Multicenter, open-label, extension trial to evaluate the long-term efficacy and safety of early versus delayed treatment with tolvaptan in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: the TEMPO 4:4 Trial
- PMID: 28379536
- PMCID: PMC6019005
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfx043
Multicenter, open-label, extension trial to evaluate the long-term efficacy and safety of early versus delayed treatment with tolvaptan in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: the TEMPO 4:4 Trial
Abstract
Background: In TEMPO 3:4, the vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist tolvaptan slowed total kidney volume (TKV) growth and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline relative to placebo.
Methods: TEMPO 4:4 was designed to provide an additional 2 years of data on the long-term safety and efficacy of tolvaptan in subjects completing TEMPO 3:4. The objective was to assess the disease-modifying effects of tolvaptan on TKV and eGFR end-points including change from baseline over the combined duration of TEMPO 3:4 and TEMPO 4:4, and non-inferiority of slopes during TEMPO 4:4.
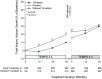
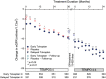
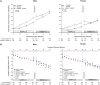
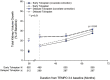
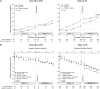
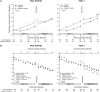
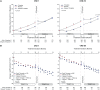
Results: Of the 1445 subjects randomized to TEMPO 3:4, 871 (60.3%) enrolled in TEMPO 4:4. Percent changes in TKV from TEMPO 3:4 baseline to TEMPO 4:4 Month 24 were 29.9% and 31.6% (prior tolvaptan versus prior placebo, P = 0.38). Adjusting for baseline covariates improved the TKV treatment difference at Month 24 in TEMPO 4:4 from -1.70% to - 4.15% between the groups (P = 0.04). Slopes of TKV growth during TEMPO 4:4 were higher in early- versus delayed-treatment groups (6.16% versus 4.96% per year, P = 0.05). Analysis of secondary eGFR endpoints demonstrated a persistent effect on eGFR (3.15 mL/min/1.73 m2, P < 0.001), and non-inferiority in eGFR slopes. The safety profile on exposure to tolvaptan in TEMPO 4:4 was similar to that in TEMPO 3:4.
Conclusions: The results of TEMPO 4:4 support a sustained disease-modifying effect of tolvaptan on eGFR. The lack of a sustained treatment difference on TKV may be accounted for by limitations of the trial design, including loss of randomization and baseline imbalances ensuing TEMPO 3:4. The safety profile was similar to that observed in TEMPO 3:4.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00428948.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of tolvaptan in Japanese patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a post hoc analysis of TEMPO 3:4 and TEMPO Extension Japan.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021 Sep;25(9):1003-1010. doi: 10.1007/s10157-021-02083-y. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34089122 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Can we further enrich autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease clinical trials for rapidly progressive patients? Application of the PROPKD score in the TEMPO trial.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018 Apr 1;33(4):645-652. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx188. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018. PMID: 28992127 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preservation of kidney function irrelevant of total kidney volume growth rate with tolvaptan treatment in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021 May;25(5):467-478. doi: 10.1007/s10157-020-02009-0. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33471240 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tolvaptan: A Review in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):303-313. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1056-1. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30689194 Review.
-
Assessing Risk of Rapid Progression in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease and Special Considerations for Disease-Modifying Therapy.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Aug;78(2):282-292. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.12.020. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 33705818 Review.
Cited by
-
Overweight and Obesity and Progression of ADPKD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Jun;16(6):908-915. doi: 10.2215/CJN.16871020. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34117082 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of tolvaptan versus placebo in the treatment of patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Mar;55(3):631-640. doi: 10.1007/s11255-022-03353-8. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36069961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Outcomes of Longitudinal Efficacy Study With Tolvaptan in ADPKD.Kidney Int Rep. 2021 Dec 8;7(2):270-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.11.034. eCollection 2022 Feb. Kidney Int Rep. 2021. PMID: 35155866 Free PMC article.
-
New treatment paradigms for ADPKD: moving towards precision medicine.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017 Dec;13(12):750-768. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.127. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28989174 Review.
-
Evaluating the impact of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy with tolvaptan to monitor liver safety in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Clin Kidney J. 2022 Mar 11;15(8):1553-1561. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfac076. eCollection 2022 Aug. Clin Kidney J. 2022. PMID: 36824061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ong AC, Devuyst O, Knebelmann B. et al. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: the changing face of clinical management. Lancet 2015; 385: 1993–2002 - PubMed
-
- Grantham JJ, Mulamalla S, Swenson-Fields KI.. Why kidneys fail in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 2011; 7: 556–566 - PubMed
-
- Gattone VH, Wang X, Harris PC. et al. Inhibition of renal cystic disease development and progression by a vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist. Nat Med 2003; 9: 1323–1326 - PubMed
-
- Torres VE, Wang X, Qian Q. et al. Effective treatment of an orthologous model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nat Med 2004; 10: 363–364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

