–damage functions consist of disparate relationships that match poorly with observations which better follow a bimodal beta distribution.
- Oliver E. J. Wing
- , Nicholas Pinter
- & Carolyn Kousky

 Pilot-scale implementation of mainstream anammox for municipal wastewater treatment against cold temperature
Pilot-scale implementation of mainstream anammox for municipal wastewater treatment against cold temperature